In the intricate realm of mobile applications, the quest for financial viability goes far beyond the straightforward notion of charging users an initial fee. The landscape is much more intricate and nuanced, with “free” apps often emerging as some of the most lucrative players in the field. But how does this paradox unfold? How can an app that is ostensibly free manage to amass substantial revenues, sometimes even reaching into the realm of thousands or millions of dollars?
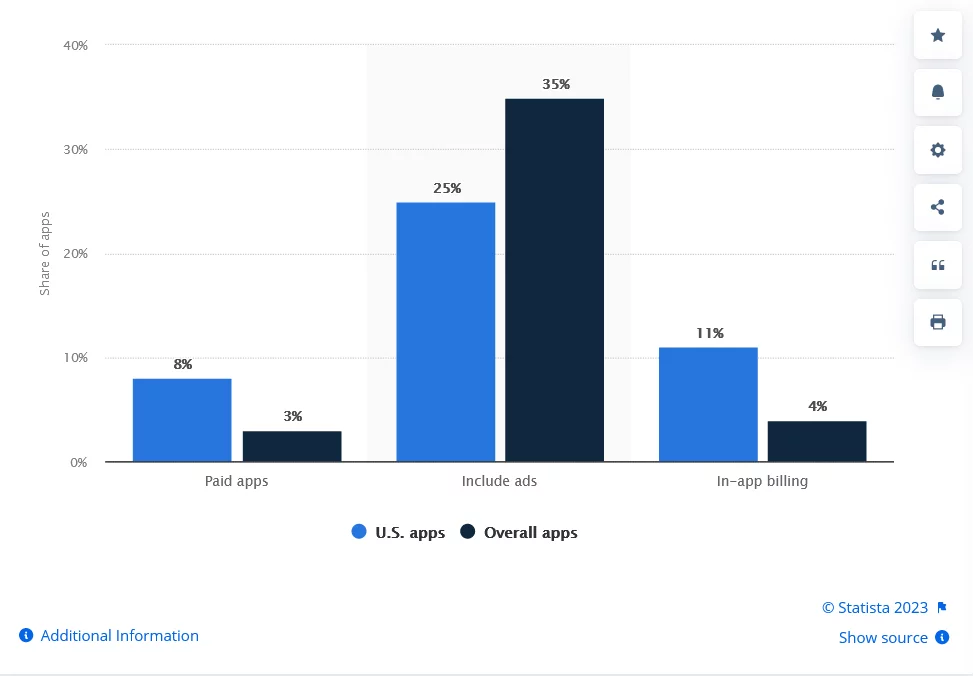
*Most popular app monetization methods by publishers from the United States as of July 2023
To understand this phenomenon, we must delve into the captivating world of app monetization strategies. At its core, app monetization refers to the art and science of transforming an app into a potent source of income. While the concept of charging users upfront remains a conspicuous strategy, it is merely one among a plethora of innovative approaches that app developers employ to generate revenue.
Consider this data point: global app revenue is anticipated to surge beyond a staggering $930 million in the year 2023. This statistic alone underscores the significant financial potential that the app market holds.
But let’s unravel the mechanics of app monetization further. It’s not a solitary method, but a diverse repertoire of techniques, each meticulously tailored to suit specific app dynamics. The essence of app monetization hinges on offering value to users while strategically integrating revenue-generating mechanisms.
In a landscape that often seems dominated by “free” apps, the question becomes: how do these apps pull off the financial feat? The answer lies in the art of captivating user engagement and subsequently introducing revenue streams that enhance rather than disrupt the user experience. From the unobtrusive integration of advertisements that cater to users’ preferences to the implementation of freemium models where basic features are provided for free while advanced functionalities require payment, the spectrum of strategies is extensive.
What is App Monetization?
The landscape of app monetization is a dynamic one, where a successful approach often involves the harmonious integration of multiple monetization methods. Crafting the right strategy hinges on a profound understanding of the user base, their motivations for engaging with the app, and the app’s core functionality.
A pivotal facet of app monetization often involves the strategic inclusion of advertisements. Within this realm, in-app ads emerge as a prominent strategy. These can manifest as unobtrusive banner ads positioned at the top of the screen, incentivizing users through points in exchange for viewing video commercials, or even collaborating with third-party ad networks to amass user data for the purpose of analytics and future marketing endeavors.
However, the monetization spectrum is far broader. Certain apps are inherently monetized, such as personal shopping applications or mobile extensions of established e-commerce platforms like eBay or Amazon. But for the majority, monetization primarily occurs through in-app purchases or subscription models. It’s important to note that even within these standard strategies, there exists a wealth of possibilities and variations, especially considering the expansion of mobile apps into realms beyond traditional mobile devices, encompassing realms like televisions, cars, and smart appliances.
This evolution implies that those seeking to monetize an app must cast their gaze beyond the confines of smartphones and tablets. While mobile devices persist as potent hubs for user engagement and potential monetization avenues, other devices are already carving out niches that are better suited for particular products, services, or experiences.
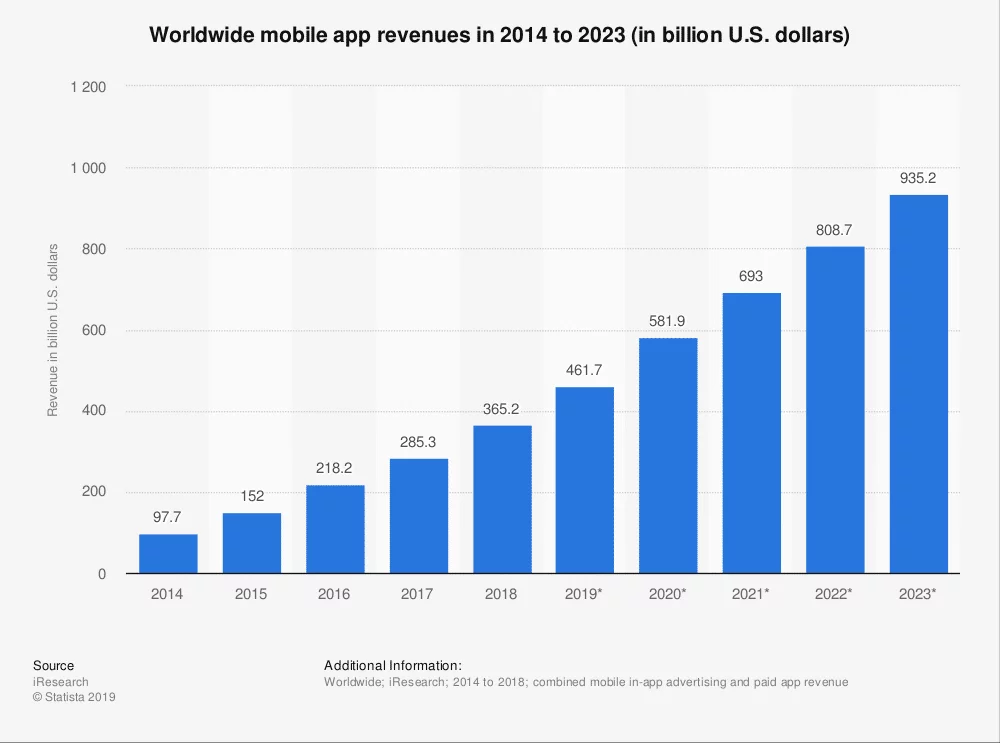
How Much Money Can Free Apps Make?

Global average eCPMs by country and device. (Source: Appodeal / Business of Apps)
The question of how much revenue free apps can generate is one that unfolds with nuances and intricacies, making it a topic governed by a resounding “it depends.”
In truth, while there are certainly instances of free apps raking in millions of dollars in annual revenue, these cases stand as exceptions rather than the norm. Yet, this reality doesn’t deter thousands of free apps from consistently earning thousands of dollars in revenue each month.
But what is the quantifiable extent of this potential earnings? Well, the answer to this question is a tapestry woven with threads of variability. The revenue generated by a free app is heavily influenced by factors as diverse as the app’s genre, the number of users it attracts, the devices utilized to access it, and the geographical location of its users.
Within this complexity, app owners and advertisers typically employ a metric known as eCPM (effective cost per mille or effective cost per thousand impressions) as a cornerstone for evaluating revenue based on impressions.
To gain perspective on this, let’s delve into some specifics. What is the average revenue generated from ads in apps?
In the year 2020, for instance, the average eCPM for banner ads in mobile apps within the United States spanned from $0.37 for Android apps to $0.46 for iPhone apps. This translates to a scenario where a US-based iPhone app showcasing a banner ad and receiving 5,000 impressions per day would yield a daily revenue averaging $2.30.
While this figure may not appear substantial, it is by no means an anomaly, particularly when considering that banner ads are merely one facet of the multifaceted array of ad types that an app can utilize to monetize user experiences. Various other ad formats, such as reward videos, boast the potential to yield significantly higher eCPMs.
However, many mobile app developers find themselves gravitating toward paid models, freemium structures, and subscription models as avenues to ensure a robust and consistent stream of revenue. This strategic diversity underscores the dynamic landscape of app monetization, where a blend of approaches can collectively contribute to financial success, even for apps that are available for free download.
10 Strategies for App Monetization:
1. Freemium plans
Freemium apps, a widely adopted monetization strategy, involve the provision of a combination of free and paid features within an application.
An exemplary instance of a freemium app is Spotify, a music streaming service that has remarkably harnessed this strategy to achieve success.
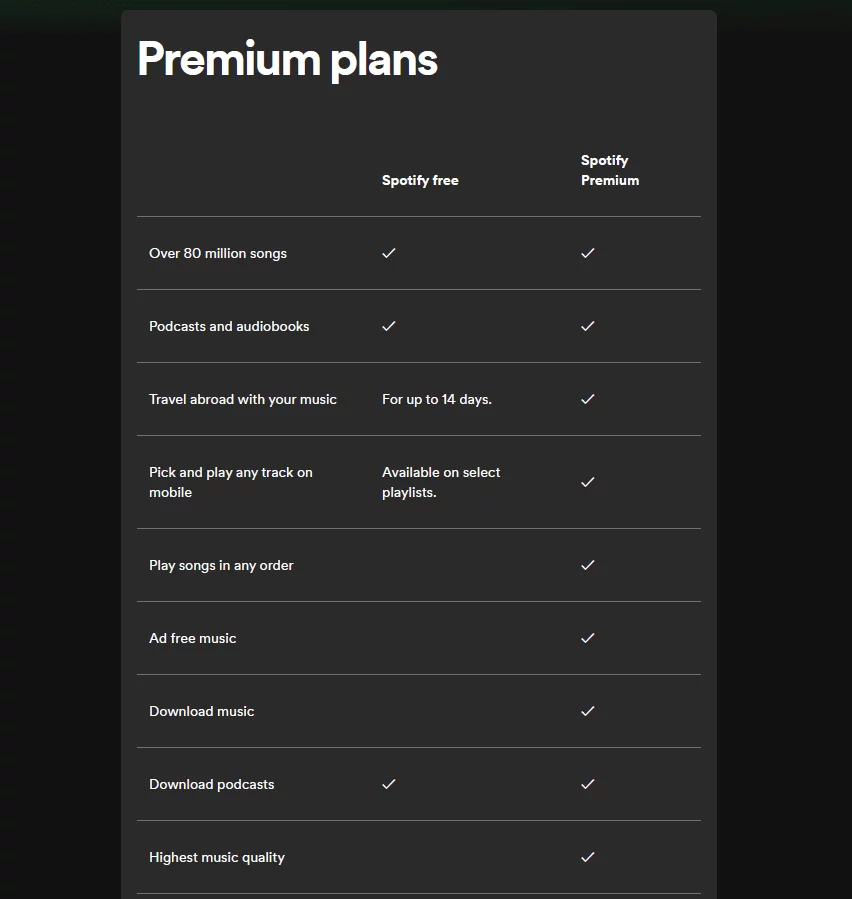
This approach is rooted in the understanding that potential users often seek a way to test the waters before fully committing to a purchase, particularly given the plethora of apps available, some of which might offer similar functionalities. Just as a free trial period provides users with an opportunity to experience an app’s capabilities and benefits, free versions of apps serve as their digital equivalent.
While a majority of users might remain content with the free version, a notable percentage might opt for the premium or paid version, thereby establishing a stable source of revenue. A pertinent example of this dynamic can be observed through Spotify, which leverages the freemium model to its advantage. In the year 2022 alone, Spotify garnered an impressive revenue of over $12 billion, underscoring the financial potential that can be unlocked through this strategy.
By combining the allure of a cost-free experience with the enticing features of a premium version, freemium apps create a win-win scenario for both users and developers. This strategy resonates with users’ desire for exploration and choice while also offering a viable path for developers to cultivate revenue streams in an increasingly competitive app landscape.
To delve further into the world of freemium apps and the strategic interplay of their features, consider exploring the success story of Spotify, which embodies the prowess of this monetization approach.
2. Premium Apps(Paid)
When pondering the question of how apps can generate revenue without relying on ads, a common answer emerges: by charging users an upfront fee for downloading the app.
This strategy, known as the premium model, offers users the opportunity to access the app’s full range of features and functionalities upon payment. While not everyone may be immediately inclined to invest in an app upfront, a significant portion of users are willing to do so if the app aligns perfectly with their needs or if it has garnered a reputation for excellence.
A compelling real-life example of the premium model is the app “Minecraft: Pocket Edition”. This game, available on various platforms including mobile devices, offers a paid version that allows users to fully experience the game without any in-app advertisements or limitations. The app’s reputation for delivering an immersive gaming experience has led many users to gladly pay the premium price for unhindered gameplay.
Successfully implementing the premium model usually involves catering to a specific market niche that boasts a dedicated and loyal customer base. As an app becomes the favored solution for addressing a particular need or desire, the price of entry becomes less of a concern for users.
For newer apps that lack a well-established reputation, a strategic path to adopting the premium model involves offering limited free trials. By allowing users to sample a portion of the app’s features and experiences, developers can entice users to explore the full range of functionalities by opting for the premium version.
3. In-app purchase
The concept of in-app purchases unfolds as an immensely potent revenue generation strategy that mirrors the effectiveness of the freemium model.
In the digital realm, in-app purchases serve as a powerful channel through which free apps can amass revenue. A prominent embodiment of this strategy lies within the realm of mobile gaming. Game apps, for instance, expertly leverage this pricing approach, enabling players to engage in digital transactions to acquire in-game currency or virtual items like exclusive loot, abilities, or cosmetic enhancements. A paradigmatic illustration of this can be witnessed in the case of the highly popular game “Candy Crush Saga,” which, in the year 2022 alone, generated an impressive revenue exceeding $600 million through this model.
However, it’s important to note that the efficacy of the in-app purchases model isn’t confined solely to the gaming domain. Even for non-game apps, this strategy holds the potential to reap substantial returns. The key lies in offering “extra content” within the app, content that enriches the user experience without compromising the app’s default functionality.
This concept is particularly appealing as it allows users to tailor their app experience according to their preferences and requirements. They can choose to enhance their interaction by making selective purchases, thereby customizing their engagement and accessing specific functionalities or premium features that align with their interests.
In essence, in-app purchases epitomize the art of capitalizing on user engagement and enriching the app experience through value-added offerings. To explore this strategy in action, consider delving into examples like the revenue triumph of “Candy Crush Saga” or the myriad of apps that offer supplementary content and experiences through in-app purchases.
4. Paid Subscription
Consider the language learning app Duolingo. Duolingo offers a range of subscription plans that cater to different segments of its user base. The app provides a free version that allows users to learn languages through interactive lessons and exercises. However, for those seeking a more immersive and feature-rich experience, Duolingo offers a subscription plan called “Duolingo Plus.”
With a Duolingo Plus subscription, users gain access to an ad-free environment, offline access to lessons, progress tracking, and the ability to download lessons for offline learning. This subscription plan resonates particularly well with users who are dedicated to learning a new language and value the convenience of an uninterrupted learning experience.
Duolingo’s approach underscores the power of paid subscription models in providing tailored experiences. The free version attracts a wide range of users, while the premium subscription addresses the needs of those who seek enhanced features and a seamless learning journey. By offering a mix of free and subscription-based options, Duolingo is able to cater to both casual learners and serious language enthusiasts.
This example further highlights how paid subscription models can be a strategic avenue for app developers to monetize their offerings while delivering value to users based on their preferences and requirements.
5. In-App Ads and Sponsorships
The in-app advertising model has become the cornerstone of revenue generation for a vast majority of apps available in the market today.
Across the app landscape, a variety of ad formats ranging from simple banner ads to full-screen pop-ups and video rewards are strategically integrated. This diversity in ad formats allows developers to cater to various user experiences while simultaneously offering different revenue tiers.
A real-life example that illustrates the ubiquity of in-app ads is evident in popular applications across different domains. For instance, casual games often incorporate banner ads that appear seamlessly within the user interface. Similarly, utility apps might showcase full-screen ads when users navigate through certain sections. This ad-driven revenue model plays a pivotal role in maintaining the “free” nature of many apps while still facilitating revenue generation.
The dynamic nature of app advertising extends beyond mere ad display. It encompasses partnerships with mobile ad networks, which can provide developers with a spectrum of incentives to place their ads before an engaged audience. One illustrative method is through Google AdWords campaigns, which allow developers to gauge the potential earnings from ad placements based on factors such as user engagement and demographics.
Furthermore, many apps capitalize on company partnerships or sponsorship models to proactively generate upfront revenue. Beyond financial gain, such partnerships often bestow new apps with a much-needed veneer of reputation and authority. This synergy benefits both parties: the app gains financial support while the sponsoring company gains exposure and association with a promising product. This ecosystem of in-app ads and sponsorships mirrors the complex interplay between developers, users, and advertisers, resulting in a harmonious blend of revenue generation and user engagement. To witness this model in practice, one can explore the ad integrations in various popular apps and observe how partnerships propel new apps into the limelight.
6. Email Lists
In the landscape of revenue generation strategies, the power of building email lists from app users emerges as a formidable contender. With the projected number of active email users slated to reach a staggering 4.37 billion in 2023, harnessing the potential of email lists can unlock multiple revenue streams and significantly bolster digital marketing endeavors. This is particularly potent given that email users tend to retain their email addresses and regularly peruse their inboxes.
A compelling real-life example that underscores the significance of email lists is evident in the world of e-commerce. Consider the popular online retailer Amazon, which adeptly leverages email lists to drive its revenue streams and foster customer engagement. Amazon’s approach involves sending personalized product recommendations, updates on deals and discounts, and reminders about abandoned shopping carts to its vast email subscriber base. By harnessing the power of email marketing, Amazon sustains its revenue momentum while also nurturing customer relationships.
The process of gathering emails from app users is often as simple as asking for them. If your app necessitates user account creation or subscription, you’re already poised on the threshold of building an email list. The subsequent step involves devising ways to maximize the potential of email marketing. This can encompass a spectrum of strategies, from notifying users about ongoing sales and promotions to sending gentle nudges that encourage heightened app engagement.
The beauty of email lists lies in their enduring potential. Once you establish a foundation of engaged email subscribers, you can continuously nurture these relationships by delivering valuable content and tailored offers. This, in turn, can culminate in a consistent flow of revenue as users respond to your strategically crafted emails.
7. Ecommerce
Visualize an ecommerce app as a gateway to a captivating shopping experience. Such apps can transcend conventional brick-and-mortar shopping by offering users an immersive digital marketplace. This dynamic is prominently seen in apps that furnish an array of products, enabling users to explore, select, and purchase items with unprecedented ease and convenience.
A real-life illustration of the ecommerce model’s prowess lies in the platform Etsy. Etsy serves as a thriving online marketplace, enabling individual artisans and crafters to showcase and sell their unique creations. By providing a seamless user experience and a platform for micro-businesses to flourish, Etsy generates revenue not only for the platform itself but also for the countless sellers who participate in its digital ecosystem.
The beauty of the ecommerce model lies in its ability to seamlessly blend user engagement, convenience, and revenue generation. By offering users a dynamic platform to explore and procure products, ecommerce apps create a symbiotic relationship where users’ needs are met, and developers earn revenue in return.
To witness the success of the ecommerce model, delve into examples like Etsy and explore how these apps enhance shopping experiences, empower sellers, and create a harmonious balance between consumer demands and app-generated revenue.
8. SMS and Text Marketing
In the realm of app monetization, SMS and text marketing emerges as a strategic avenue, harnessing the inherent intimacy of mobile devices to boost user engagement and revenue-generation efforts.
The ubiquity of mobile phones enhances the viability of SMS marketing. With the number of active mobile users soaring, text messages provide a swift and efficient channel to connect with app users. A real-life example of the effectiveness of SMS marketing can be witnessed in the world of retail. Retail giants often employ text marketing to notify customers about flash sales, exclusive offers, and time-sensitive deals. Brands like Victoria’s Secret, for instance, leverage text marketing to instantly inform subscribers about promotions, prompting users to engage with the brand and potentially make purchases.
While sending texts to users might not directly translate into revenue, it serves as an effective means of enhancing user engagement. SMS marketing allows app developers to quickly dispatch reminders, updates, alerts, and promotional content to their entire user base. This direct line of communication plays a pivotal role in keeping users informed and invested in the app’s offerings.
The true potential of SMS marketing lies in its ability to catalyze revenue generation through user engagement. By employing persuasive messaging and strategic incentives, developers can entice users to interact with the app in ways that generate revenue. For instance, texts can encourage users to explore new content, watch advertisements, take advantage of discounted products, make purchases, or preview exclusive features before subscribing.
9. White Labeling
White labeling is a mutually beneficial strategy where up-and-coming app developers and established brands collaborate to create successful apps. While a new app idea might be promising, it can often struggle to gain traction without proper support and backing. This is where white labeling comes into play, offering a solution that benefits both parties involved.

In this approach, a mobile app development company creates an app and then sells or licenses it to existing business owners. These businesses can then rebrand the app and market it as their own, effectively putting it under their label. This arrangement provides several advantages for both the app developers and the brand owners.
For app developers, white labeling offers a swift way to generate revenue. Instead of waiting for an app to gain popularity in a crowded market, they can sell their proven app directly to businesses that are in need of such solutions. This immediate monetization opportunity can be particularly attractive for new developers or companies looking to boost their financial resources.
On the other side, established businesses benefit from white labeling by gaining access to a ready-made app that aligns with their needs. They can introduce a new and exciting product to their customers without the substantial investment of time and resources that go into app development. This strategy is especially useful when businesses want to diversify their offerings or extend their brand’s reach into the digital space.
A real-life example of white labeling is the practice of offering mobile apps for small businesses in various industries. Many restaurants, salons, fitness centers, and other local businesses rely on white-labeled apps to provide services like online reservations, order placement, loyalty programs, and more. These businesses can leverage the expertise of app developers while delivering a tailored app experience to their customers.
10. Data Licensing
In today’s data-centric world, businesses highly value accurate and relevant user data to fuel their operations, make informed decisions, and understand market trends. This has led to an emerging trend where popular apps monetize their amassed user data by licensing it to third parties.
Mobile devices have become a goldmine of behavioral data, providing insights into user preferences, behaviors, and patterns. For instance, an app that tracks fitness activities can provide valuable information about users’ exercise routines and health goals, which can be of great interest to health-related companies or insurance providers. Similarly, a social media app can offer insights into user interactions and interests, enabling advertisers to target their campaigns more effectively.
Data licensing involves entering into agreements with third-party businesses that are willing to pay for access to this valuable user data. These businesses might include marketing firms, research organizations, advertisers, and more. By analyzing the aggregated and anonymized user data, these parties can gain insights into consumer behaviors, preferences, and trends, allowing them to tailor their strategies and offerings accordingly.
However, it’s important to note that data privacy and security are paramount in this context. Apps need to handle user data responsibly and transparently, ensuring that users’ privacy rights are respected. Many jurisdictions have stringent data protection regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the European Union and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) in the United States.
To successfully implement data licensing, apps should clearly outline data usage policies and obtain users’ explicit consent to collect and share their data. Transparency in how data will be utilized and ensuring compliance with relevant data protection laws are crucial steps in building trust with users.
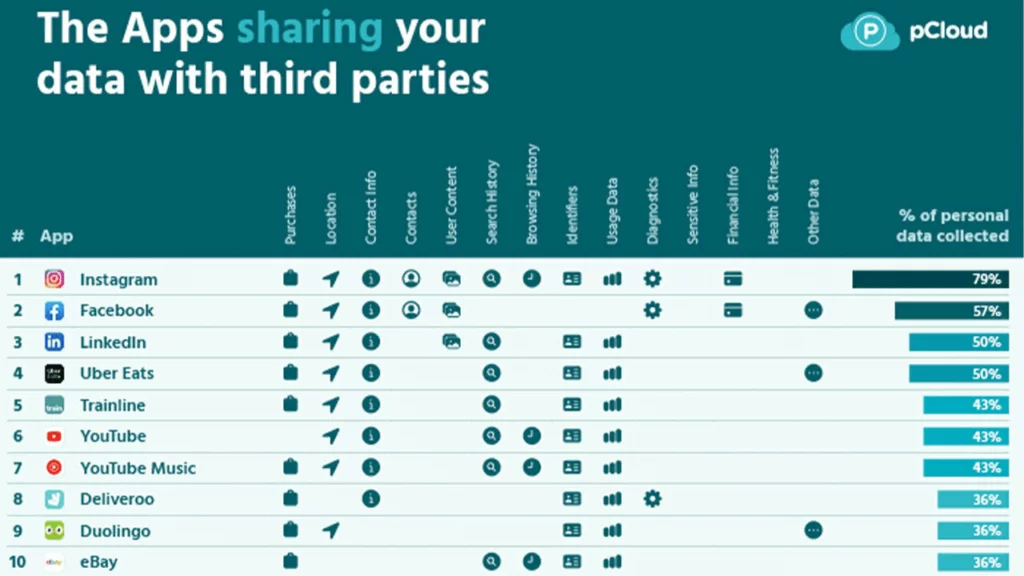
A real-life example of data licensing can be seen in the collaboration between popular fitness tracking app Strava and urban planning organizations. Strava gathers data from users’ exercise activities, including running and cycling routes. This data is then aggregated and shared with city planners and transportation agencies to assist in urban mobility and infrastructure planning. By licensing this data, Strava contributes to making cities more bike-friendly and enhancing transportation planning.
Factors to Consider Before Choosing an App Monetization Strategy
- Understand Your App’s Value Proposition: Begin by thoroughly understanding your app’s features, benefits, and unique value proposition. Consider what problem your app solves for users and how it enhances their lives.
- Analyze Your Target Audience: Identify your target audience’s preferences, behaviors, and spending habits. Understand their willingness to pay for specific features or benefits.
- Evaluate App Category: The category of your app (e.g., gaming, productivity, social networking) can influence the suitability of certain monetization strategies. For example, gaming apps often excel with in-app purchases, while subscription models are popular for content-driven apps.
- Assess Competitors: Research your competitors and analyze their monetization strategies. Understand what works for similar apps and identify gaps or opportunities that you can leverage.
- App Store Research: Study successful apps within your category on app stores. Examine their pricing models, in-app purchases, and reviews to gain insights into user preferences.
- Consider User Experience: Choose a monetization strategy that enhances, rather than hinders, the user experience. Users should perceive value in the payment they make.
- Experiment with Hybrid Models: Consider combining multiple monetization methods to diversify your revenue streams. For example, a freemium model can be combined with in-app purchases and advertising.
- Set Clear Monetization Goals: Define clear financial goals for your app. Determine how much revenue you aim to generate and over what time frame.
- Analyze User Acquisition Costs: Calculate the cost of acquiring new users through different marketing channels. Ensure that your chosen monetization strategy allows you to cover these costs while generating profit.
- Balance Between Free and Paid: Strike a balance between offering a free version of your app to attract users and offering premium features for those willing to pay.
- User Feedback and Testing: Collect user feedback through surveys or beta testing to understand how they perceive different monetization options. This can provide valuable insights into what users are willing to pay for.
- Consider Long-Term Sustainability: Choose a monetization strategy that can be sustained over the long term. Ensure that users continue to find value in your app and are willing to engage with it.
- Adapt and Iterate: Be prepared to adapt and iterate your monetization strategy based on user behavior, market trends, and feedback. Flexibility is key to staying competitive.
- Monitor and Optimize: Continuously monitor the performance of your chosen monetization strategy. Use analytics to track user engagement, conversion rates, and revenue generation.
- Legal and Ethical Considerations: Ensure that your chosen monetization strategy complies with relevant laws and regulations. Also, prioritize user privacy and data protection.
Conculsion:
App monetization, in essence, is about weaving value into every interaction. It’s about turning ads into opportunities for discovery, purchases into exciting experiences, and subscriptions into memberships to an exclusive club. When done right, it becomes a win-win – your users enjoy enhanced functionality, while you build a sustainable revenue stream to support continuous innovation and growth.
So, as you navigate the realm of app monetization, remember that it’s not a one-size-fits-all equation. It’s a dynamic puzzle that requires constant evaluation, adaptation, and evolution. By choosing a monetization strategy that speaks to your app’s soul and resonates with your users, you’re not just generating income; you’re cultivating a thriving ecosystem of value and success. After all, in the world of app monetization, the real currency is user satisfaction.
FAQs on App Monetization:
Can I use multiple monetization strategies for my app?
Yes, many successful apps employ hybrid strategies that combine multiple monetization methods. For example, you can offer a free version with ads while also providing a premium version with additional features.
How do I ensure a positive user experience while monetizing my app?
User experience is crucial. Choose monetization methods that enhance the user experience rather than interrupting it. Avoid intrusive ads, provide value through premium features, and offer clear benefits to paying users.
What if my app is new and doesn’t have a large user base yet?
For newer apps, it’s important to focus on attracting and engaging users before aggressively monetizing. Offering a free version with limited features or a trial period can help build a user base and gather feedback.



