Handling technical SEO for a large website with thousands of URLs presents unique challenges compared to smaller sites. Large enterprise sites often encounter significant issues with page indexing, which impacts their visibility in Google’s search rankings.
Common indexing pitfalls include duplicate content, inefficient crawl budget allocation, and incorrect sitemap configurations. These issues can hinder a site’s ability to achieve optimal search engine visibility and traffic.
Whether you’re a website owner, marketer, or SEO specialist, this blog offers valuable insights and actionable solutions to help large sites overcome page indexing issues and maximize their online presence.
Reasons for Indexing Issues:
A. Duplicate Content
Duplicate content occurs when identical or similar content exists on multiple website pages or across domains. This issue is prevalent on large ecommerce websites due to the sheer volume of the product pages and dynamic content.
Challenges:
- Indexing and Crawling Errors: Search engines may need help determining which version of the duplicated content to index, leading to inefficiencies in crawling and indexing.
- Wasted Crawl Budget: Crawlers may expend resources crawling multiple versions of the same content, which will exhaust the crawl budget without fully indexing essential pages.
B. Content Quality
High-quality content is vital for SEO success, as it enhances user engagement and signals relevance to search engines. Conversely, poor-quality content can harm rankings and user experience.
Challenges:
- Deprioritized Crawling: Search engines may prioritize low-quality or irrelevant content, reducing its visibility in search results.
- SEO Penalties: Outdated SEO tactics like keyword stuffing can lead to penalties, negatively impacting indexing and ranking performance.
C. XML Sitemap Issues
XML sitemaps are essential for guiding search engine crawlers to important pages on your website. However, issues with XML sitemaps can hinder proper indexing, especially for large websites with complex structures.
Challenges:
- Incomplete or Outdated Sitemaps: Search engines may not crawl or index the latest pages if the XML sitemap needs to be updated with new or modified content.
- Structural Discrepancies: Differences between the sitemap and actual site structure can confuse crawlers, leading to indexing errors.
D. Crawl Budget Limitations
A crawl budget refers to the number of pages that ansearch engine crawler can crawl and index within a given period. Large websites often need help utilizing their crawl budget efficiently.
Challenges:
- Resource Intensity: Large websites require more resources to fully index, potentially leading to incomplete indexing and missed opportunities.
- Missed Content: Pages more profound in the site hierarchy may not get crawled and indexed if the crawl budget is exhausted prematurely.
E. JavaScript and AJAX Challenges
Many large websites rely on JavaScript and AJAX to deliver dynamic content and enhance the user experience. However, these technologies can pose challenges for search engine crawlers, delaying the indexing of critical content.
Challenges:
- Rendering Delays: Search engines may not immediately render JavaScript content, leading to delayed indexing of dynamic content.
- Accessibility Issues: AJAX-generated content may not be accessible or interpretable by crawlers, resulting in incomplete indexing.
Strategies to Prevent Indexing Issues:
A. Use a Well-Structured Sitemap
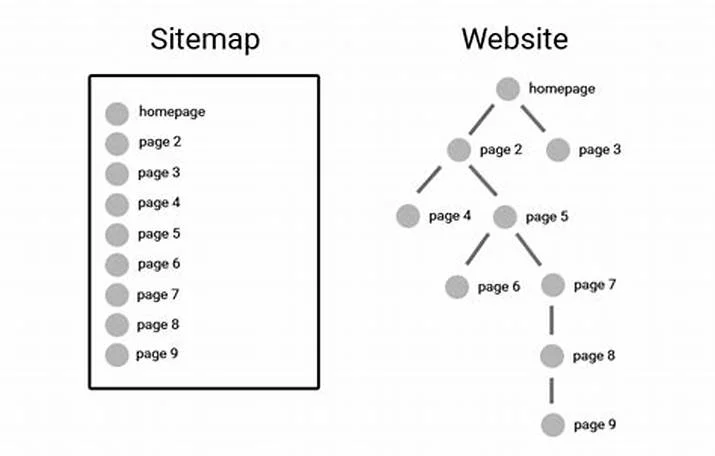
XML Sitemap:
An XML sitemap is a file which lists all the important URLs on your website, providing search engines with a roadmap of the site’s structure. This helps search engines like Google in discovering and indexing your pages efficiently. Maintaining an up-to-date XML sitemap ensures that new and updated content gets indexed quickly for large websites. The XML sitemap should include URLs for all key pages, including posts, category pages, and important subpages. Regularly updating the sitemap and submitting it to the search engines can significantly improve your site’s crawlability.
Plugins/Tools:
- Yoast SEO (WordPress): This popular SEO plugin automatically generates an XML sitemap for your site, ensuring that all important pages are included and updated regularly.
- Google XML Sitemaps (WordPress): A dedicated plugin for creating comprehensive XML sitemaps. It supports all kinds of WordPress-generated pages and custom URLs.
- Screaming Frog SEO Spider: A desktop program that allows you to crawl websites and generate XML sitemaps. It’s particularly useful for large websites with complex structures.
HTML Sitemap:
An HTML sitemap is a page on your website that lists important links in a human-readable format. It helps the users and search engines navigate your site more effectively. While XML sitemaps are designed for search engines, HTML sitemaps are beneficial for users, providing them with a clear overview of your site’s content. This can be particularly helpful on large websites where it might be challenging for users to find specific information through the main navigation alone.
Plugins/Tools:
- WP Sitemap Page (WordPress): A simple plugin that allows you to create a customized HTML sitemap. It automatically updates as you add new content to your site.
- Slick Sitemap (Joomla): This Joomla plugin creates an HTML sitemap that improves site navigation and helps users find information quickly.
B. Optimize Robots.txt
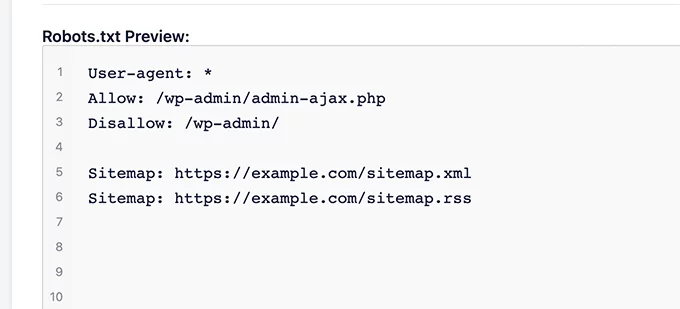
Allow Important Pages:
The robots.txt file instructs search engine bots which pages or sections of your site they can or cannot crawl. Ensure that your robots.txt file allows access to important pages for optimal SEO performance. Blocking essential pages can prevent them from being indexed, negatively impacting your search engine rankings. Regularly review and update your robots.txt file to ensure it aligns with your current SEO strategy and site structure.
Plugins/Tools:
- Yoast SEO (WordPress): This plugin includes a feature to easily edit the robots.txt file, allowing you to manage which pages are crawled by search engines without needing to access your server files.
Disallow Non-Essential Pages:
In contrast to allowing important pages, you should use the robots.txt file to block access to non-essential or sensitive pages. These might include admin pages, login pages, or dynamically generated pages with URL parameters that do not need to be indexed. Blocking these pages helps conserve your site’s crawl budget and ensures that the search engines focus on indexing your important content.
Plugins/Tools:
- All in One SEO Pack (WordPress): Another popular SEO plugin that allows you to easily manage and edit your robots.txt file to ensure non-essential pages are properly blocked.
C. Canonicalization
Source: SAP
Canonical Tags:
Canonical tags indicate the preferred version of a webpage when there are multiple URLs with similar content. This helps prevent duplicate content and ensures search engines understand which page to index and rank. For large websites, it’s common to have different URLs that lead to similar content (e.g., due to tracking parameters or different categorization paths). Canonical tags can consolidate link equity and improve your site’s overall SEO.
Plugins/Tools:
- Yoast SEO (WordPress): This plugin automatically adds canonical tags to your pages, ensuring that search engines know which version of a page to index. It also allows manual adjustments if needed.
Consistent URL Structure:
Maintaining a consistent URL structure is crucial for SEO. Inconsistent URLs can lead to duplicate content issues and confuse users and search engines. Ensure that each page on your site has a unique and standardized URL format. This includes using lowercase letters, hyphens instead of underscores, and avoiding unnecessary parameters. Consistent URLs make it easier for search engines to crawl and index the site and also improve the user experience.
Plugins/Tools:
- Redirection (WordPress): This plugin helps manage 301 redirects and track 404 errors, ensuring URL changes are handled correctly without creating duplicate content issues.
D. Avoid Duplicate Content

Unique Content:
Ensuring all pages on your site have unique and valuable content is essential for avoiding duplicate content issues. Duplicate content can confuse the search engines, leading to lower rankings or penalties. Each page should offer distinct information, targeting different keywords or aspects of your niche. Regularly audit your site in order to identify and remove or consolidate duplicate content and ensure that new content is always original.
Plugins/Tools:
- Copyscape: An online tool that checks for duplicate content across the web, helping you ensure your content is unique.
- Siteliner: This tool scans your website for internal duplicate content and provides detailed reports.
URL Parameters:
URL parameters can create multiple versions of the same page, leading to duplicate content issues. Common URL parameters include tracking codes, session IDs, and sorting options. Use URL parameter handling tools to specify how search engines should treat these parameters, ensuring they do not index multiple versions of the same content.
Plugins/Tools:
- Google Search Console: Allows you to set URL parameter handling preferences directly in the tool, helping search engines understand how to treat different parameters.
E. Internal Linking
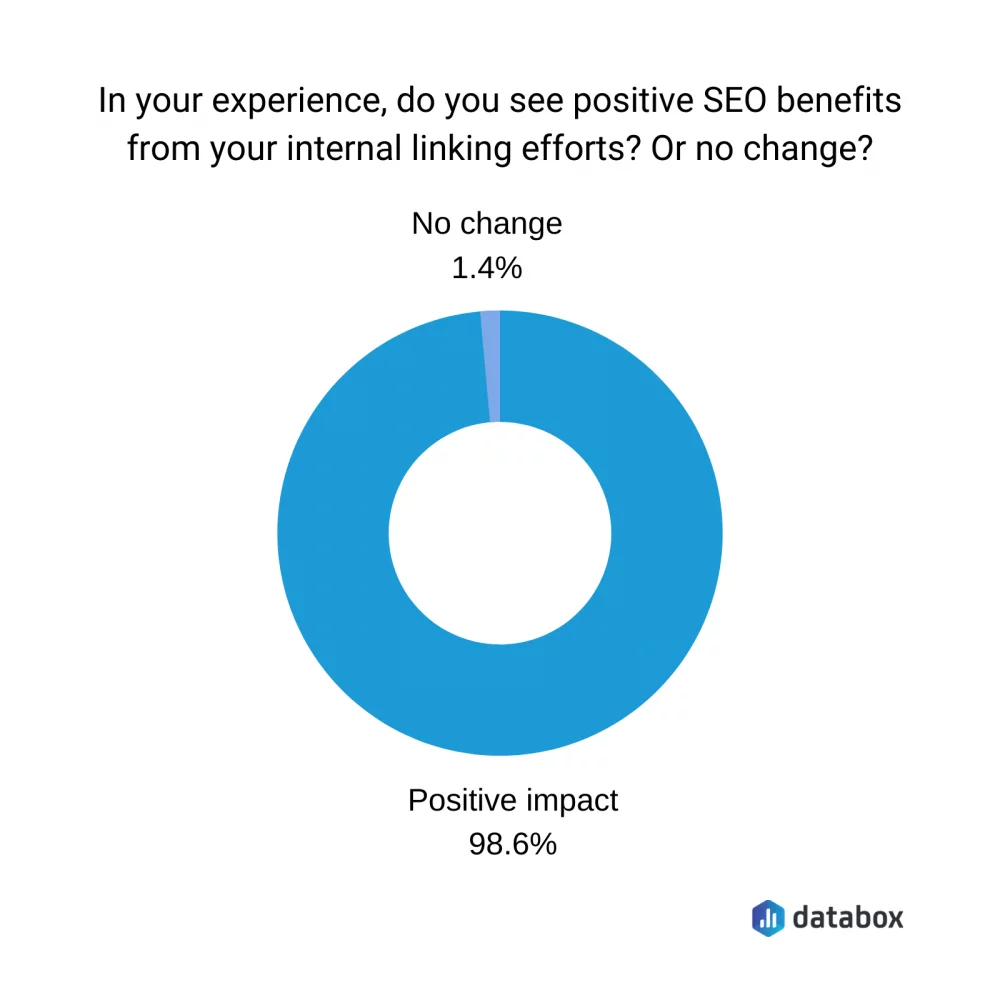
Logical Structure:
Implementing a logical and hierarchical internal linking structure ensures that critical pages are easily discoverable by search engines and users. Internal links help distribute link equity throughout your site, boosting the SEO of key pages. Organize your content into categories and sub-categories, and ensure every page is linked from at least one other page on your site.
Plugins/Tools:
- Yoast SEO (WordPress): Offers internal linking suggestions based on your editing content, helping you create a well-structured internal link network.
- Internal Link Juicer (WordPress): Automates internal linking based on keywords and content relevancy.
Anchor Text:
Use descriptive and relevant anchor text for internal links. Anchor text helps search engines understand the context of the linked page, improving its relevance for specific keywords. Avoid generic anchor texts like “click here” and use keyword-rich phrases that accurately describe the linked content.
Plugins/Tools:
- Link Whisper (WordPress): An advanced internal linking tool that provides smart suggestions for relevant anchor texts based on your content.
F. Pagination Handling

Rel=”next” and Rel=”prev”:
Use rel=”next” and rel=”prev” tags to indicate the relationship between paginated pages. Pagination is common on large websites, especially for blogs, e-commerce sites, and content-rich portals. These tags help search engines understand that the pages are part of a series, improving indexing and avoiding duplicate content issues.
Plugins/Tools:
- Yoast SEO (WordPress): Automatically adds rel=”next” and rel=”prev” tags to paginated pages.
View-All Page:
If feasible, consider creating a “view-all” version of paginated content. This allows users and search engines to access the entire content on a single page, improving user experience and indexing efficiency. Ensure the view-all page is optimized correctly and not lead to performance issues due to excessive content loading.
Plugins/Tools:
- WP-PageNavi (WordPress): Enhances pagination on WordPress sites, making managing and presenting paginated content easier.
G. Use of Meta Tags

Noindex Tag:
Use the noindex meta tag to prevent indexing of pages that should not appear in search results, such as thank-you pages, admin pages, or certain low-value content pages. This helps focus the search engine’s crawl budget on more important pages and keeps unnecessary pages out of the index.
- Plugins/Tools:
- Yoast SEO (WordPress): Allows you to easily add no-index tags to specific pages of the site.
Nofollow Links:
Use nofollow on links to pages that should not pass link equity. This is useful for links to low-value or untrusted pages, sponsored content, or login and registration pages. Nofollowing these links ensures your site’s link equity is concentrated on high-value pages.
Plugins/Tools:
- Rel Nofollow Checkbox (WordPress): Adds a simple checkbox in the WordPress editor to mark links as nofollow.
H. Regular Audits
Technical SEO Audits:
Regularly perform technical SEO audits to identify and fix crawling and indexing issues. These audits should cover site speed, mobile-friendliness, broken links, duplicate content, and security. Regular audits help maintain optimal site performance and quickly address any indexing issues.
Plugins/Tools:
- Screaming Frog SEO Spider: A comprehensive tool for conducting in-depth technical SEO audits.
- SEMrush Site Audit: Provides detailed reports on technical SEO issues and suggestions for fixes.
Content Audits:
Conduct content audits to remove or update outdated or low-quality content. Regular content audits ensure that all the content on your site is relevant, valuable, and up-to-date, which improves user experience and helps maintain strong search engine rankings.
Plugins/Tools:
- Content Audit (WordPress): Helps track the quality and status of content across your site.
I. Mobile Optimization
Responsive Design:
Ensure your site is mobile-friendly and offers a consistent device experience. Responsive design automatically adjusts the layout and content based on screen size, providing a seamless user experience. With a major portion of web traffic from mobile devices, mobile optimization is crucial for user experience and search engine rankings.
Plugins/Tools:
- Jetpack (WordPress): Includes tools for optimizing your site for mobile devices.
- AMP for WP (WordPress): Helps implement Accelerated Mobile Pages (AMP) to improve mobile performance.
Mobile Sitemap:
If your site has URLs different from your desktop site, create a separate mobile sitemap. This ensures that the search engines can properly index the mobile versions of your pages. While responsive design is generally recommended, some sites may still use separate URLs for mobile content.
Plugins/Tools:
- Google Mobile-Friendly Test: Ensures your mobile site is optimized correctly.
- Yoast SEO (WordPress): Can help manage mobile sitemaps if needed.
J. Monitor Google Search Console
Coverage Report:
Regularly check the Coverage report in Google Search Console for any indexing errors or warnings. This report provides insights into which pages are indexed, which have errors, and why certain pages may not be indexed. Monitoring this report helps you quickly identify and resolve indexing issues.
Plugins/Tools:
- Google Search Console: Direct integration with your website for comprehensive monitoring and reporting.
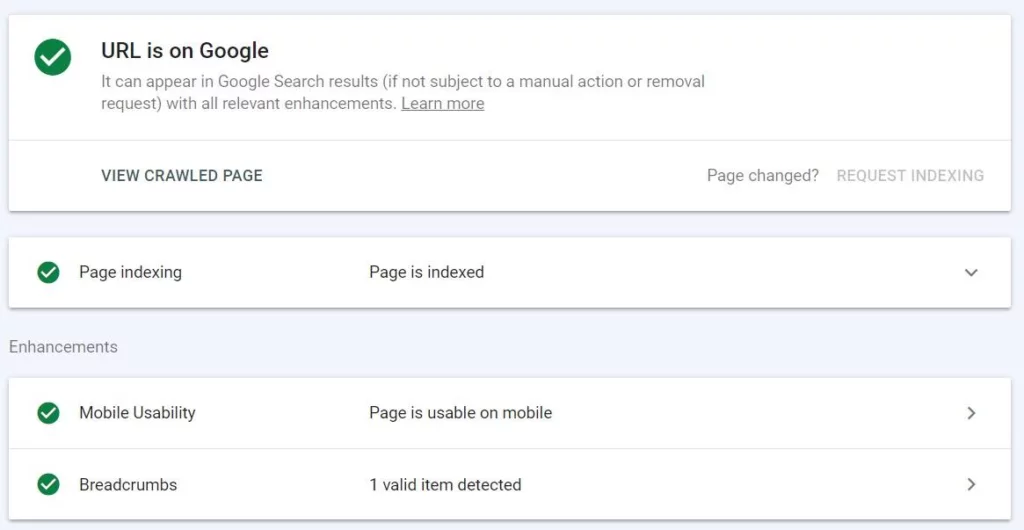
URL Inspection Tool:
Use the URL Inspection tool in Google Search Console to check the indexing status of individual pages. This tool lets you observe how Google views a specific page and provides detailed information on indexing status, mobile usability, and any detected issues.
Plugins/Tools:
- Google Search Console: Direct access to the URL Inspection tool for detailed page analysis.
K. Performance Optimization
Page Speed:
Optimize your website for fast loading times to ensure efficient crawling and a better user experience. Page speed is a crucial ranking factor, and slow-loading pages may lead to higher bounce rates and lower rankings. Techniques include optimizing images, leveraging browser caching, minifying the CSS and JavaScript, and using a Content Delivery Network.
Plugins/Tools:
- WP Rocket (WordPress): A powerful caching plugin significantly improving site speed.
- W3 Total Cache (WordPress): Enhances your site’s performance through caching and minification.
Server Performance:
Ensure your server can handle the load, especially for large websites with high traffic. Server performance impacts how quickly your site loads and how efficiently search engines can crawl it. Regularly monitor server performance and consider upgrading hosting plans or using a dedicated server if needed.
Plugins/Tools:
- New Relic: Provides detailed performance monitoring and analysis for your server.
- Pingdom: Helps monitor server performance and uptime.
L. Structured Data
Schema Markup:
Implement schema markup to help search engines understand your content better and improve indexing. Schema markup provides context to the data on your pages, which can enhance search visibility through rich snippets and other SERP features. Common schema types include articles, products, reviews, events, and recipes.
Plugins/Tools:
- Schema Pro (WordPress): Simplifies the implementation of schema markup on your site.
- Yoast SEO (WordPress): Includes built-in support for basic schema markup.
Rich Results Testing:
Use Google’s Rich Results Testing tool to ensure your structured data is implemented correctly. This tool checks whether your pages are eligible for rich results in search engines, providing insights and recommendations for improvements.
Plugins/Tools:
- Google Rich Results Test: Direct access to Google’s tool for testing and validating structured data.
M. Manage Crawl Budget
Efficient Crawling:
Use Google Search Console and server logs to monitor how search engines are crawling your site. Efficient crawling ensures that important pages are indexed while avoiding excessive crawling of low-value pages. Regularly reviewing crawl stats helps identify any issues or inefficiencies in the crawling process.
Plugins/Tools:
- Screaming Frog SEO Spider: Provides detailed crawling reports and insights.
- Google Search Console: Offers crawl stats and insights directly from Google.
Prioritize Key Pages:
Ensure important pages are easily accessible and not buried deep within your site’s structure. Key pages should be linked from the homepage or other high-traffic pages to ensure they receive sufficient crawl attention. Use internal linking and sitemaps to highlight these pages.
Plugins/Tools:
- Yoast SEO (WordPress): Helps manage internal linking and page prioritization.
- SEMrush Site Audit: Provides recommendations for improving site structure and page accessibility.
Conclusion:
Effective crawling and indexing management is crucial for large websites to maintain optimal search engine visibility and performance. By addressing common issues such as duplicate content, low-quality content, XML sitemap errors, crawl budget limitations, and JavaScript challenges, you can ensure that your site is efficiently indexed and ranks well in search engine results. Regular audits, strategic content management, and advanced tools and technologies are essential for overcoming these challenges and achieving long-term SEO success.
FAQs on Page Indexing Issues:
Why is content quality important for SEO?
High-quality content improves user engagement, signals relevance to search engines, and enhances overall site performance. Poor-quality content can lead to decreased visibility and potential SEO penalties.
How often should I update my XML sitemap?
XML sitemaps should be updated regularly to reflect new and modified content. This ensures that the search engine crawlers can find and index the latest pages on your site.
What are the benefits of using prerendering for JavaScript content?
Prerendering generates static HTML versions of JavaScript-rendered pages, making it easy or search engine crawlers to index dynamic content. This improves indexing speed and ensures critical content is visible in search results.
How can I optimize my crawl budget?
Optimize your crawl budget by prioritizing important pages, using robots.txt to control crawler access, and regularly updating your XML sitemap. Addressing duplicate content and improving site structure also helps efficiently use your crawl budget.



