Google Analytics is undoubtedly a powerful tool for understanding website performance, but its accuracy can sometimes be questioned. Have you ever found yourself scratching your head over discrepancies between Google Analytics reports and your server logs? If so, you’re not alone.
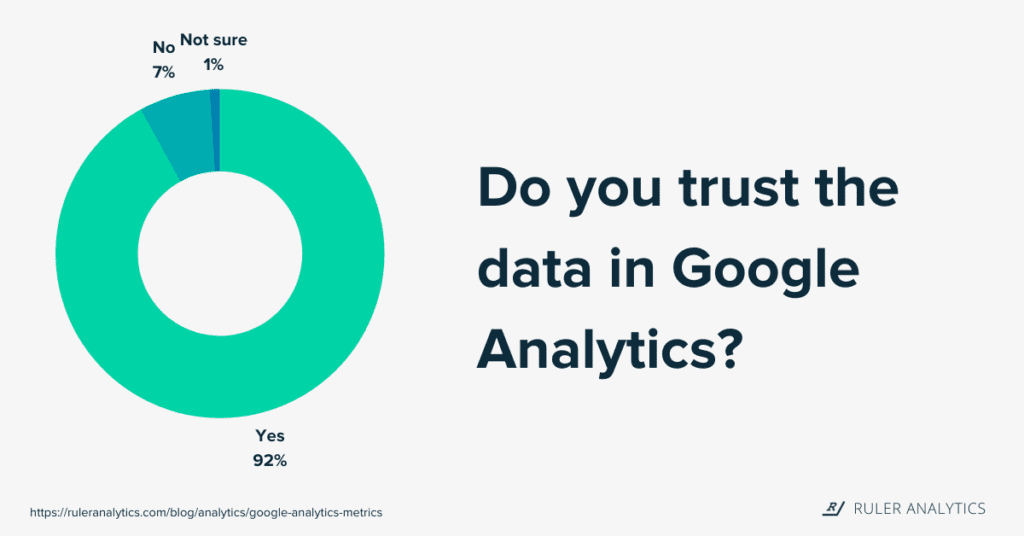
In the quest for reliable data, many businesses rely heavily on Google Analytics to inform their decision-making processes. After all, accessing accurate insights is crucial for understanding user behavior, optimizing marketing efforts, and ultimately driving business growth. However, achieving perfect accuracy in data analysis is often an elusive goal.
Key Google Analytics Errors and Resolutions:

- Offline Campaigns Not Tracked
Offline campaigns, such as magazine or newspaper advertisements, present a unique challenge in terms of tracking their effectiveness. Unlike online campaigns with readily available metrics, it can be difficult to attribute website visits directly to offline sources. However, dismissing offline tracking altogether can lead to missed opportunities to understand the full impact of your marketing efforts.
Addressing Offline Tracking Challenges:
- Utilize Tracking Mechanisms: Implementing strategies like discount codes or unique landing pages with shortened links can help attribute website visits to specific offline campaigns. By providing incentives or directing users to customized landing pages, you create opportunities to track the success of your offline marketing efforts.
- Two-Step Marketing Campaigns: Employing two-step marketing campaigns, where initial contact is made offline (e.g., via print advertisement) and followed up with online engagement (e.g., visiting a website), allows for better tracking of conversion pathways. By prompting users to take a specific action online, such as entering a code or visiting a designated URL, you can better gauge the effectiveness of your offline initiatives.
- Interactive Engagement: Incorporating interactive elements such as “How did you find us?” popup forms on your website can provide valuable insights into the sources of your website traffic. Encouraging users to provide feedback on how they discovered your business can help bridge the gap between offline campaigns and online interactions.
- Cross-Domain Tracking Errors
Google Analytics defaults to tracking sessions using a single domain across all subdomains, which can lead to inaccuracies when users navigate between different domains. Without proper cross-domain tracking in place, traffic from external sources may be incorrectly attributed, skewing your analytics data.
Implementing Cross-Domain Tracking Solutions:
- Google Analytics Configuration: Google Analytics provides instructions for implementing cross-domain tracking directly within the platform. Alternatively, you can utilize the official Google Linker plugin for seamless integration and accurate tracking across multiple domains.
- Google Tag Manager Integration: Leveraging Google Tag Manager offers flexibility and convenience in setting up cross-domain tracking. You can choose between options such as Link Click / Form Submit Tags or Auto Link Domains, depending on your tracking requirements and preferences.
Benefits of Cross-Domain Tracking:
By accurately tracking user interactions across different domains and subdomains, you gain deeper insights into visitor behavior and conversion paths. This enables you to assess the performance of your marketing campaigns more accurately and make informed decisions to optimize your online presence.
3. Duplicate Pages in Analytics Reports
Duplicate data in Google Analytics reports can distort your analytics insights and hinder accurate analysis. One common source of duplicate data is variations in URL capitalization, where users enter your URL with uppercase letters, resulting in multiple versions of the same page being recorded. Although users may still reach the intended page, the duplication can lead to inaccuracies in your analytics data.
Addressing Duplicate Data:
- Identify Duplicate Patterns: Look for patterns in your data where duplicate URLs are recorded due to differences in capitalization or other factors.
- Preventative Measures:
- Create Filters: Utilize Google Analytics filters to standardize URL capitalization and prevent duplicate data from appearing in reports.
- Force Lowercase Filter: Implement a “Force Lowercase” filter in Google Analytics to ensure uniformity in URL formatting.
- Go to your Analytics admin menu & select “Filters” from the “All Web Site Data” section.
- Choose “New Filter” and select “Create New Filter”.
- Enter “Force Lowercase” into the Filter Name field.
- Set the Filter Type to “Custom” and check the “Lowercase” option.
- Select “Request URI” from the dropdown menu and save the filter.
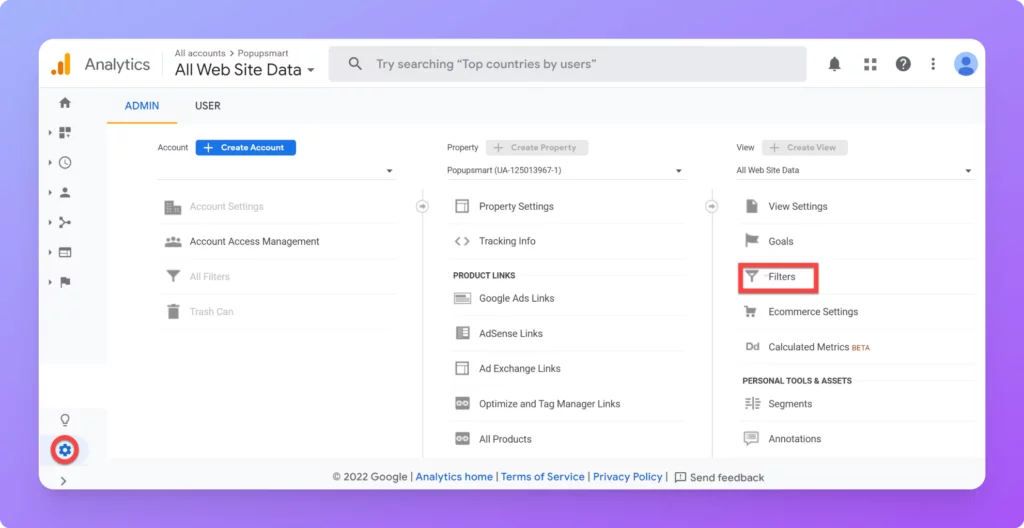
By implementing preventative measures such as filters, you can maintain data consistency and accuracy in your Google Analytics reports.
4. Raw Data Missing from Reports
Raw data in Google Analytics provides valuable insights into visitor behavior, traffic sources, and website performance. However, it’s essential to ensure that raw data is properly preserved and accessible for analysis.
Protecting Raw Data:
- Retain Raw Data View: Maintain an All Website Data view, which serves as the default view for raw data when creating a new property in Google Analytics.
- Avoid Filtering Primary Data: Refrain from applying filters directly to your primary data view to prevent irreversible data loss.
- Use Separate Properties: If you need to apply filters or adjustments to your data, create separate properties to preserve raw data integrity.
Importance of Raw Data:
- Analytics Integrity: Raw data serves as the foundation for accurate analysis and reporting, allowing you to uncover insights without data manipulation.
- Historical Analysis: Preserving raw data enables retrospective analysis and ensures that historical trends and patterns remain accessible for reference.
- Data Validation: Compare filtered data with raw data to validate the accuracy of applied filters and identify any discrepancies or inconsistencies.
By safeguarding raw data and adopting best practices for data management, you can maintain the integrity and reliability of your Google Analytics reports.
5. Self-Referrals Show Up in Reports
Self-referrals occur when a website refers traffic to itself, leading to inaccuracies in acquisition, behavior, and conversion data within Google Analytics reports. These self-referrals can compromise the integrity of your analytics data and distort insights into user behavior.
Mitigating Self-Referrals:
Referral Exclusion List: Utilize the Referral Exclusion List feature in Google Analytics to exclude self-referrals from traffic reports.
- Access the setting under Google Analytics > Admin > Account >Property >Tracking Info >Referral Exclusion List.
- Add domains that should not be reflected in the traffic reports to prevent self-referrals from skewing data.
6. Cross-Domain Tracking:
Ensure proper configuration of cross-domain tracking to accurately attribute traffic between different domains and subdomains.
- Implement correct settings for cross-domain tracking to prevent self-referrals resulting from incorrect domain configurations.
Address Technical Issues: Check for technical issues such as missing tracking codes or incorrect use of UTM tags on internal links that may contribute to self-referrals.
Learn about Woocommerce and GA here.
7. Bounce Rate Extremely Low
Discovering an abnormally low bounce rate in your Google Analytics account can be perplexing. A bounce rate measures the percentage of single-page sessions on your website where users leave without further interaction. A significantly low bounce rate may indicate potential issues with data collection or interpretation.
Understanding the Problem:
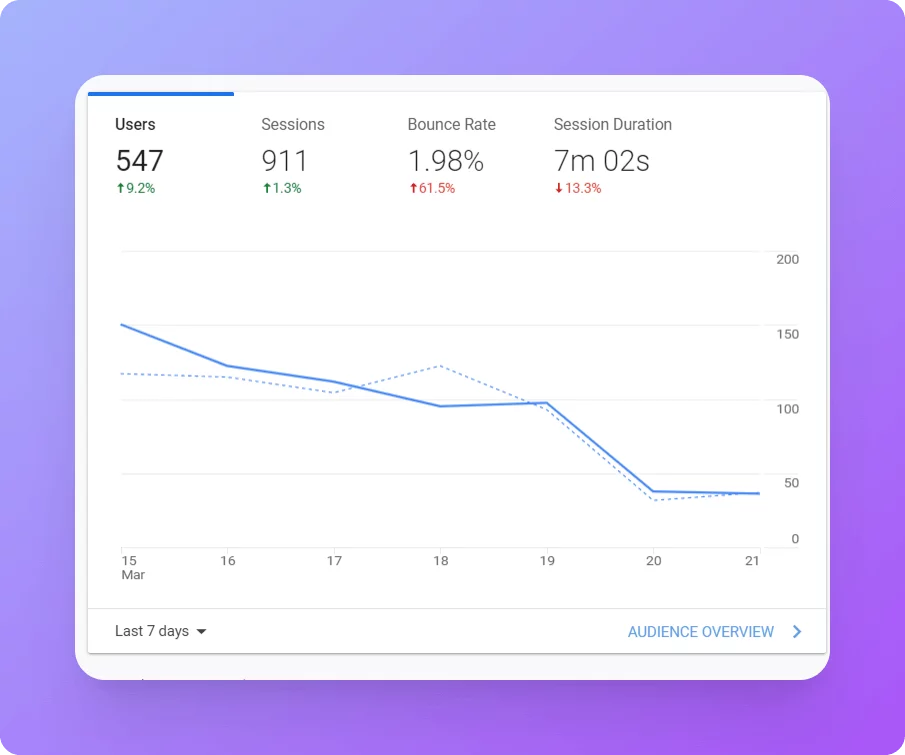
- Normal Bounce Rate Range: Bounce rates typically range from 40% to 60%, but this can vary depending on the type of content and website. An exceptionally low bounce rate, such as below 20%, may signal an anomaly that requires investigation.
- Potential Causes of Low Bounce Rate:
- Duplicate Code Snippets: Check for duplicate Google Analytics tracking codes, which can skew data collection and lead to inaccuracies in bounce rate measurement.
- Google Tag Manager (GTM) Overlap: Ensure that Google Tag Manager is not running concurrently with standalone Google Analytics tracking codes, as this can result in duplicate tracking and artificially low bounce rates.
- Non-Interaction Events: Features such as popups or live chat windows may trigger events in Google Analytics without constituting meaningful user interaction. Configure these events as “non-interaction” to prevent them from affecting bounce rate calculations.
Addressing Low Bounce Rate Issues:
- Remove Duplicate Code Snippets: Identify and remove duplicate Google Analytics tracking codes to prevent data duplication and ensure accurate bounce rate measurement.
- Review Google Tag Manager Setup: Verify that Google Tag Manager is configured correctly and not conflict with standalone Google Analytics tracking codes. Choose the appropriate triggers and remove redundant tracking to avoid overlap.
- Configure Non-Interaction Events: Set up non-interaction events for features like popups or live chat windows to prevent them from impacting bounce rate calculations. This ensures that only meaningful user interactions contribute to bounce rate metrics.
Conclusion:
While Google Analytics provides valuable insights into website performance, it’s essential to recognize and address potential inaccuracies in data collection and interpretation. By identifying and resolving issues such as low bounce rates, businesses can ensure the reliability and relevance of their analytics reports.
Take proactive steps to audit your tracking setup, eliminate duplicate codes, and configure events accurately to maintain the integrity of your analytics data. Continuously monitor your analytics metrics and adjust settings as needed to optimize data accuracy and gain actionable insights for informed decision-making.
Remember, understanding the intricacies of your analytics software and staying updated on best practices are key to maximizing the value of your data and driving business growth.
FAQs on Google Analytics Errors:
How can I identify and troubleshoot Google Analytics errors?
To identify and troubleshoot Google Analytics errors, you can start by reviewing your tracking implementation to ensure that the tracking code is correctly installed on all pages of your website. You can also check the configuration settings in your Google Analytics account, such as filters, goals, and view settings, to make sure they are set up correctly. Additionally, you can use tools like Google Tag Assistant or Google Analytics Debugger to debug tracking issues and identify potential errors.
What should I do if I encounter discrepancies in my Google Analytics data?
If you encounter discrepancies in your Google Analytics data, the first step is to identify the source of the discrepancy. Check for any differences between your tracking implementation, configuration settings, and data collection methods. You can also compare data from different reports within Google Analytics or cross-reference it with other analytics platforms or data sources to identify discrepancies.
Why is data sampling a common issue in Google Analytics?
Data sampling occurs when Google Analytics processes a subset of your data instead of analyzing the entire dataset. This typically happens when you query large volumes of data or apply complex segmentation or filtering options. Data sampling can lead to inaccuracies or distortions in your reporting, especially when analyzing specific segments or dimensions with limited data.



