In a time that is characterized by rapid technological advancement, revolutionary cloud paradigms constantly redefine our interactions with technology and software services.
Among these groundbreaking cloud concepts, XaaS (Anything-as-a-Service) shines brightly. It represents more than mere industry jargon; it embodies a fundamental transformation in how we perceive service delivery within the ubiquitous cloud infrastructure.
The XaaS model enables businesses to adapt quickly to market volatility and unpredictability, overcoming traditional infrastructure limitations that often hinder agility and innovation.
What is XaaS?
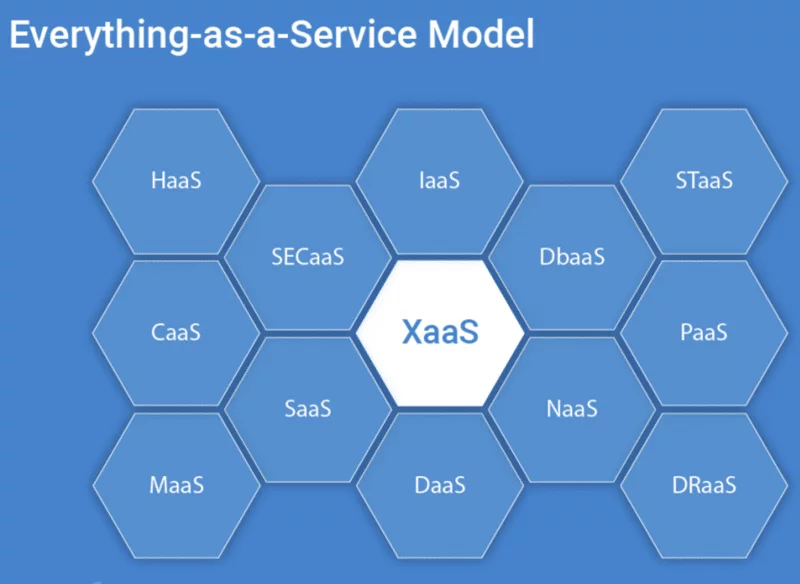
Advantages and hurdles of embracing XaaS XaaS have garnered significant favor for numerous reasons, such as:
- Cost-effectiveness: Transitioning to XaaS liberates businesses from hefty upfront investments, opting instead for a pay-as-you-go model that promotes resource allocation efficiency and reduces financial strain.
- Scalability and adaptability: XaaS empowers businesses to swiftly scale operations in response to demand fluctuations, ensuring startups and enterprises can seize opportunities without being hindered by infrastructure limitations.
- Accelerated time-to-market: Compared to traditional software development and deployment, XaaS expedites processes, offering readily deployable solutions that integrate seamlessly and swiftly.
- Improved collaboration: Anything-as-a-Service fosters seamless collaboration through shared platforms accessible from any location, eradicating geographical barriers and enabling real-time teamwork.
- Automated updates and maintenance: With XaaS, businesses constantly access the latest features and security patches, obviating manual intervention for software updates and maintenance, as service providers shoulder this responsibility.
Types of XaaS Real Life Examples:
A. SaaS
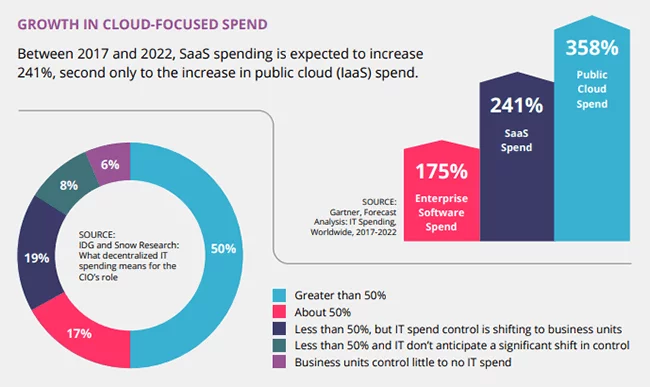
SaaS, as the name suggests, provides software services over the Internet, eliminating the need for users to handle installation, maintenance, and updates. Users simply subscribe to the software on a pay-as-you-go basis, accessing it through a web browser or application interface.
Key Characteristics of SaaS:
- Subscription Model: SaaS operates on a subscription-based pricing model. Users typically pay a recurring fee, often monthly or annually, based on factors such as the number of users or usage levels.
- Accessibility: SaaS applications are accessible from any internet-connected device, allowing users to easily work from anywhere.
- Scalability: SaaS solutions are designed to be scalable, allowing businesses to adjust their usage levels according to their needs. This scalability makes it suitable for both small businesses and large enterprises.
- Automatic Updates: SaaS providers handle software updates and maintenance, ensuring that the users have access to the latest features and security patches without the need to manually update the software.
- Multi-Tenancy: SaaS applications are typically multi-tenant, meaning that multiple users or organizations share a single instance of the software, with each user’s data being securely isolated from others.
- Integration: SaaS applications often offer integration capabilities, allowing them to seamlessly connect with software systems, such as CRM platforms or accounting software.
Examples of SaaS:
- HubSpot: HubSpot offers an all-in-one marketing, sales, and customer service platform, helping businesses attract, engage, and delight customers.
- Salesforce: Salesforce is a cloud-based CRM platform that helps businesses manage their customer relationships, sales processes, and marketing campaigns.
- Microsoft Office 365: Office 365 provides a suite of productivity tools, including Word, Excel, and PowerPoint, accessible via the cloud.
- Google Workspace: Formerly known as G Suite, Google Workspace offers a range of productivity and collaboration tools, such as Gmail, Google Drive, and Google Docs.
B. PaaS
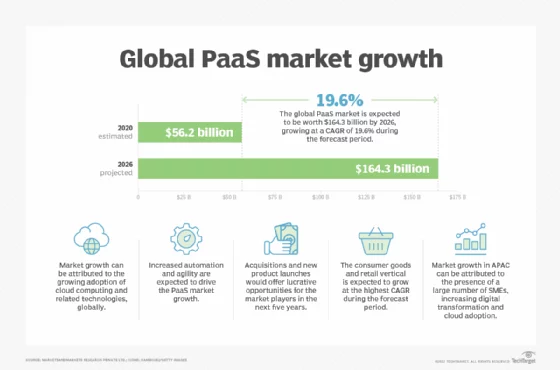
Platform as a Service (PaaS) offers users with a cloud-based platform for developing, deploying, and managing applications without the need to build and maintain underlying infrastructure. PaaS companies offer a range of services including servers, storage, databases, and development tools, enabling users to focus on the app development rather than infrastructure management.
Key Characteristics of PaaS:
- Cloud-Based Platform: PaaS operates on cloud infrastructure, allowing users to access development tools and services over the internet.
- Comprehensive Services: PaaS providers offer a wide range of services including computing resources, storage, databases, and development frameworks.
- Ownership and Management: The platform is owned and managed by the PaaS company, relieving users of the burden of purchasing, managing, and maintaining hardware and infrastructure.
- Scalability: PaaS platforms are designed to be scalable, allowing users to easily scale their applications as demand grows.
- Development Tools: PaaS platforms provide a variety of development tools, libraries, and frameworks to streamline the application development process.
Examples of PaaS:
- AWS Elastic Beanstalk: AWS Elastic Beanstalk is a PaaS offering from Amazon Web Services that enables users to deploy and manage web applications and services on familiar servers.
- Google App Engine: Google App Engine is a fully managed platform that enables users to build and deploy scalable web applications and backend services.
- Microsoft Azure App Service: Azure App Service is a PaaS offering from Microsoft Azure that provides a platform for building, deploying, and managing web and mobile applications.
- Heroku: Heroku is a cloud platform that enables developers to build, deploy, and manage applications in multiple programming languages.
C. IaaS
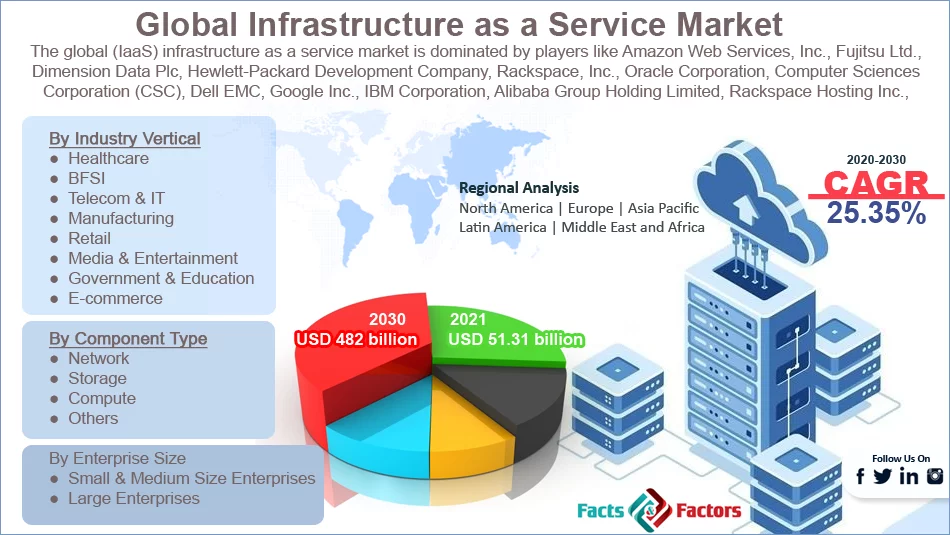
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) provides users with on-demand access to the computing resources such as servers, storage, and networking infrastructure over the internet. IaaS companies offer a flexible and scalable solution for developing, running, and scaling products and applications without the need of physical hardware investments.
Key Characteristics of IaaS:
- Network-Based Solutions: IaaS companies offer infrastructure components such as servers, storage, and networking resources over the internet.
- Compute Power: Users can leverage the computing power provided by IaaS companies to develop, run, and scale their applications.
- Pay-As-You-Go Model: IaaS services are typically offered on a pay-as-you-go basis, allowing customers to pay only for the resources they use over a specified time period.
- Reliance on Provider: Users become wholly reliant on the IaaS provider for their infrastructure needs, including reliability and uptime.
Examples of IaaS:
- Amazon Web Services (AWS): AWS provides a wide range of IaaS services, including computing power, storage options, and networking infrastructure.
- Microsoft Azure: Microsoft Azure offers IaaS solutions for virtual machines, storage, and networking, enabling users to build, deploy, and manage applications with flexibility and scalability.
- Google Cloud Platform (GCP): GCP provides IaaS services such as virtual machines, storage, and networking infrastructure, allowing users to leverage Google’s global network infrastructure for their applications.
D. AaaS:
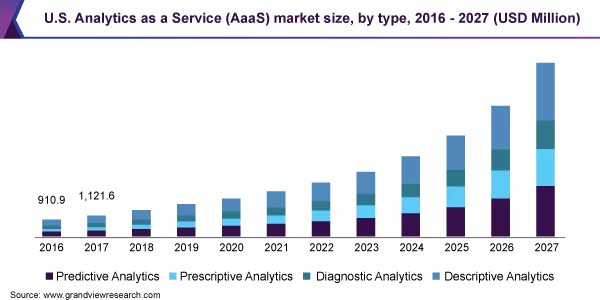
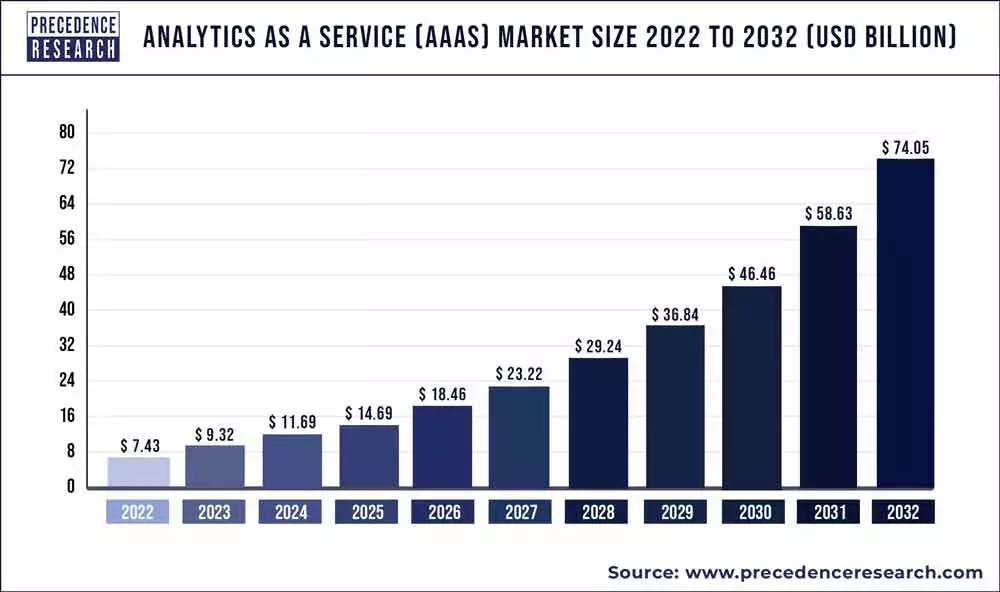
Analytics as a Service (AaaS) enables companies to leverage data analytics tools and services to gain insights into their business operations and drive informed decision-making. With the increasing digitalization of business processes, AaaS products have become essential for tracking and analyzing key metrics.
Key Characteristics of AaaS:
- Data-Driven Insights: AaaS products provide companies with tools and services to analyze data and derive actionable insights to improve business performance.
- Market Growth: The AaaS industry has experienced significant growth, with a market worth nearly $5 billion in 2019 and anticipated compound growth of over 25% through 2027.
- Strategic Advantage: Companies that leverage analytics effectively are better positioned to overcome the challenges and capitalize on opportunities in their respective industries.
Examples of AaaS:
- Sisense: Sisense offers a powerful analytics platform that helps companies convert data into revenue by embedding analytics. Users can connect, analyze, and collaborate to uncover valuable insights with or without code.
Learn about the difference between PaaS, SaaS and IaaS here.
E. DaaS:
Desktop as a Service (DaaS) empowers users to manage their workforce remotely through a secure web interface. With individual logins, employees can access necessary files and applications regardless of their location, making remote work seamless and efficient.
Key Characteristics of DaaS:
- Remote Management: DaaS platforms enable centralized management of the workforce, allowing employees to access desktop environments securely via a web browser.
- Accessibility: Employees can easily access files, programs, and software from anywhere, promoting flexibility and productivity, especially in remote work setups.
- Market Growth: With the increasing adoption of remote work, the DaaS market is projected to exceed $10.7 billion by 2023, reflecting the rising demand for flexible and accessible desktop solutions.
- Flexibility and Reliability: DaaS solutions offer flexibility and reliability, eliminating the need for businesses to build and maintain custom desktop environments.
Example of DaaS:
- Citrix: Citrix offers a suite of DaaS solutions, including Citrix Workspace, which consolidates apps and software into a secure desktop environment accessible from various devices and platforms.
F. FaaS
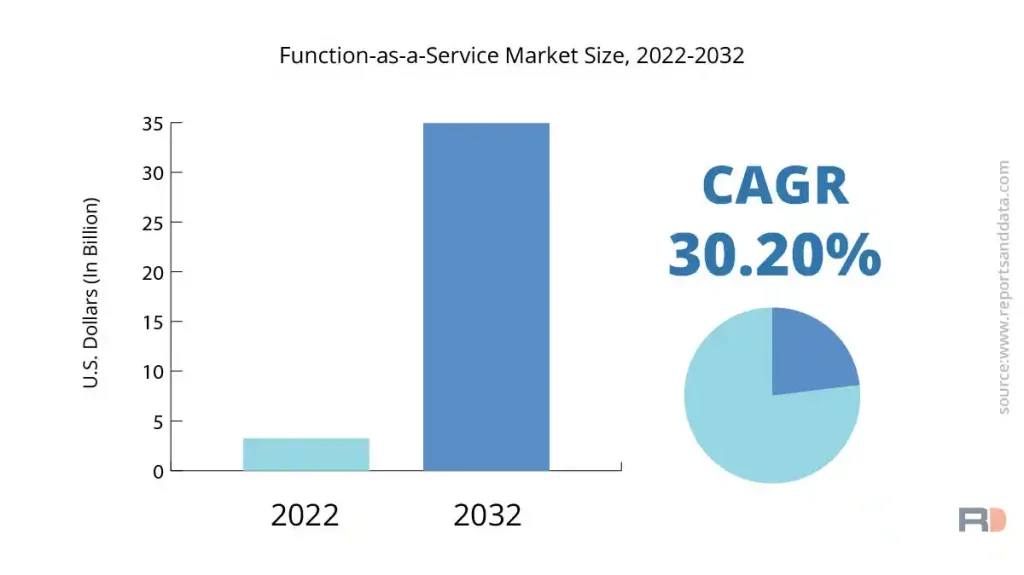
Functions as a Service (FaaS) allows businesses to execute specific functions or outcomes without the need to develop or manage the entire application. FaaS companies offer scalable solutions, enabling businesses to pay only for the functions they use.
Key Characteristics of FaaS:
- Specific Function Execution: FaaS enables businesses to run specific app or software functions without the overhead of managing the entire application.
- Scalability: FaaS solutions are scalable, allowing businesses to pay only for the functions they use and scale up or down as needed.
- Market Growth: The FaaS industry is rapidly expanding, with an estimated worth of about $7.7 billion, driven by the demand for streamlined function execution.
- Zero Server Management: FaaS platforms, like Google Cloud Functions, offer the convenience of running code without the need for server management, reducing operational overhead.
Examples of FaaS:
- Google Cloud Functions: Google Cloud Functions allows companies to run app and software functions in a streamlined manner, offering scalable solutions with zero server management.
- AWS Lambda: AWS Lambda, offered by Amazon Web Services, is another example of a FaaS platform that enables businesses to run the coding without provisioning or managing servers.
G. StaaS

Storage as a Service (STaaS) provides businesses with scalable storage solutions without managing internal infrastructure. STaaS providers offer reliable storage options, freeing up internal resources and reducing costs associated with in-house data storage.
Key Characteristics of STaaS:
- Scalable Storage Solutions: STaaS providers offer scalable storage solutions, allowing businesses to expand or reduce storage capacity as needed.
- Cost Reduction: Offloading data storage to STaaS providers can reduce costs associated with internal infrastructure maintenance and management.
- Market Growth: The STaaS industry is rapidly expanding, with a projected worth of over $100 billion by 2027, driven by the demand for scalable and cost-effective storage solutions.
- Cloud-Based Solutions: STaaS solutions are typically cloud-based, offering flexibility and accessibility for all businesses.
Examples of STaaS:
- HPE Greenlake: HPE Greenlake, a product of Hewlett Packard Enterprise, offers cloud services for storage optimized for various workloads, providing scalable storage solutions as a service.
- IBM Cloud Object Storage: IBM Cloud Object Storage is another example of a STaaS solution, offering scalable and cost-effective storage options for businesses of all sizes.
H. DBaaS
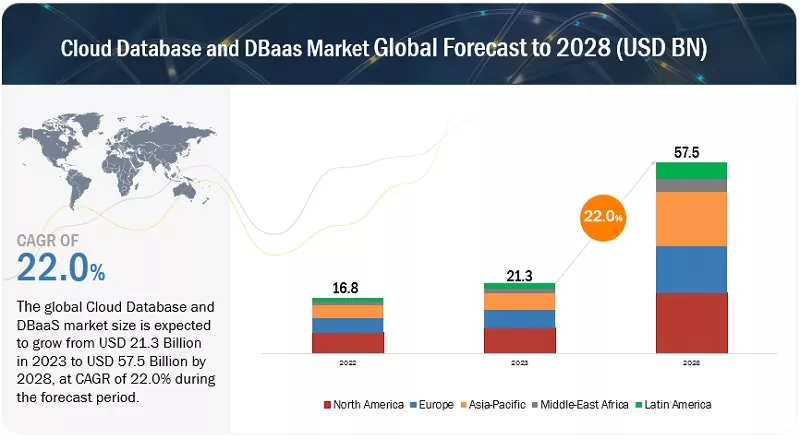
Database as a Service (DBaaS) allows businesses to manage customer data efficiently by providing easily accessible and customizable database solutions. With DBaaS, businesses can avoid the complexities of building databases from scratch and instead utilize trusted cloud-based solutions.
Key Characteristics of DBaaS:
- Data Organization and Storage: DBaaS solutions enable businesses to organize, filter, and store customer data securely in software accessible by authorized employees.
- Customization: Businesses can customize and create personalized databases in the cloud using DBaaS solutions, tailoring them to their specific needs and preferences.
- Ease of Use: DBaaS eliminates businesses needing to handle database management tasks, providing intuitive interfaces and streamlined processes for database operations.
Examples of DBaaS:
- Oracle Database: Oracle Database is a leading DBaaS product that offers a converged multi-model database management system, unifying in-memory, NoSQL, and MySQL databases. It enables businesses to build connected databases that streamline operations across business units.
I. AaaS:
Authentication as a Service (AaaS) provides businesses with access control solutions, allowing them to manage user access across devices and networks. AaaS solutions, such as those provided by Duo Security, offer modern access security features like two-factor or multi-factor authentication.
Key Characteristics of AaaS:
- Access Control Solutions: AaaS solutions enable businesses to implement access control measures, managing user authentication and authorization across various platforms and devices.
- Security Features: AaaS solutions offer advanced security features such as two-factor or multi-factor authentication, ensuring secure access to business applications and resources.
- Market Growth: The AaaS industry is growing rapidly, with a projected worth of $2.4 billion by 2026, driven by the increasing demand for secure access control solutions.
Examples of AaaS:
- Duo Security: Duo Security offers modern access security solutions designed to safeguard users, devices, and applications. Their AaaS product provides businesses with robust authentication features, including two-factor or multi-factor authentication, to ensure secure access control.
Pros of the XaaS Model:
The XaaS model offers several advantages for businesses, including flexible customer plans, lean operations, enhanced technical support, and scalability.
- Customers Can Pay on a Subscription Basis:
XaaS companies operate using a subscription model, providing customers with flexibility in payment and service usage. This subscription-based approach allows customers to adjust or cancel services as needed, facilitating scalability and cost-efficiency.
- Companies Can Become Leaner:
By leveraging XaaS solutions, businesses can avoid investing in bulky hardware and infrastructure, as well as reduce the need for extensive recruitment efforts. Instead, they can rely on XaaS companies to manage infrastructure and support services, enabling leaner operations and faster scalability.
- Businesses Receive More Technical Support:
XaaS companies often offer technical support services, providing businesses with assistance in troubleshooting software issues and optimizing business functions. This enhanced technical support can help businesses overcome challenges and maximize the value of XaaS solutions.
- Scalability is Easier with XaaS Products:
XaaS solutions offer scalability, allowing businesses to quickly scale their operations up or down by adjusting their chosen plans. This flexibility enables businesses to adapt to changing needs and market conditions more efficiently than traditional scaling methods.
The Cons of the XaaS Model:
Despite its advantages, the XaaS model presents several challenges, including security issues, performance outages, and hidden fees.
- Security Issues Can Arise:
Entrusting sensitive data and operations to XaaS companies can make businesses vulnerable to security breaches and data leaks. It is vital for businesses to conduct thorough research when selecting XaaS partners, ensuring they have robust security measures to protect against cyber threats.
- Performance Issues and Outages May Happen:
Businesses relying on XaaS solutions are susceptible to performance outages, which can disrupt operations and impact customer experience. It is crucial for businesses to evaluate XaaS providers’ uptime and maintenance schedules to minimize the impact of potential outages.
- Hidden Fees and Licenses Can Add Up:
XaaS contracts may include hidden fees and expensive licenses, leading to unexpected costs for businesses. It is imperative for businesses to carefully review contracts and subscription plans to understand the full cost implications and scalability options of XaaS solutions.
Summary:
The XaaS model offers businesses greater flexibility, efficiency, and scalability compared to traditional models. However, it also arises challenges such as security risks, performance outages, and hidden costs. By understanding the pros and cons of the XaaS model, businesses can make informed decisions and leverage XaaS solutions effectively to drive growth and innovation.
FAQs on XaaS:
What are the security implications of using XaaS?
While XaaS solutions offer convenience and scalability, they also raise security concerns related to data privacy, compliance, and vulnerability to cyber threats. Businesses must assess the security measures implemented by XaaS providers and implement additional security controls as needed to protect sensitive data and ensure regulatory compliance.
How can businesses ensure data portability with XaaS solutions?
Data portability refers to the ability to transfer data between different systems and platforms. To ensure data portability with XaaS solutions, businesses should carefully review data migration capabilities and compatibility requirements before selecting a provider. Additionally, businesses should establish data governance policies and procedures to facilitate smooth data transfer and integration across XaaS platforms.
What factors should businesses consider when choosing XaaS providers?
When choosing XaaS providers, businesses should consider factors such as reliability, scalability, security, pricing, support, and integration capabilities. It’s essential to evaluate each provider’s reputation, track records or customer reviews to ensure they can meet the business’s specific needs and requirements effectively.
How can businesses mitigate risks associated with XaaS solutions?
To mitigate risks associated with XaaS solutions, businesses should implement robust security measures, including encryption, access controls, and regular security audits. Additionally, businesses should maintain backups of critical data and develop contingency plans to address potential service outages or disruptions.



