Since its inception in 2003 as a straightforward blogging platform, the WordPress user interface (UI) has undergone significant evolution. What initially commenced as a simple tool for bloggers has transformed into a versatile CMS platform and a powerful web application framework. Over time, the user interface has also seen substantial growth and refinement.

Source: W3Tech
WordPress Journey So Far:
In 2003, the emergence of WordPress stemmed from the cessation of development for the prevalent blogging software, b2/cafelog. Matt Mullenweg and Mike Little, both avid users of b2/cafelog, recognized the void left by its discontinuation and embarked on creating a new platform based on this blogging software. This initiative led to the birth of WordPress, officially launched on May 27, 2003. For a deeper dive into WordPress’s origin story, explore our detailed article on the history of WordPress.
Following its inception, WP has undergone numerous updates and iterations. Specifically, this article focuses on pivotal WordPress releases that brought about significant changes to the user interface within the admin panel.
1. WordPress 0.71
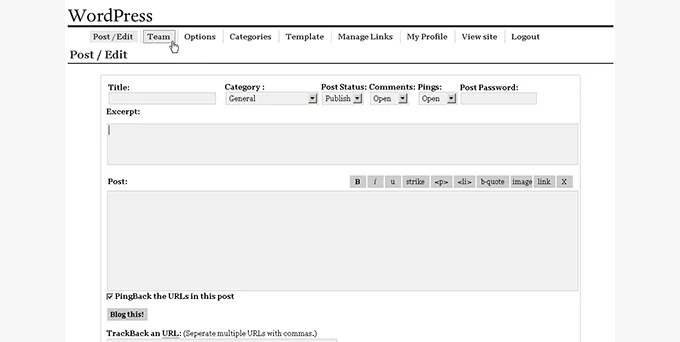
WordPress 0.71, introduced in June 2003, marked the early stages of WordPress’s journey, characterized by a rudimentary yet functional interface. The admin panel primarily focused on facilitating blog post creation, serving as a direct platform for writing posts without elaborate functionalities beyond the post-editor interface.
Simplicity defined this version, evident in its limited feature set. Users were restricted to assigning a single category to each post, reflecting the basic nature of the content management system during its nascent phase.
However, despite its functional aspects, the installation process for WP 0.71 was cumbersome and intricate. Installing the software involved manually editing core files, a process that demanded a significant amount of technical knowledge and effort from users.
2. WordPress 1.0.1
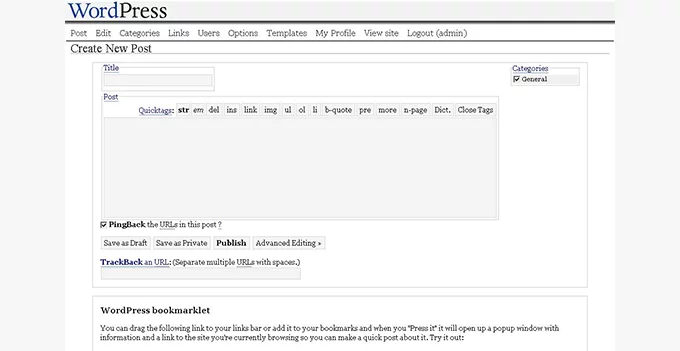
WordPress 1.0.1, fondly named “Miles” and released in 2004, marked a significant turning point as it transitioned away from the b2 file structure, establishing its unique filing system. This version also initiated the tradition of naming major releases after legendary Jazz musicians, honoring Miles Davis with its name.
This milestone release introduced a range of pivotal features and improvements that substantially enhanced the platform’s functionality. Notable among these were:
- Multiple Category Selections: Users gained the ability to assign posts to multiple categories, offering greater flexibility in organizing content.
- SEO-Friendly URL Structure: WordPress made strides in search engine optimization by introducing a more SEO-friendly URL structure. This feature significantly enhanced the visibility of WP sites in search engine results.
- Comment Moderation: The inclusion of comment moderation tools empowered site owners to manage and moderate comments more effectively, ensuring a more engaging and controlled discussion environment.
- Enhanced Installer: The introduction of a revamped installer streamlined the installation process, making it more user-friendly and accessible for users, even those with minimal technical expertise.
3. WordPress 1.2

WordPress 1.2, dubbed “Mingus” in honor of the legendary jazz musician Charles Mingus, marked a significant leap forward for the platform. This release introduced several pivotal features that continue to shape the WordPress ecosystem today.
Key Upgrades:
- Plugins: Arguably the most influential addition, WP 1.2 introduced the concept of plugins. This feature revolutionized the platform’s extendability, allowing users to enhance functionality by installing and activating various plugins tailored to their specific needs. It opened the door to a vast array of customization possibilities, fostering the growth of a vibrant plugin ecosystem.
- Subcategories: Enhancing the categorization system, WordPress 1.2 introduced the ability to create subcategories. This organizational feature granted users more flexibility in organizing and structuring content hierarchically.
- Custom Fields: Another significant addition was the inclusion of custom fields, enabling users to add additional metadata to posts. This feature laid the groundwork for advanced content structuring and paved the way for the development of more complex content types.
- Thumbnail Creation: The release introduced the ability to generate thumbnails, offering users a convenient way to include smaller preview images alongside their content, enhancing visual appeal and usability.
- Post Preview: WP 1.2 also brought a much-desired functionality: the post preview feature. This allowed authors to preview their posts before publishing, ensuring content accuracy and layout precision.
- Encrypted Passwords: Enhancing security measures, the update introduced encrypted passwords, bolstering the platform’s overall security and protecting user credentials.
- Enhanced Pinging: The version enabled users to ping multiple services simultaneously, streamlining the process of notifying various services about new content.
4. WordPress 1.5
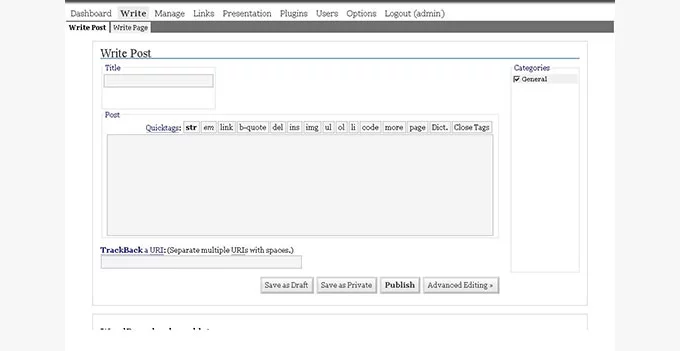
WordPress 1.5, known as “Strayhorn” in honor of Billy Strayhorn, brought forth notable advancements that contributed to the platform’s evolution and set the stage for more robust functionality.
Major Features:
- Dashboard Overhaul: Strayhorn marked the introduction of a revamped dashboard interface, presenting users with an initial glimpse of a new administrative panel. While this version didn’t utilize Ajax technology, which would enhance web interactions in subsequent releases, it laid the foundation for the modern dashboard structure.
- Pages Introduced: A pivotal addition was the incorporation of static pages alongside the traditional blog posts. This allowed users to create non-chronological, stand-alone pages that didn’t appear within the blog feed. It opened doors for websites to encompass broader content structures, incorporating both dynamic blog posts and static, evergreen pages like ‘About Us,’ ‘Contact,’ and ‘Services.’
- Enhanced Theming: WP 1.5 embraced multiple themes within a single installation, granting users the ability to install and switch between different themes seamlessly. This extended customization and personalization options, empowering users to alter the appearance and functionality of their websites with greater flexibility.
- Performance and Usability: While Strayhorn lacked the speed and fluidity characteristic of modern iterations, it laid the groundwork for subsequent improvements in performance and user experience. The version may have been slower by contemporary standards, but its introduction of significant features provided an essential framework for WordPress’s growth.
Learn about WP Database here.
5. WordPress 2.0

WordPress 2.0, dubbed “Duke,” represented a significant leap forward in the WordPress journey, heralding transformative changes in both design and functionality.
Key Enhancements:
- Redesigned Admin Interface: The standout feature of WordPress 2.0 was its revamped administrative interface. Sporting a distinctive large blue header, this version introduced a reimagined admin area, laying the groundwork for the contemporary WP dashboard that users are familiar with today.
- Improved Performance: Notably faster than its predecessors, WordPress 2.0 leveraged Ajax technology to execute specific tasks, enhancing user interactions and considerably boosting performance. This implementation of Ajax contributed to a more seamless and responsive user experience within the WP environment.
- WYSIWYG Editor: This release introduced a comprehensive WYSIWYG (What You See Is What You Get) editor, empowering users to compose and edit content visually, resembling the final appearance on the published page. The editor significantly simplified content creation, enabling users to craft sophisticated posts without the need for coding or technical expertise.
- Akismet Integration: To combat the escalating issue of comment spam, the Akismet plugin was introduced as part of the core functionality. This anti-spam tool became instrumental in filtering out unwanted comments, enhancing the overall integrity and quality of discussions on WordPress sites.
- File Uploading and Theme Preview: WP 2.0 brought in image and file uploading capabilities, allowing users to seamlessly upload media directly within the platform. Moreover, it introduced theme preview via thumbnails (screenshot.png), enabling users to visualize how a theme would appear before activation.
- Developer-Focused Improvements: Catering to developers, this release offered new hooks and functionalities, providing expanded capabilities for customization and extensibility, fostering an environment conducive to plugin and theme development.
6. WordPress 2.1
WordPress 2.1, known as “Ella,” marked a milestone in WP’s evolution by focusing on enhancing the management of comments, streamlining the user experience for website administrators.
Key Enhancements:
- Revamped Comment Management: A notable innovation in WordPress 2.1 was the introduction of a redesigned admin screen dedicated to comment management. This interface overhaul was geared towards simplifying and expediting the process of handling comments on WordPress sites.
- Enhanced User Interaction: With the new comment management screen, administrators gained the ability to perform crucial actions such as approving or deleting comments without the need to reload entire admin screens. This feature significantly expedited the moderation process, enabling swift and efficient management of user-generated content.
7. WordPress 2.3

WordPress 2.3, codenamed “Dexter,” introduced pivotal enhancements without a dramatic alteration to the user interface, focusing on functionality and usability.
Key Features:
- Tag Support: WordPress 2.3 brought a noteworthy addition by integrating native support for adding tags to posts. This update was crucial as it enabled users to categorize and organize content more efficiently by incorporating tags alongside categories, enhancing content organization and searchability.
- Update Notification System: Another significant addition was the implementation of an update notification system. This feature allowed WP core and plugins to prompt users with notifications whenever a new version was available. This not only facilitated timely updates but also contributed to improving the platform’s security and performance by encouraging users to install the latest versions.
- URL Auto-Redirection: Dexter also introduced an essential functionality that automatically redirected users to the correct WP URL as defined in the site settings. This feature ensured consistency in URL structure and navigation, enhancing user experience and SEO adherence.
8. WordPress 2.5
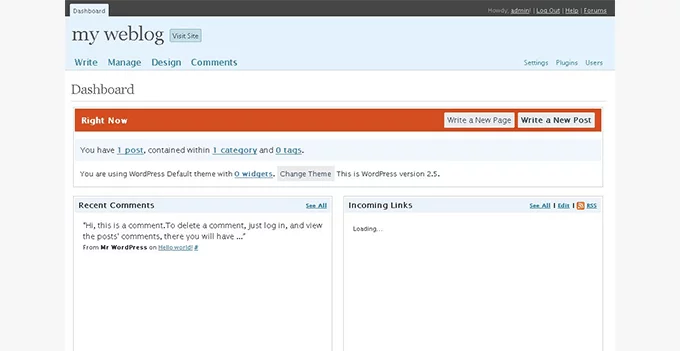
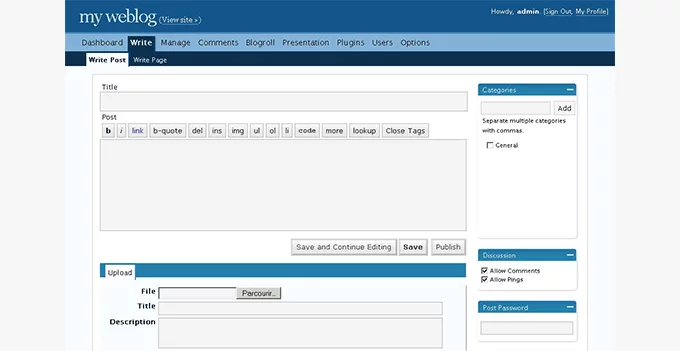
WordPress 2.5, nicknamed “Brecker,” marked a significant milestone in WordPress’s journey by introducing a revamped admin user interface designed in collaboration with Happy Cog, a renowned web design consultancy. This release, having a profound impact on the platform’s usability, reflected a significant redesign and functionality enhancement.
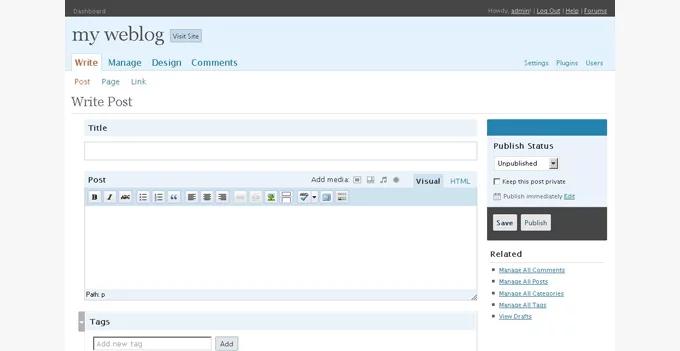
Key Features:
- Redesigned User Interface: The most conspicuous change was the complete redesign of the admin user interface, offering a more intuitive and aesthetically pleasing experience. The updated UI incorporated streamlined navigation and reorganized sections, enhancing usability and accessibility for users.
- Dashboard Enhancements: The dashboard received substantial improvements with added useful information, providing users with a more comprehensive overview of their site’s performance and activities. This overhaul transformed the dashboard into a more informative and user-friendly space.
- One-Click Plugin Upgrade: WordPress 2.5 introduced a groundbreaking feature allowing users to perform one-click upgrades for plugins directly from the WordPress plugin directory. This simplified and expedited the process of updating plugins, promoting better security and functionality.
- Enhanced Visual Editor and Built-in Gallery: This release introduced a significantly improved visual editor, offering better editing capabilities and a more user-friendly interface. Additionally, it integrated a built-in gallery feature, simplifying the process of adding and managing image galleries within posts and pages.
9. WordPress 2.7
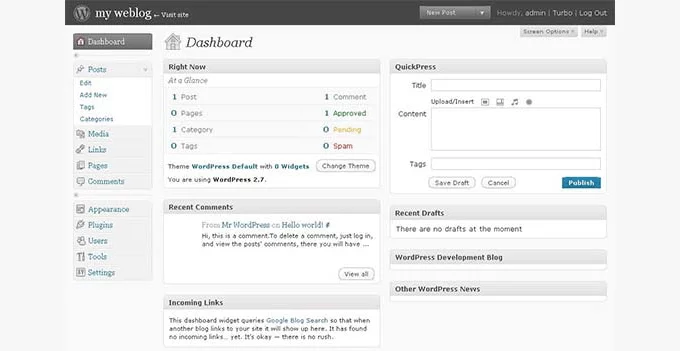
WordPress 2.7, codenamed “Coltrane,” was a milestone release that brought significant improvements to the WordPress admin user interface and introduced several key features to enhance user experience and functionality.
Key Features:
- Redesigned Dashboard: The WP admin dashboard underwent a major overhaul, allowing users to customize its elements. The addition of ‘Screen Options’ enabled users to personalize their dashboard by showing or hiding specific elements based on their preferences or workflow.
- Streamlined Plugin Installation: This release streamlined the process of plugin installation by enabling users to install plugins directly from the WordPress admin panel with greater ease and efficiency. This simplified approach enhanced the user experience and encouraged the use of plugins.
- Enhanced Comment Management: Administrators gained improved comment management capabilities with the ability to reply to comments directly from the admin panel. Additionally, the introduction of threaded comments facilitated more engaging discussions on WordPress websites.
- Additional Features: WordPress 2.7 introduced several other notable features, including support for sticky posts, comment pagination for improved navigation within comment sections, keyboard shortcuts for enhanced user productivity, and various administrative enhancements.
10. WordPress 2.9

WordPress 2.9, named “Carmen,” introduced a series of new features that seamlessly integrated into the existing WordPress interface, enriching the user experience and functionality without substantial changes to the user interface itself.
Key Features:
- Plugin Update System: This release introduced a streamlined plugin update system, enabling users to update their plugins to the latest versions with a single click directly from the WordPress admin panel. This simplified process enhanced user convenience and ensured that WordPress sites remained up-to-date with the latest plugin versions and improvements.
- Image Editing Features: WordPress 2.9 brought significant enhancements to image handling capabilities within the platform. Users gained the ability to perform basic image editing functions directly within WP. This included functionalities such as cropping, resizing, rotating, scaling, and flipping images, empowering users to manage and customize their images more effectively without relying on external editing tools.
11. WordPress 3.0
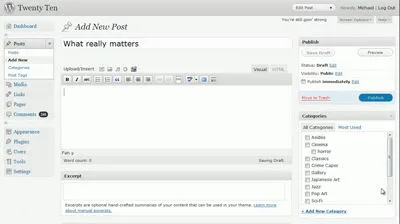
WordPress 3.0, codenamed “Thelonious,” marked a significant milestone in WordPress’s evolution, transitioning it from a simple blogging platform to a comprehensive Content Management System (CMS) with a range of new and advanced features.
Key Enhancements:
- Custom Post Types and Taxonomies: WP 3.0 introduced the capability to create and manage custom post types and taxonomies, allowing users to structure their content beyond traditional blog posts and pages. This pivotal change enabled the creation of diverse content types tailored to specific needs, such as portfolios, testimonials, products, and more.
- Customization Options: The update incorporated customization elements like custom backgrounds and headers, empowering users to personalize their website’s visual appeal without delving into complex coding. Users gained the ability to tailor the look and feel of their sites with ease.
- Shortlinks and Navigation Menus: The inclusion of shortlinks provided a concise way to share posts, enhancing accessibility and user experience. Additionally, the introduction of navigation menus brought a more intuitive and customizable approach to managing site navigation, facilitating better site organization and user navigation.
- Default Theme – Twenty Ten: WordPress 3.0 debuted the Twenty Ten default theme, setting the precedent for subsequent years to introduce a new default theme, each named after its respective year. This practice showcased WordPress’s commitment to contemporary design trends and provided users with modern, adaptable themes.
- WordPress Multisite: The release merged the WP Multi-User (MU) project into the core, introducing the WordPress Multisite feature. This functionality enabled users to create and manage multiple sites from a single WP installation, catering to various site management needs efficiently.
12. WordPress 3.1 – Django Reinhardt (2011)
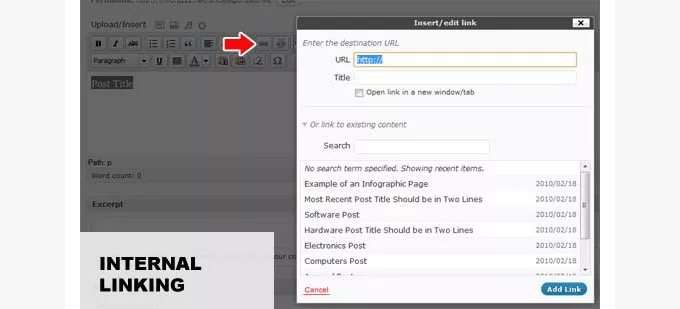
In WP 3.1 – Django Reinhardt (2011), several key features were introduced that significantly enhanced the user experience and content management capabilities:
a. Admin Bar:
- Streamlined Site Management: Implemented a convenient toolbar displayed across the top of the site when logged in.
- Quick Access to Functions: Provided easy-to-access links for creating posts, managing comments, customizing themes, and accessing the dashboard.
- Enhanced Efficiency: Enabled users to navigate backend functionalities swiftly, simplifying site administration.
b. Post Formats:
- Enhanced Content Presentation: Introduced the concept of post formats to customize the display of different content types.
- Flexibility in Styling: Allowed content creators to tailor the presentation of posts, including galleries, quotes, videos, links, images, etc.
- Visual Appeal: Offered diverse formatting options, making content more visually engaging and appealing to site visitors.
c. Internal Improvements:
- Advanced Queries: Backend enhancements for developers, improving performance in query handling.
- Security Enhancements: Internal improvements to reinforce site security and stability.
- Refinements and Bug Fixes: Addressed various bugs and made refinements for smoother user experience.
13. WordPress 3.3 – Sonny (2011):

Fly-out Menus and Admin Bar Redesign:
- Optimized Navigation: Introduced fly-out menus in the admin area for more intuitive access to different sections and tools.
- Enhanced User Interface: Redesigned admin bar provided additional features and shortcuts, optimizing user experience.
Drag-and-Drop Media Uploads:
- Simplified Media Management: Implemented drag-and-drop functionality for media uploads, streamlining the process of adding and organizing media files.
- Improved User Efficiency: Enabled users to seamlessly upload and arrange media content within the WordPress environment.
14. WordPress 3.5 – Elvin (2012):
Optimized User Interface for Modern Devices:
- Catering to Device Evolution: Addressed the rise of high-resolution displays and mobile devices in the digital landscape.
- Enhanced Visual Experience: Upgraded icons and adaptive styles ensured consistent visual quality across various screen resolutions and devices.
- Improved Accessibility: Optimized the user interface to provide a visually appealing and accessible experience on modern devices.
Emphasis on Retina Display Screens:
- Visual Fidelity: Specifically targeted retina display screens to ensure high-quality visuals for users on such advanced displays.
- Consistent Experience: Aimed for a consistent and visually appealing interface regardless of the device’s screen resolution.
15. WordPress 3.8 – Parker (2013):
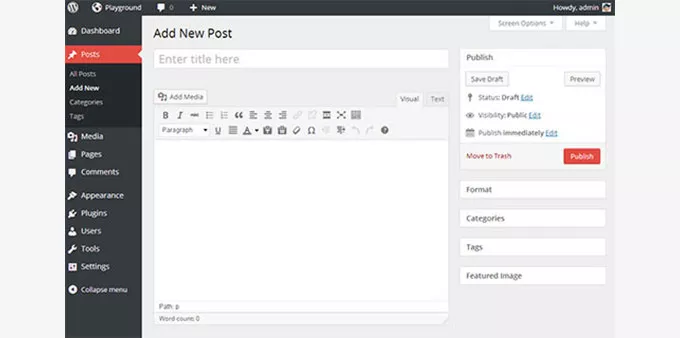
Modernized User Interface:
- Responsive Design: Overhauled the dashboard to be more mobile-responsive, adapting fluidly across various screen sizes and devices.
- Improved Adaptability: Introduced design elements optimizing the interface for better usability on mobile devices.
Customizable Color Schemes:
- Personalization Options: Multiple color schemes allowed users to personalize their dashboard based on individual preferences.
- Enhanced Aesthetics: Provided flexibility in appearance, allowing users to choose a color scheme that suited their taste.
Aesthetic Enhancements:
- Icon Fonts: Implemented icon fonts for a more aesthetically pleasing and modern interface.
- Typography Optimization: Utilized the Open Sans font for improved typography, enhancing readability across the dashboard.
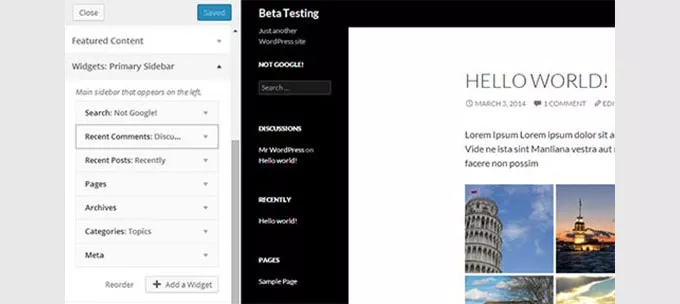
16. WordPress 3.9 – Smith (2014):
Streamlined Post Editor:
- Flat Buttons: Simplified the post editor interface by incorporating flat buttons for a sleek and contemporary appearance.
- Improved Visuals: Offered a clean, modern look for a more user-friendly editing experience.
Enhanced Media Handling:
- Drag-and-Drop Image Uploads: Introduced an intuitive way to upload images through drag-and-drop functionality.
- Image Gallery Preview: Enhanced the image gallery preview for better visual representation of content.
Interactive Customization Features:
- Live Widget Previews: Enabled live previews for widgets within the theme customizer, facilitating real-time customization and previewing.
- Simplified Customization: Streamlined the process of customizing and previewing content for a more interactive editing experience.
17. WordPress 4.0 – Benny (2014):
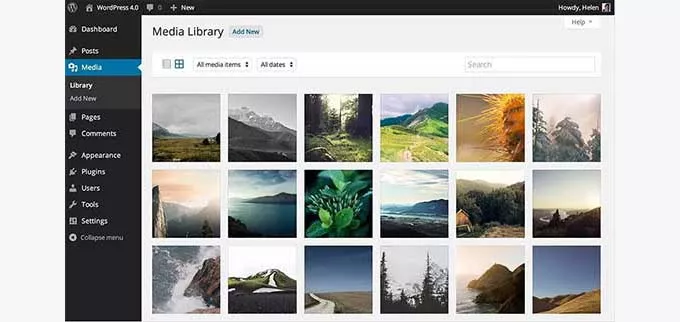
Media Library Enhancements:
- Grid View: Introduced a new grid view for the Media gallery, offering an organized and visually appealing display of media files.
- Infinite Scroll: Enabled infinite scroll functionality, allowing users to browse through media files seamlessly without pagination.
- Enhanced Editing: Improved the editing experience with smoother transitions and interactions while managing media items.
User Interface Refinements:
- Admin Interface Extension: Extended existing WordPress admin interface with subtle enhancements, focusing on media management.
18. WordPress 4.2 – Powell (2015):
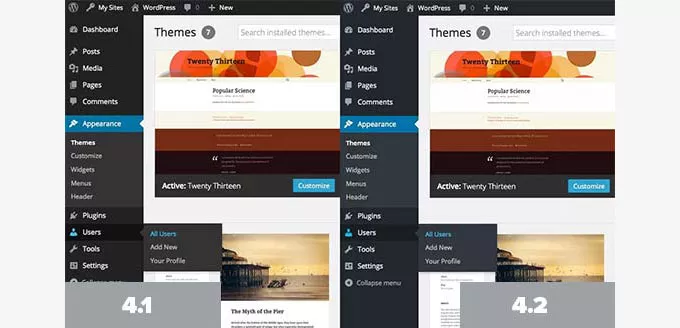
Admin Area Color Scheme:
- Color Scheme Update: Tweaked the admin area color scheme for improved visual aesthetics and readability.
- Blue Hue Addition: Applied a slight blue hue to grays for a more visually appealing interface.
- Color Consistency: Adjusted blues to a pure blue shade without the red channel, ensuring a consistent color palette.
Minor Yet Impactful Enhancement:
- Visual Enhancement: Although a minor alteration, the color scheme adjustment enhanced the overall visual experience of the admin area.
19. WordPress 4.5 – Coleman (2016):
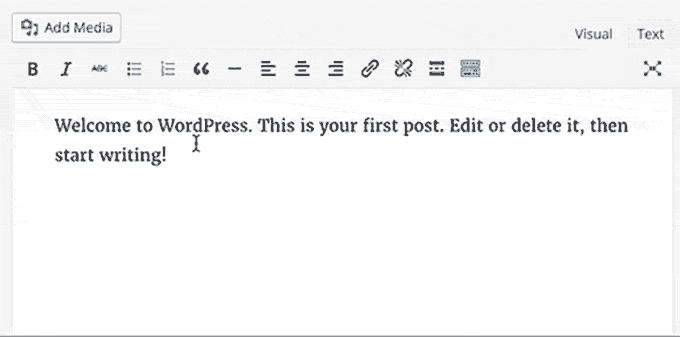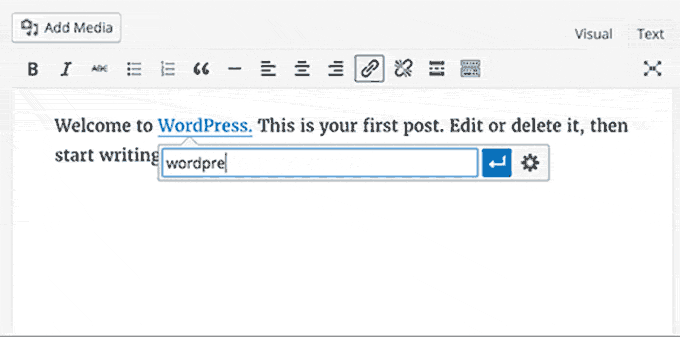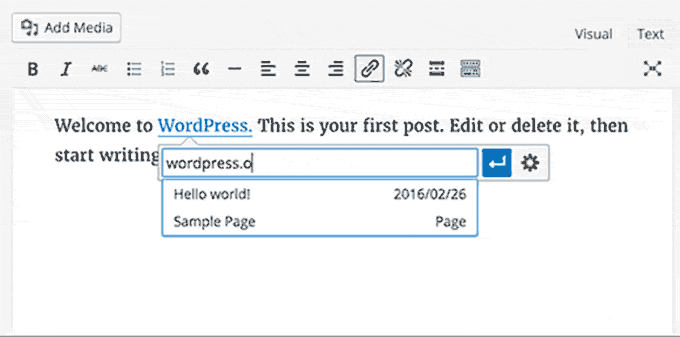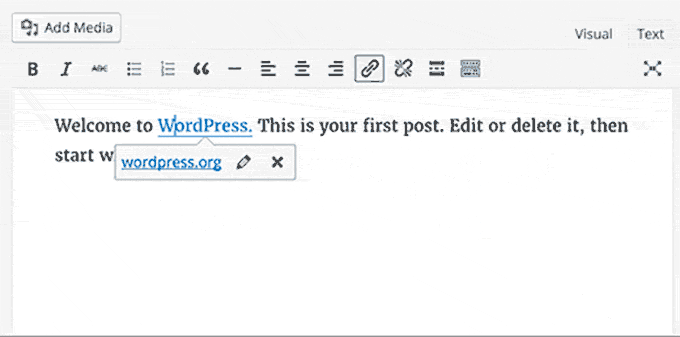
Post Editor Improvements:
- Inline Link Editing: Introduced a convenient inline link editing feature in the post editor for quicker link management.
- Inline Text Shortcuts: Added new inline text shortcuts, enhancing text formatting options for users.
Theme Customizer Enhancements:
- Responsive Previews: Enhanced the theme customizer with responsive previews, allowing users to visualize their themes across various devices without device changes.
20. WordPress 4.6 – Pepper (2016):
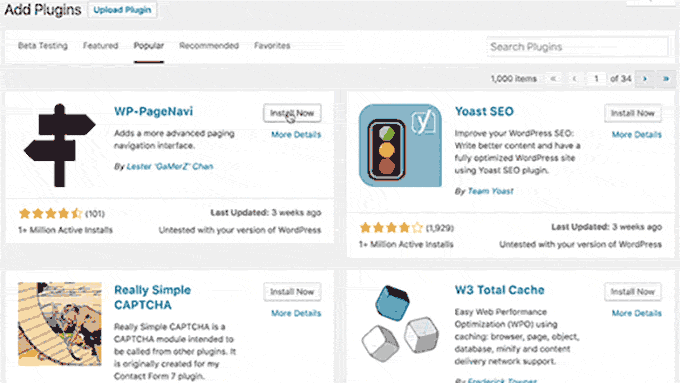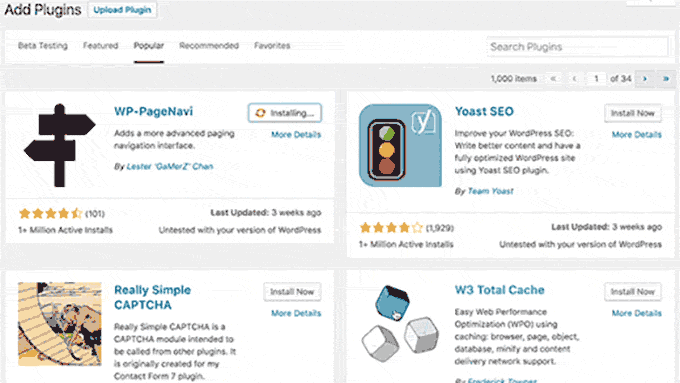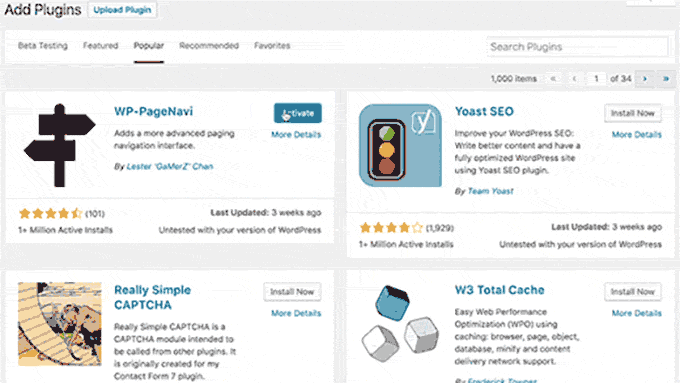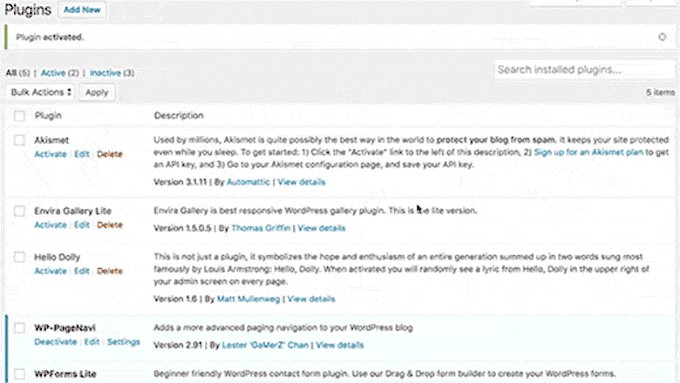
Backend Enhancements:
- Font Change: Transitioned from loading Open Sans via Google servers to using native fonts, optimizing performance.
- Streamlined Updates: Improved the update process, enabling users to install, update, and delete plugins/themes without reloading pages.
21. WordPress 4.8 – Vaughan (2017):
Widget and Dashboard Improvements:
- Media Widgets: Introduced a new set of widgets to easily add media (images, audio, video, rich text) to WordPress sites.
- WordPress News Dashboard Widget: Added a dashboard widget displaying WordPress news and events for user engagement.
22. WordPress 4.9 – Tipton (2017):

Theme Customizer and Editor Enhancements:
- Enhanced Theme Customizer: Improved the theme browsing and preview experience within the theme customizer for better theme exploration.
- Code Editor Features: Added syntax highlighting and auto-completion to code editors for custom CSS and theme/plugin editing.
User-Centric Features:
- Editorial Efficiency: Inline link editing and text shortcuts aimed to streamline content creation and editing processes.
- Enhanced User Experience: Responsive previews, native fonts, and streamlined updates contributed to a more seamless and efficient user interface.
Content Management and Customization:
- Content Diversity: Media widgets expanded content options, while theme customizer enhancements offered better theme exploration and editing capabilities.
- Developer-Friendly Tools: Code editor improvements catered to developers, enhancing the coding experience within WordPress.
23. WordPress 5.0 – Bebo (2018)
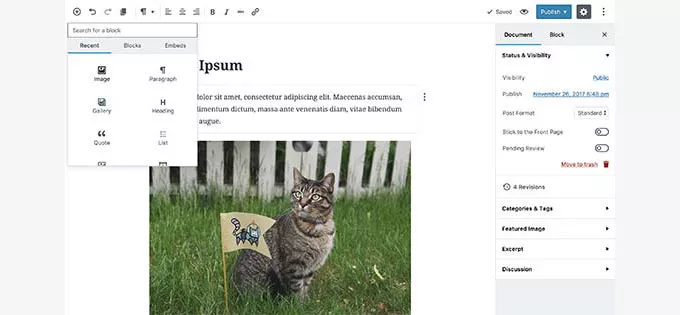
WordPress 5.0 – Bebo (2018) was a groundbreaking release primarily known for introducing the revolutionary block-based editor, Gutenberg, which transformed the content creation experience within WordPress.
Block-Based Editor:
- Content Segmentation: Gutenberg revolutionized content creation by breaking content into individual blocks.
- Versatile Blocks: Each block provided specific settings and customization options tailored to its content element.
Simplified Content Creation:
- Ease of Use: Allowed users to create, customize, and arrange content elements more intuitively.
- Streamlined Editing: Simplified the process of editing and rearranging content blocks within the editor.
Foundation for Future Development:
- Innovative Approach: While not as feature-rich as full-fledged page builders, Gutenberg laid the foundation for future iterations of the block editor.
24. WordPress 5.2 – Jaco (2019):

Recovery Mode:
WordPress 5.2 aimed to enhance error handling and administrator accessibility:
- Error Handling Improvement: Introduced recovery mode, replacing fatal errors with a user-friendly error page to ensure a smoother user experience.
- Administrator Accessibility: Enabled site administrators to swiftly access the admin area by receiving a recovery mode link via email, simplifying issue resolution and reducing troubleshooting time.

Source: Kinsta
25. WordPress 5.4 – Adderley (2020):
Block Editor Enhancement:
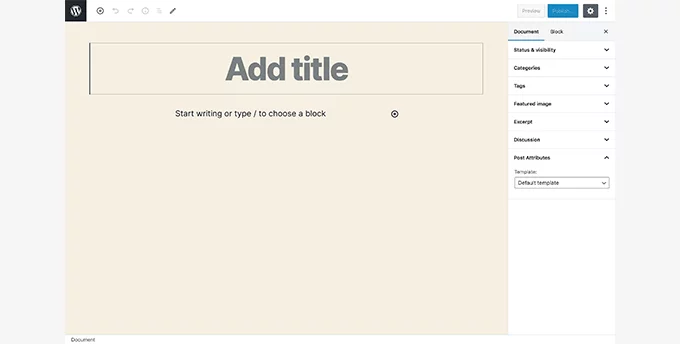
WordPress 5.4 focused on refining the block editor to improve the editing experience:
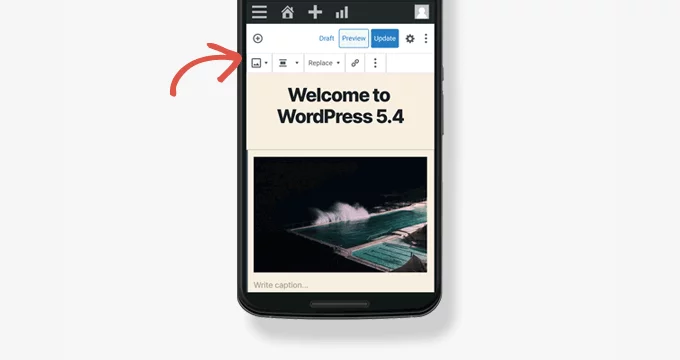
- Full-Screen Editor: Elevated user immersion by making the full-screen editing mode the default setting within the block editor, enhancing the overall editing experience.
- Mobile-Optimized Toolbar: Integrated a dedicated toolbar tailored for mobile screens, ensuring improved usability and functionality on smaller devices.
26. WordPress 5.5 – Eckstine (2020):
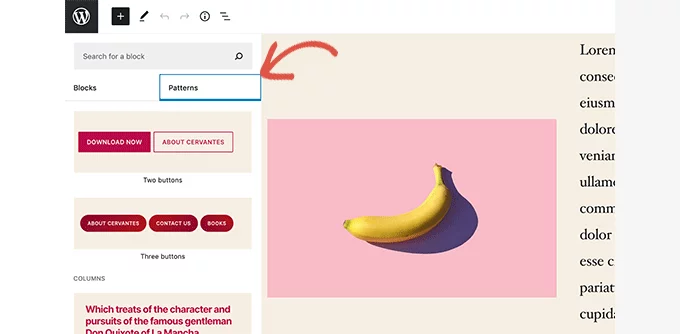
Block Patterns Introduction:
WP 5.5 emphasized the introduction of block patterns for streamlined content creation:
- Block Patterns: Introduced pre-defined block arrangements to expedite the creation of commonly used design elements, promoting efficiency in content creation.
- Design Element Efficiency: Provided readily available design patterns such as headers, footers, intros, and calls to action, empowering users with quicker content creation tools.
27. WordPress 5.8 – Tatum (2021):
Site-Wide Editing Tools:
WordPress 5.8 concentrated on empowering users with site-wide editing capabilities:
- Templates and Site-Wide Blocks: Simplified the creation of site-wide templates by introducing templates and site-wide blocks, offering effortless site-wide design consistency.
- Block-Based Widgets: Transformed traditional widgets into blocks, enabling effortless customization of widget-ready areas directly within the editor interface.
28. WordPress 5.9 – Josephine (2022):

Full Site Editor Debut:
WP 5.9 marked the debut of a comprehensive site editor and block-based theme integration:
- Site Editor Introduction: Unveiled the full site editor, replacing traditional admin links with direct access to the site editor, ensuring a seamless transition to block-based site editing.
- Block-Based Theme Integration: Utilized Twenty Twenty-Two as the default theme, fully supporting the site editor and harnessing the block editor for comprehensive and intuitive site editing capabilities.
- Evolving Editor: Served as a starting point for refining content creation tools and functionalities within WordPress.
29. WordPress 6.0 – Arturo (May 2022):
Site Editor Upgrades:
WordPress 6.0 primarily concentrated on enriching the site editor experience:
- Template Support Enhancement: Strengthened the site editor by adding support for editing additional templates, augmenting customization options.
- Block Settings Enrichment: Integrated more tools into various block settings, empowering users with enhanced block customization capabilities.
30. WordPress 6.1 – Misha (November 2022):
Continued Site Editor Improvements:
WP 6.1 further amplified the site editor’s functionality, specifically focusing on templates and block editing:
- Template and Template Parts Refinement: Continued refining templates and template parts within the site editor, fostering a more versatile editing environment.
- Block Editor Enhancements: Introduced several new tools and enhancements within the block editor, aiming to streamline editing functionalities.
- Consistency in Block Tools: Initiated efforts towards achieving consistency in block tools and settings, enhancing user interface coherence.
31. WordPress 6.2 – Dolphy (First Half of 2023):
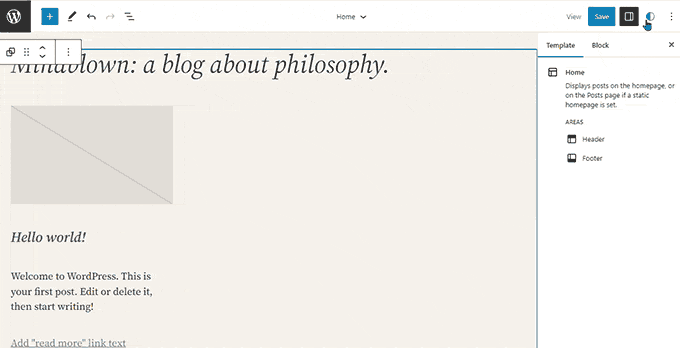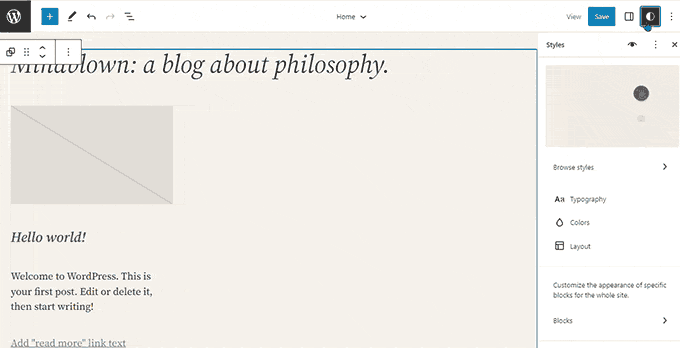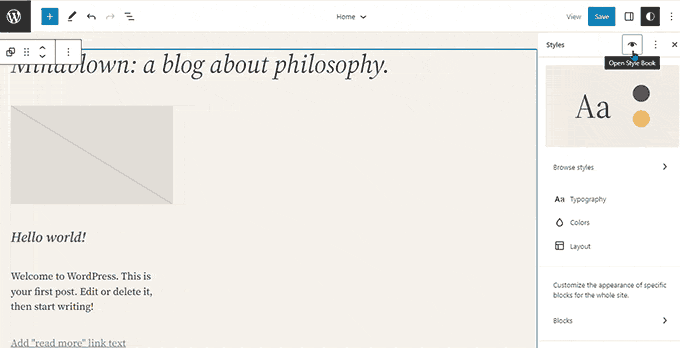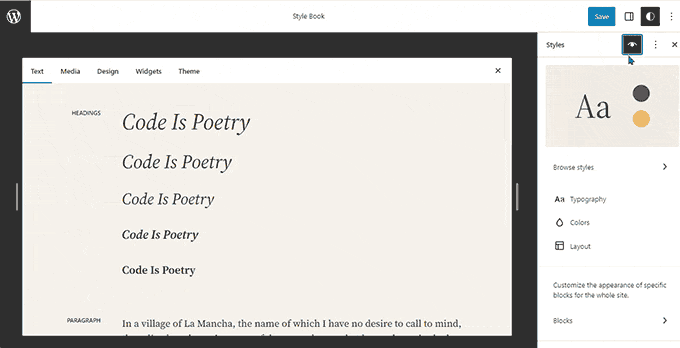
Advancements in Site Editing and Customization:
WP 6.2 shifted towards easier site editing and customization, notably promoting block-based editing:
- Full Site Editor Exit from Beta: Officially launched the block-based site editor out of beta, empowering users to leverage the block editor extensively for theme customization, layout creation, styling, and more.
- Style Editing Integration: Introduced comprehensive style editing capabilities within the block editor, enabling users to fine-tune design elements and customize styles seamlessly.
32. WordPress 6.3 – Lionel (Second Half of 2023):
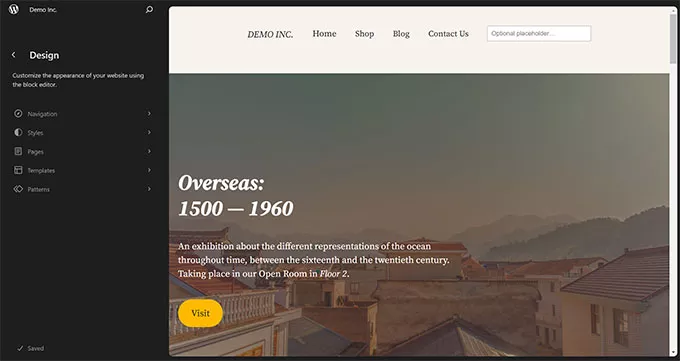
Site Editor and Navigation Enhancements:
WordPress 6.3 brought substantial updates to the site editor’s functionality and navigation interface:
- Revamped Navigation Screen: Introduced a revamped navigation screen within the site editor, offering convenient access to templates, pages, patterns, styles, and navigation menus for a more intuitive editing experience.
- Command Palette Integration: Introduced the ‘Command Palette’ feature, accessible via keyboard shortcuts (Command+K or CTRL+K), facilitating quicker access to WordPress shortcuts, content search, blocks, patterns, and templates.
Conclusion:
WordPress has been instrumental in shaping the web by simplifying website creation and content management. Its open-source nature fosters a thriving community, encouraging collaboration and continuous improvement. The platform’s evolution has been marked by adaptability, catering to diverse user needs and technological advancements.
As for its future, WP continues to evolve, emphasizing performance, security, and user experience. It strives to remain a versatile, accessible, and reliable platform for individuals and businesses worldwide.
FAQs on WordPress:
How does WordPress impact the web?
WordPress powers a significant portion of the internet, democratizing web publishing. It has empowered individuals, businesses, and organizations to establish an online presence efficiently.
What’s the difference between WordPress.com and WordPress.org?
WordPress.com offers hosting services with limited customization options. WordPress.org provides the free software to download and install on your hosting, giving you complete control and customization freedom.
What challenges has WordPress faced?
Security vulnerabilities, plugin compatibility issues, and maintaining backward compatibility while innovating are some challenges WordPress has encountered.



