Large language models are trained on extensive datasets and utilize natural language processing to accomplish various linguistic tasks, including text generation, code completion, and paraphrasing.
The initial launch of ChatGPT catalyzed the swift adoption of generative AI, spurring innovations in large language models and fostering industry growth.
92% of Fortune 500 companies have incorporated generative AI into their operations.
As adoption rates continue to rise, the LLM industry is also expanding. The global market for large language models is expected to surge from $6.5 billion in 2024 to $140.8 billion by 2033.
Large language models, known for their extensive training on vast datasets, leverage natural language processing to perform various linguistic tasks such as text generation, code completion, and paraphrasing. These models have revolutionized the field of artificial intelligence by demonstrating the ability to understand and generate human-like text with remarkable accuracy and coherence.
The release of ChatGPT marked a significant milestone in the AI landscape, igniting a rapid adoption of generative AI technologies across various industries. This breakthrough has driven innovation in the development of large language models and fueled substantial growth within the AI industry. The impact of these advancements is evident, as a striking 92% of Fortune 500 companies have integrated generative AI into their workflows, enhancing efficiency and productivity.
As the adoption of generative AI continues to accelerate, the large language model industry is poised for tremendous growth. Projections indicate that the global market for large language models will expand from $6.5 billion in 2024 to $140.8 billion by 2033. This rapid growth underscores large language models’ transformative potential and increasing importance in the technological landscape.
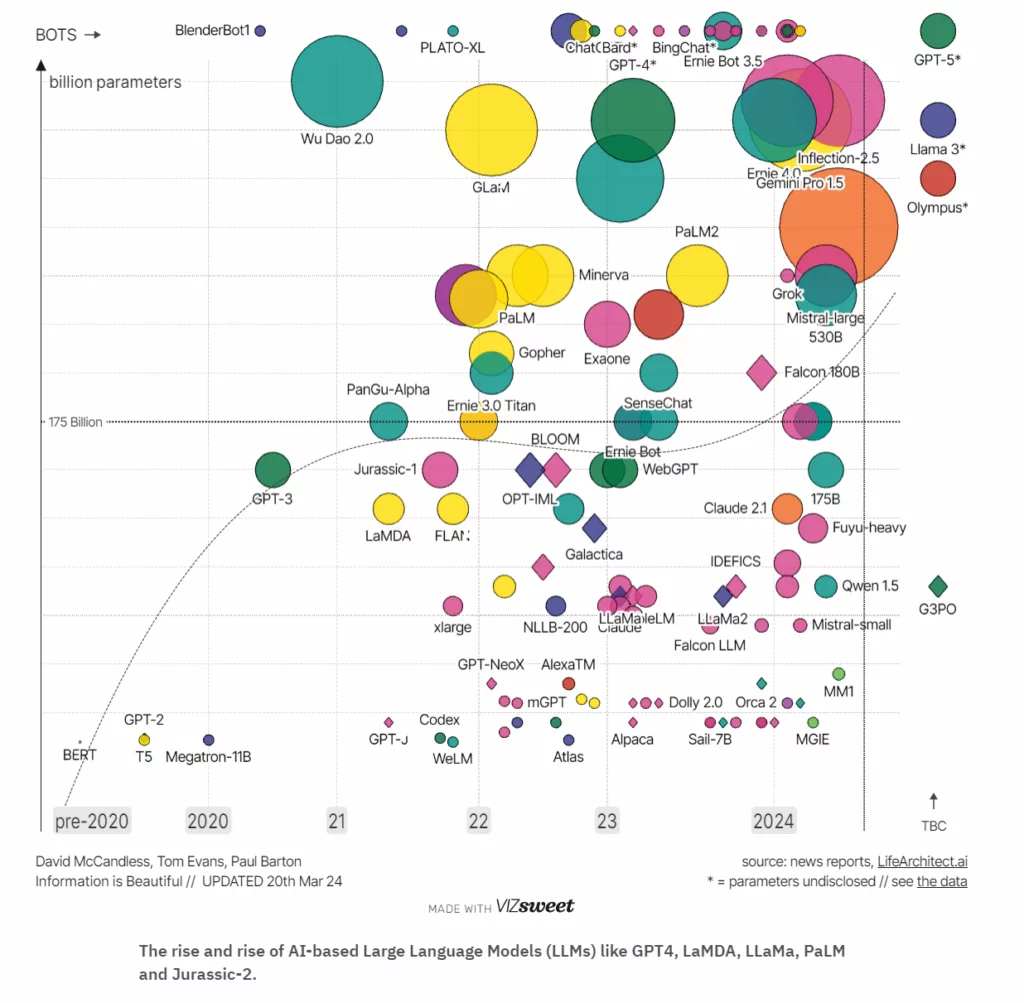
What is Large Language Model Concepts, LLM Application in 2024
Top Large Language Models of 2024:
1. GPT-4o
Developer: OpenAI
Release Date: May 13, 2024
Number of Parameters: Unknown
GPT-4o is the latest and most advanced language model developed by OpenAI, following GPT-4, GPT-3.5, and GPT-3 releases. OpenAI boasts that GPT-4o is 50% cheaper to operate than GPT-4 while being twice as fast at generating tokens. This multimodal model supports text, image, video, and voice capabilities within a single package.
One of the most significant upgrades in GPT-4o is its Voice-to-Voice function, which dramatically improves input response times to an average of 320 milliseconds, compared to several seconds with GPT-4. This feature is anticipated to launch in the coming weeks.
2. Claude 3
Developer: Anthropic
Release Date: March 14, 2024
Number of Parameters: Unknown
Claude 3 is the latest iteration of Anthropic’s language models, comprising Claude 3 Haiku, Claude 3 Sonnet, and Claude 3 Opus. It is considered one of the primary competitors to GPT-4 and ChatGPT, capable of processing up to 200,000 tokens (approximately 150,000 words), significantly surpassing GPT-4’s 32,000 token limit.
Amazon’s over $4 billion investment in Anthropic has elevated the startup’s valuation to $15 billion. Additionally, the Claude mobile app was released in May 2024.
3. Grok-1
Developer: xAI
Release Date: November 4, 2023
Number of Parameters: 314 billion
Developed by Elon Musk’s AI startup xAI, Grok-1 is the largest open-source large language model, with 314 billion parameters. Grok is integrated with X (formerly Twitter), and access requires an X Premium+ subscription.
Due to its massive size, Grok employs a mixture-of-experts (MoE) architecture, utilizing only 25% of its weights for any given input token to enhance calculation efficiency.
4. Mistral 7B
Developer: Mistral AI
Release Date: September 27, 2023
Number of Parameters: 7.3 billion
Mistral 7B is an open-source language model featuring 32 layers, 32 attention heads, and eight key-value heads. Despite having fewer parameters, it surpasses the Llama 2 family of models across almost all metrics, including MMLU, reading comprehension, math, and coding.
Mistral 7B is distributed under an Apache 2.0 license, allowing users to download it locally, deploy it on the cloud, or run it on HuggingFace. The Paris-based startup is nearing a new $600 million funding round, which would value the company at $6 billion.
5. PaLM 2
Developer: Google
Release Date: May 10, 2023
Number of Parameters: 340 billion
PaLM 2 is an advanced large language model developed by Google. As the successor to the original Pathways Language Model (PaLM), it is trained on 3.6 trillion tokens and comprises 340 billion parameters. Initially used to power Google’s first generative AI chatbot, Bard (rebranded to Gemini in February 2024), PaLM 2 marks a significant evolution in Google’s AI capabilities.
6. Falcon 180B
Developer: Technology Innovation Institute (TII)
Release Date: September 6, 2023
Number of Parameters: 180 billion
Falcon 180B, developed and funded by the Technology Innovation Institute, is an advanced version of the earlier Falcon 40B LLM. With 180 billion parameters, it is 4.5 times larger than its predecessor. Falcon 180B outperforms other large language models like GPT-3.5 and LLaMA 2 in reasoning, question answering, and coding tasks. In February 2024, TII allocated $300 million to the Falcon Foundation.
7. Stable LM 2
Developer: Stability AI
Release Date: January 19, 2024
Number of Parameters: 1.6 billion and 12 billion
Stability AI, creators of the Stable Diffusion text-to-image model, developed the Stable LM 2 series of large language models, which include Stable LM 2 12B (12 billion parameters) and Stable LM 2 1.6B (1.6 billion parameters). Released in January 2024, the larger 12B model outperforms models like LLaMA 2 70B on key benchmarks despite its smaller size.
8. Gemini 1.5
Developer: Google DeepMind
Release Date: February 2, 2024
Number of Parameters: Unknown

Gemini 1.5 is Google’s next-generation large language model, significantly upgrading over its predecessor, Gemini 1.0. Available for early testing, Gemini 1.5 Pro boasts a one million-token context window (equivalent to 1 hour of video, 700,000 words, or 30,000 lines of code), the largest among all current LLMs and chatbots. This upgrade is 35 times larger than Gemini 1.0 Pro and surpasses the previous record of 200,000 tokens held by Anthropic’s Claude 2.1.
9. Llama 3
Developer: Meta AI
Release Date: April 18, 2024
Number of Parameters: 8 billion and 70 billion
Llama 3 is the latest installment in Meta’s series of autoregressive large language models. The 8B and 70B versions surpass other open-source models, such as Mistral 7B and Google’s Gemma 7B, in MMLU, reasoning, coding, and math benchmarks. The open-sourced Llama 3 model is freely accessible through the Meta AI chatbot.
Customers can still use its predecessor, Llama 2, available in three versions: 7 billion, 13 billion, and 70 billion parameters. Meta also plans to release a larger 400 billion-parameter version of Llama 3 later this year.
10. Mixtral 8x22B
Developer: Mistral AI
Release Date: April 10, 2024
Number of Parameters: 141 billion
Mixtral 8x22B is Mistral AI’s latest and most advanced large language model. This sparse Mixture-of-Experts (SMoE) model contains 141 billion parameters but only uses 39 billion active parameters simultaneously to enhance the performance-to-cost ratio.
Additionally, Mistral AI has released Mistral Large, an alternative to ChatGPT, which ranks second only to GPT-4 among API-based LLMs.
11. Inflection-2.5
Developer: Inflection AI
Release Date: March 10, 2024
Number of Parameters: Unknown

Inflection-2.5 is the latest large language model developed by Inflection AI to power its conversational AI assistant, Pi. The model has been significantly upgraded and now achieves over 94% of GPT-4’s average performance while utilizing only 40% of the training FLOPs. In March 2024, the Microsoft-backed startup reached over one million daily active users on Pi.
12. Jamba
Developer: AI21 Labs
Release Date: March 29, 2024
Number of Parameters: 52 billion
Jamba is the world’s first production-grade Mamba-style large language model created by AI21 Labs. It integrates SSM technology with elements of a traditional transformer model, resulting in a hybrid architecture. Jamba is efficient and highly scalable, featuring a context window of 256K and supporting the deployment of 140K context on a single GPU.
Factors to Consider Before Choosing a Large Language Model (LLM):
- Purpose and Use Case: Determine the tasks you need the LLM to perform, such as text generation, summarization, translation, question answering, or code generation.
- Model Size and Parameters: Consider the model’s size regarding the number of parameters. More extensive models often offer better performance but require more computational resources.
- Accuracy and Performance: Evaluate the model’s performance on relevant benchmarks and tasks. Look for metrics such as accuracy, fluency, and contextual relevance.
- Computational Requirements: Assess the hardware and infrastructure needed to run the model. Larger models may require powerful GPUs or TPUs and significant memory.
- Cost: Consider deploying and maintaining the model, including infrastructure, licensing fees, and ongoing operational expenses.
- Scalability: Ensure the model can scale to meet your needs, whether you require handling a large volume of requests or processing extensive datasets.
- Latency: Check the response time of the model, especially if real-time processing is crucial for your application.
- Training Data: Look into the data on which the model was trained. Models trained on diverse and high-quality datasets typically perform better in various contexts.
- Fine-tuning and Customization: Determine if the model allows for fine-tuning or customization to suit your specific requirements better and improve performance on domain-specific tasks.
- Security and Privacy: Evaluate the model’s compliance with security and privacy standards, mainly if you handle sensitive or confidential information.
- Ease of Integration: Consider how easily the model can be integrated into your existing systems and workflows. Look for available APIs, SDKs, and documentation.
- Community and Support: Check if an active community and support is available for the model. This can be valuable for troubleshooting, updates, and leveraging shared knowledge.
- Ethical Considerations: Reflect on the ethical implications of using the model, including potential biases and the impact on users. Ensure the model aligns with your organization’s values and moral standards.
- Open Source vs. Proprietary: Decide between open-source models, which offer more flexibility and control, and proprietary models, which may come with additional support and features
Conclusion:
The landscape of large language models is rapidly evolving, with breakthroughs and innovations emerging at an unprecedented pace.
From compact models like Phi-2 and Alpaca 7B to cutting-edge architectures like Jamba and DBRX, the field of LLMs is pushing the boundaries of what’s possible in natural language processing (NLP).
FAQs on Large Language Models:
What are the benefits of using compact models like Phi-2 and Alpaca 7B?
Compact models like Phi-2 and Alpaca 7B offer significant benefits, such as lower computational requirements, faster processing times, and the ability to be deployed on devices with limited resources. They are ideal for applications where efficiency and scalability are crucial.
What distinguishes cutting-edge architectures like Jamba and DBRX?
Cutting-edge architectures like Jamba and DBRX introduce innovative techniques and hybrid models that enhance performance, scalability, and context handling. These advancements push the limits of what is achievable in NLP, offering more accurate and versatile language understanding capabilities.
How is the field of LLMs expected to evolve?
The field of LLMs is expected to continue growing with ongoing research and development. Future advancements may include more efficient models, better handling of multimodal data (such as text, image, and video), and improved real-time processing capabilities, further expanding the applications and impact of LLMs.



