Product returns are an inevitable aspect of retail business operations, and despite efforts to minimize them, they remain a significant factor to contend with. According to a report by the National Retail Federation and Appriss Retail, the average return rate for most U.S. retailers stands at 16.5%. However, with strategic management, returns present an opportunity not only to regain lost business but also to cultivate enduring customer loyalty.
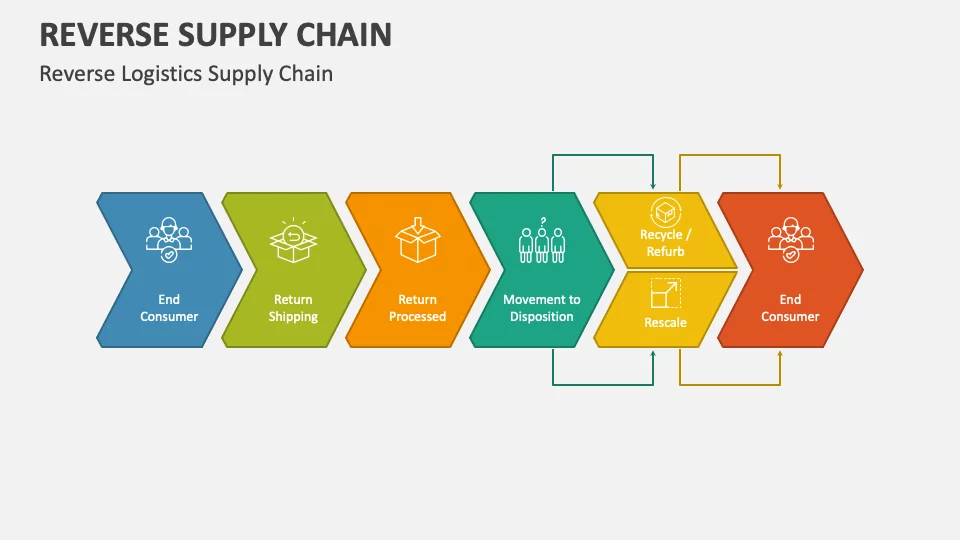
Reverse logistics, the process of managing returned goods, poses unique challenges compared to traditional eCommerce logistics. While the latter focuses on the efficient movement of goods from seller to buyer, reverse logistics comes into play when products need to be returned, exchanged, refunded, or replaced. It involves a multifaceted approach encompassing various elements:
- Ecommerce Technology: Implementing eCommerce technology is crucial for facilitating returns. Self-service links on your online store allow customers to initiate returns seamlessly, streamlining the process and enhancing customer satisfaction.
- Customer Service: A robust customer service infrastructure is essential for addressing return-related inquiries and issues promptly and efficiently. Whether it’s resolving shipping concerns or providing self-service content, responsive customer service fosters positive experiences and reinforces trust.
- Physical Stores: For omnichannel retailers, brick-and-mortar store locations can serve as return centers, offering customers the option to return items in-person. This integration of online and offline channels enhances convenience and flexibility for customers while optimizing operational efficiency.
- Ecommerce Warehousing: Handling returned items at the warehouse requires meticulous processes and technology. Upon receipt, returned products need to be inspected, sorted, and either restocked or disposed of appropriately. Efficient warehouse management ensures swift resolution of returns, minimizing disruptions to inventory and fulfillment operations.
- Marketing: Leveraging marketing strategies is essential for retaining customers and mitigating the impact of returns on business. By ensuring a smooth and accessible return process, businesses can enhance customer satisfaction and loyalty. Personalized offers and tailored experiences can further incentivize customers to continue patronizing the brand despite encountering returns.
Benefits of Efficient Reverse Logistics:
- Enhanced Customer Experience: Providing a seamless returns and refunds process demonstrates your commitment to customer satisfaction. When customers encounter hassle-free returns, they are more likely to trust and continue purchasing from your brand.
- Improved Brand Reputation: Efficient reverse logistics operations contribute to a positive brand image. Customers perceive brands that handle returns professionally and promptly as reliable and trustworthy partners, enhancing brand reputation and credibility.
- Increased Customer Loyalty: By prioritizing customer needs throughout the returns process, you foster loyalty and long-term relationships. Satisfied customers are more likely to become repeat buyers and brand advocates, driving sustained revenue growth.
- Competitive Advantage: In today’s competitive landscape, offering hassle-free returns can set your brand apart from competitors. A customer-centric approach to reverse logistics can become a unique selling point that attracts and retains customers.
Types of Reverse Logistics:
Let’s delve into seven key types of reverse logistics operations:
- Customer Returns: Customer returns are perhaps the most common type of reverse logistics operation. Return rates can vary significantly across product categories, with apparel sellers often facing high return rates, especially in online sales. Factors such as sizing issues, “bracketing” (buying multiple sizes and returning the ones that don’t fit), and “wardrobing” (returning items after single-use) contribute to the complexity of managing customer returns. Effective reverse logistics processes must address these challenges, including inspection, restocking, and potentially disposing of From Returns to Revivalreturned items.
- Rental Returns: Businesses that offer rental services, such as fashion rentals or equipment rentals, require specialized reverse logistics operations. Managing rental timeframes, inspecting items for damage, and replenishing stock are essential components of this process. Robust systems must be in place to ensure a seamless experience for customers returning rented items.
- Product Recalls: In the event of safety concerns or product defects, companies may need to issue recalls, requiring a swift and efficient reverse logistics response. Clear communication with customers regarding the return, repair, or exchange process is crucial during recalls, which can place significant strain on reverse logistics operations due to the sudden influx of returned items.
- Unsold Merchandise: Managing unsold inventory is another facet of reverse logistics. Retailers may need to return unsold merchandise to manufacturers, allocate it to liquidators for resale at discounted prices, donate it, or hold it in warehouses for future sales. Effective inventory management strategies are essential to optimize these processes and minimize losses.
- Repair and Refurbishment: As sustainability becomes increasingly important, businesses may offer repair, refurbishment, or upgrade services to extend the life of products. Reverse logistics operations for repair and refurbishment involve shipping products back to service centers or store locations, where they undergo inspection, repair, and repackaging before being returned to customers.
- Trade-In and Resale: Trade-in and resale programs offer customers the opportunity to exchange used items for credit or purchase new products at a discount. Implementing effective reverse logistics processes for trade-in and resale programs involves assessing the condition and resale value of returned items before reintroducing them into inventory or resale channels.
- End-of-Life Disposal: Responsible disposal of end-of-life products is an increasingly important aspect of reverse logistics, particularly for environmentally-conscious businesses. Offering incentives for customers to return worn-out or used-up products for recycling, repurposing, or environmentally-responsible disposal requires careful sorting, disassembly, and processing of inbound merchandise.
Best Practices for Reverse Logistics:
1. Learn about existing trends and patterns
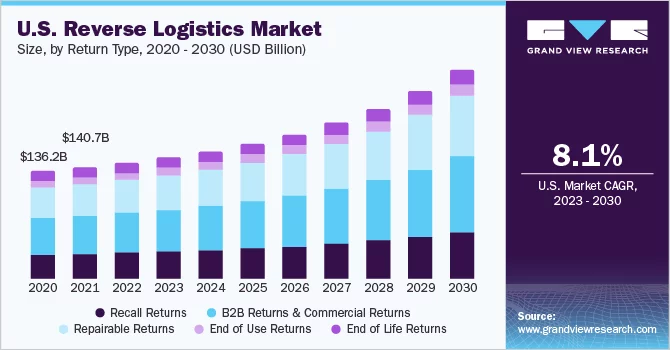
Analyzing existing patterns and identifying opportunities to mitigate returns are essential steps in optimizing reverse logistics operations. Let’s delve into each of these steps in detail:
A. Take Stock of Existing Patterns: Start by delving into your sales and return data to gain insights into existing patterns. Here’s what to consider:
- Most Frequently Returned Products: Identify which products are returned most frequently. This can help pinpoint potential issues with product quality, size, or description.
- Return Methods: Determine whether customers prefer shipping returns or dropping off items at physical stores. Understanding customer preferences can inform your reverse logistics strategy.
- Customer Service Feedback: Analyze common questions and feedback received by your customer service team regarding the returns process. Addressing information gaps can streamline the returns experience for customers.
- Second-Hand Sales: Monitor second-hand sales on platforms like eBay and Craigslist to gauge customer interest in trade-in or resale programs.If customer data is limited, gather insights from industry trends, competitor offerings, trade publications, and events to inform your analysis.
2. Identify Opportunities to Reverse the Returns Tide:
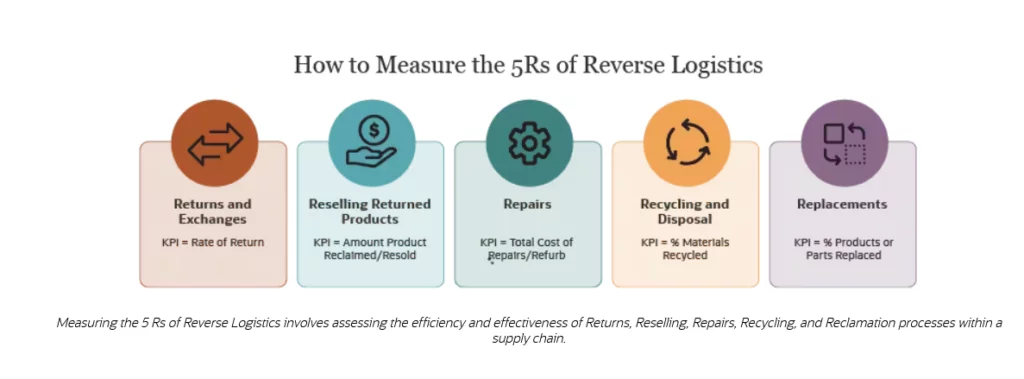
Once you’ve identified existing patterns, focus on strategies to minimize returns and improve customer satisfaction:
- Help Customers Find a Better Size: Size and fit issues are common reasons for returns. Provide comprehensive size information, such as size charts and dimensions, to assist customers in selecting the right size. Encourage customer feedback specifically related to size and fit, and consider implementing augmented reality experiences for virtual try-ons.
- Align Expectations with Reality: Ensure that product photos and descriptions accurately represent the product. Guide customers towards compatible parts and accessories to reduce the likelihood of returns. Conduct quality checks to verify product quality before shipment, promptly removing defective items from inventory.
- Provide Shipping Timeframes Upfront: Clearly communicate estimated delivery dates to customers before checkout. During peak selling seasons, encourage early orders to guarantee timely delivery, reducing the likelihood of returns due to delayed shipments.
3. Evaluate Packaging for Return Journeys:
When designing product packaging, it’s crucial to consider its suitability for reverse logistics. Here’s what to consider:
- Reusability and Recyclability: Design product packaging with the intention of reuse, refill, or recycling. Opt for materials that are environmentally-friendly and easily recyclable, such as cardboard or biodegradable plastics.
- Resealability: Ensure that the outer shipping box or bag is easy for customers to reseal and send back with a fresh label in case of returns. This simplifies the returns process for customers and facilitates efficient reverse logistics.
- Durable Materials: Consider using pouches or bins made of durable materials intended for multiple trips. For example, Rent the Runway’s custom-made garment bags are designed with materials similar to those used for soft luggage, enhancing durability and longevity.
By prioritizing packaging that facilitates reverse logistics, businesses can streamline the returns process, reduce waste, and enhance sustainability efforts.
Learn about the best practices in returns management here.
4. Devise an Inspection Protocol for Returned Goods:
Inspection is a critical aspect of the reverse logistics process, particularly for businesses venturing into resale or considering returning used products to store shelves. Here’s how to approach it:
- Standardized Evaluation Criteria: Develop standardized evaluation criteria to ensure consistency in assessing returned merchandise. This includes criteria such as product condition, completeness, and functionality.
- Documentation and Logging: Log inspection results systematically for future reference. This documentation not only aids in decision-making but also facilitates transparency and accountability in the reverse logistics process.
- Consumer Assurance: Consider sharing inspection reports on product pages for resold items to reassure second-hand shoppers about the quality and condition of each item. This transparency enhances trust and confidence in the resale process.
5. Evaluate Fulfillment Partner Capabilities:
It’s crucial to ensure that your fulfillment partners are equipped to handle reverse logistics effectively. Here’s what to consider:
- Responsibility and Accountability: Even if you outsource fulfillment services and returns management, your brand remains responsible for providing a smooth reverse logistics experience. Understand how your logistics partners manage and charge for returned merchandise to maintain control over the process.
- Capabilities Alignment: Assess whether your fulfillment partners have the necessary capabilities to support your reverse logistics initiatives, such as resale or refurbishment services. Close collaboration with partners is essential, especially for complex operations.
- Consider Additional Providers: Depending on your partners’ capabilities and your business needs, you may consider adding a dedicated returns management provider to your network. These providers specialize in managing reverse logistics processes and can offer tailored solutions to optimize efficiency.
6. Map and Integrate Back-End Systems:
Integrating back-end systems is essential for ensuring seamless and efficient operations across the reverse logistics process. Here’s how to approach it:
- Visibility: Aim to have visibility into specific products and their associated original orders at every stage of the returns process. This enables you to track returns, manage inventory, and provide timely updates to customers.
- Accuracy: Maintain accurate inventory counts by updating stock levels regularly to reflect returned merchandise that has been reintegrated into inventory. This prevents discrepancies and ensures inventory accuracy.
- Control: Enable capabilities such as rerouting, expediting, and custom handling to respond effectively to different return scenarios. Having control over the process allows for flexibility and proactive problem-solving.
- Transparency: Provide customers with transparency throughout the returns process by allowing them to check the status of their refunds or repairs. Timely and accurate information builds trust and enhances the customer experience.
7. Allow for effective communication:
Effective communication is key to ensuring customers can navigate the returns process smoothly. Here’s how to communicate clearly and comprehensively with customers:
Highlight Return Policies and Exchange Options:
- Make return policies and exchange options easily accessible at multiple touchpoints during the purchasing journey. Ensure that your terms are competitive and up-to-date with industry standards.
- Avoid burying return policies in obscure sections of your website. Instead, prominently link to them from the shopping cart page and throughout the checkout process. Collaborate with legal experts to translate complex legal language into clear, shopper-friendly terms.
Promote Policy Benefits:
- Emphasize the benefits of your return policies to customers. Highlight conveniences such as the ability to return items purchased online in-store, or vice versa. If you offer additional perks like free recycling of old electronics, make sure to communicate these benefits clearly.
Automate Messaging for Status Updates:
- When testing reverse logistics scenarios, identify critical steps that warrant communication with customers. Automate messaging via email or SMS to provide timely updates on the status of returns.
- Ensure that customers are informed about the progress of their returns, from initiation to completion. This proactive approach reduces uncertainty and enhances the overall customer experience.
Conclusion:
Navigating the complexities of reverse logistics requires careful consideration and strategic investment. While dedicating resources to refining returns and refunds processes may initially appear costly, effectively managing reverse logistics can ultimately enhance your brand’s reputation for customer-centric efficiency. This, in turn, can lead to increased sales and customer loyalty over time.
FAQs on Reverse Logistics:
Will investing in reverse logistics negatively impact my bottom line?
While there may be initial costs associated with optimizing reverse logistics, the long-term benefits, including improved customer loyalty and increased sales, often outweigh the investment.
How can I measure the effectiveness of my reverse logistics efforts?
Track key metrics such as return rates, customer satisfaction scores, and repeat purchase behavior to assess the impact of your reverse logistics initiatives.
What role does customer feedback play in refining reverse logistics processes?
Customer feedback provides valuable insights into pain points and areas for improvement within the returns process. Incorporate feedback to refine procedures and enhance the overall customer experience.



