Experiencing a sudden slowdown in your network can be incredibly frustrating, especially during critical business activities such as client presentations or urgent tasks. Network latency issues can significantly impact productivity and disrupt operations.
As networks expand, managing network latency becomes increasingly challenging. With more connections and potential delay points, effectively troubleshooting network latency is essential—particularly as your business integrates with cloud servers, adopts new applications, or supports remote employees and branch offices.
To reduce network latency effectively, it’s vital to implement and maintain the right processes. Proactively addressing network latency issues involves having the appropriate tools and strategies to resolve problems swiftly when they arise.
What is Meant by Troubleshooting Network Latency?
Troubleshooting network latency involves diagnosing and resolving delays in data transmission within a network. Latency can significantly affect user experience, leading to slow-loading websites, buffering during streaming, and lag in online gaming. Addressing these issues is essential for ensuring a smooth and efficient network experience.
Key aspects of troubleshooting include:
- Identifying Symptoms: Recognizing signs of high latency, such as slow application performance and delayed file transfers.
- Analyzing Network Configuration: Examining network setup for potential bottlenecks, including bandwidth limitations and hardware performance.
- Utilizing Diagnostic Tools: Employing tools to continuously monitor and analyze network performance.
Signs of High Network Latency
High network latency can really put a damper on your online experience. Here are some telltale signs that your latency might be too high:
- Delayed File Transfers: If sending or receiving large files takes much longer than usual, that’s a strong indication of high latency.
- Slow Application Performance: Web apps might feel sluggish, with noticeable delays when you try to use them, making it frustrating to get things done.
- Buffering During Streaming: When you’re streaming videos and they keep pausing to buffer, high latency could be the culprit.
- Lag in Online Gaming: In multiplayer games, if your actions aren’t registering in real-time and there’s a noticeable delay, you’re likely facing high latency.
- Choppy Voice or Video Calls: During video conferences, if you notice poor audio quality, echoes, or delays, it’s a sign of latency issues affecting communication.
- Websites Failing to Load: If websites are taking ages to load or time out completely, high latency is probably the reason behind that frustrating experience.
- Increased Ping Times: Running a Ping test and seeing response times over 100 ms is a clear indicator that latency is an issue.
Signs of Low Network Latency
On the flip side, low network latency usually leads to a smoother and more enjoyable online experience. Here are the signs that indicate everything’s running smoothly:
- Fast File Transfers: Sending and receiving files happens quickly, allowing you to stay productive without delays.
- Responsive Applications: Web apps load quickly and operate seamlessly, making your workflow feel efficient.
- Buffer-Free Streaming: Videos stream without interruptions, providing a great viewing experience.
- Smooth Online Gaming: Actions in games register almost instantly, leading to a more immersive and enjoyable gaming session.
- Clear Voice and Video Calls: During video conferences, audio and video sync up perfectly, making communication effective.
- Quick Website Load Times: Websites load in a snap, enhancing your browsing experience without frustrating wait times.
- Consistent Ping Times: If your Ping tests show low response times (generally under 50 ms), that’s a great sign of a responsive network.
Revving Up the Engine: Understand What Causes Network Latency
Latency can be likened to a traffic jam on the information superhighway, causing delays that make everything feel sluggish. Let’s explore the key factors that contribute to these frustrating delays, particularly how Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) can help mitigate them.
1. Distance
Just as the speed of light limits data travel, the distance between network nodes affects latency. Data travels through fiber optic cables, and factors like cable quality and router efficiency can weaken the signal.
For example, a distance of 1,000 kilometers with data traveling at 70% of light speed results in a round-trip time (RTT) of approximately 9.524 milliseconds. Typically, latency is about 1 ms per 100 km. For instance, a route of 1,100 km from New York to Montreal with an RTT of 33 ms indicates less-than-optimal latency, possibly due to network inefficiencies.
How Distance Impacts Latency:
- Increased latency for businesses far from their cloud service provider.
- Higher latency for remote workers connecting to their offices.
- Slower online experiences for customers distant from your servers.
- Data replication delays between distant data centers.
- CDN Advantage: Proximity to CDN nodes can significantly reduce latency, ensuring faster content delivery by caching data closer to users.
2. Network Congestion
Network congestion arises when too many “cars”—or data packets—attempt to use the same “road” at once, similar to traffic jams. This congestion can slow down data transfer rates, especially during peak usage times.
How Congestion Impacts Latency:
- Increased latency during peak internet usage.
- Local congestion affecting data transfer speeds.
- Latency issues on cloud service providers’ networks.
- Slower VPN connections due to public internet congestion.
- Website performance drops during high-traffic periods.
- CDN Advantage: CDNs distribute content across multiple servers, alleviating congestion by balancing the load and ensuring that users access data from the nearest server, reducing bottlenecks.
3. Network Hardware
Just as a well-maintained car engine performs better, high-quality network hardware is essential for keeping latency low. Outdated or faulty hardware, such as routers or modems, can significantly slow down data transmission.
How Network Hardware Impacts Latency:
- Outdated routers causing delays.
- Poorly configured switches leading to congestion.
- Servers lacking sufficient RAM or processing power affecting latency.
- Malfunctioning network interface cards (NICs) impacting performance.
- CDN Advantage: CDNs use advanced infrastructure and optimized hardware to ensure high performance and reliability, minimizing latency by maintaining top-tier technology at their edge servers.
Explore the Tactical Approach to Troubleshoot Network Latency
Step 1: Comparative Analysis of Network Sessions
To troubleshoot network latency issues, begin by accurately identifying the issue through a comparative analysis of monitoring data from your network tools. This step is crucial for pinpointing where latency occurs, enabling effective solutions. A robust hosting solution with integrated monitoring can enhance this process by providing vital performance metrics.
1.1 User or Application-Related Latency
If network-wide issues aren’t the cause, examine user workstations or specific applications. Install monitoring tools on user devices to capture latency data. Resource-intensive applications, like video conferencing, can strain CPU and RAM. Efficient monitoring will highlight these issues, and hosting solutions with optimization features can enhance application performance.
1.2 Latency Across Multiple Network Sessions
If latency appears across multiple sessions, this indicates a broader network issue, potentially involving components like the LAN or firewall. Assess your hosting solution to troubleshoot network latency issues and resolve them one and for all.
1.3 Single Network Session Latency
When latency is limited to a single session, focus your investigation there. Review performance metrics from the service provider involved to address any session-specific issues effectively.
Step 2: Device Monitoring
If latency persists, utilize network monitoring tools to determine if the issue is internal or related to your service provider. Analyzing this data helps distinguish the source of the problem.
2.1 Internal Latency
If monitoring reveals CPU or bandwidth issues, investigate further. Common problems include:
- Network Traffic Examination: Review firewall logs to ensure traffic is legitimate and not overloaded.
- Firewall Prioritization: Adjust settings to prioritize critical traffic, reducing congestion impact.
- Bandwidth Upgrade: Evaluate your internet bandwidth and consider upgrading if necessary.
- Resource Investigation: Address any high CPU usage due to software inefficiencies or hardware limitations.
2.2 ISP-Related Issues
If no internal problems are found, contact your ISP with detailed monitoring data to address potential external latency issues.
Step 3: Analyzing Traceroute Data
To effectively identify the sources of reducing network latency issues, utilize network monitoring tools to map the path of data packets to the target server. This process allows you to pinpoint specific delays at each hop along the route.
3.1. Running Traceroute
Execute traceroute commands from your device to the problematic server in the network path. Review the output for each hop, noting any significant increases in response times that indicate potential bottlenecks.
3.2. Identifying Delays
Focus on hops with higher latency. These may reveal issues with specific routers or network segments that need attention to resolve the network latency issues.
3.3. Collaboration with Providers
Share your traceroute findings with your ISP and hosting provider, including screenshots and detailed results. This collaboration is essential for diagnosing and resolving latency issues.
3.4. Temporary User Account
Create a temporary read-only user account in your network performance monitoring tool to allow support teams from your providers to conduct a more in-depth analysis of the network traffic.
3.5. Utilizing Performance Management Tools
Leverage any integrated performance management features in the network path from your hosting solution for deeper insights into network traffic patterns and latency sources.
Advanced AWS Features for Troubleshooting Network Latency
1. AWS Direct Connect
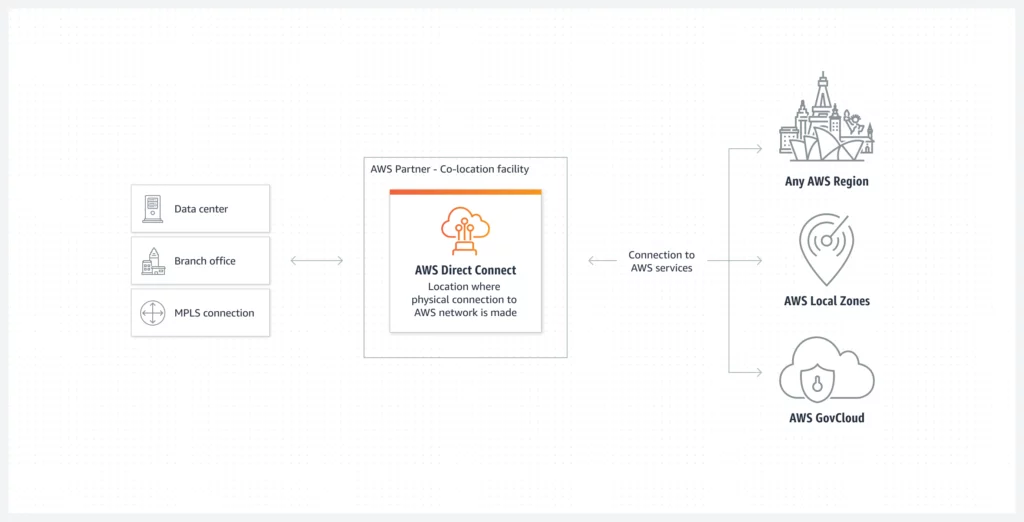
AWS Direct Connect enables a dedicated, private network connection between your on-premises infrastructure and AWS in order to troubleshoot network latency issues. This private connection bypasses the public internet, leading to more stable network performance and help reduce latency. AWS Direct Connect offers two key configurations:
- Hosted Connections: These are facilitated through AWS Direct Connect Delivery Partners. This option simplifies the setup process and offers flexible bandwidth choices, making it a convenient solution if you prefer a managed service with varying bandwidth needs. This managed setup is ideal for organizations that want to minimize the complexity of establishing and maintaining the connection.
- Dedicated Connections: With Dedicated Connections, you establish a direct, private connection with AWS. This option typically offers higher bandwidth and more consistent performance. By selecting from over 100 Direct Connect locations worldwide, you can choose a facility that is geographically close to your operations. This proximity helps further reduce latency and improve network performance by minimizing the distance data must travel.
2. Amazon CloudFront
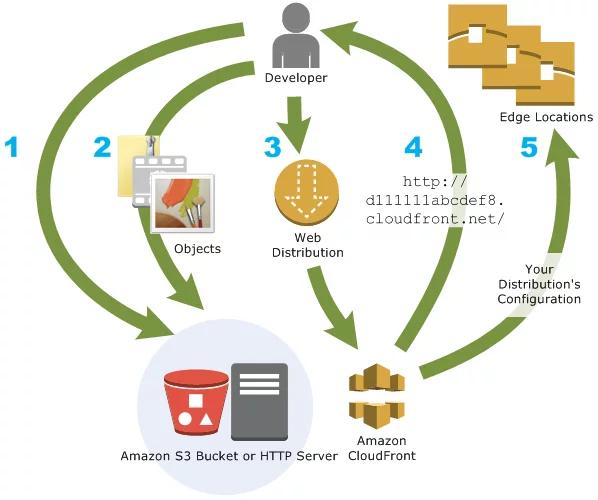
Amazon CloudFront is a global content delivery network (CDN) designed to accelerate the delivery of your web content. CloudFront improves network performance by caching content at edge locations distributed globally. When users request content, CloudFront serves it from the nearest edge location, which significantly reduces latency and enhances transfer speeds.
Additionally, CloudFront integrates seamlessly with other AWS services and includes advanced security features. This makes it a robust solution for both improving performance and protecting your content from potential threats.
3. AWS Global Accelerator
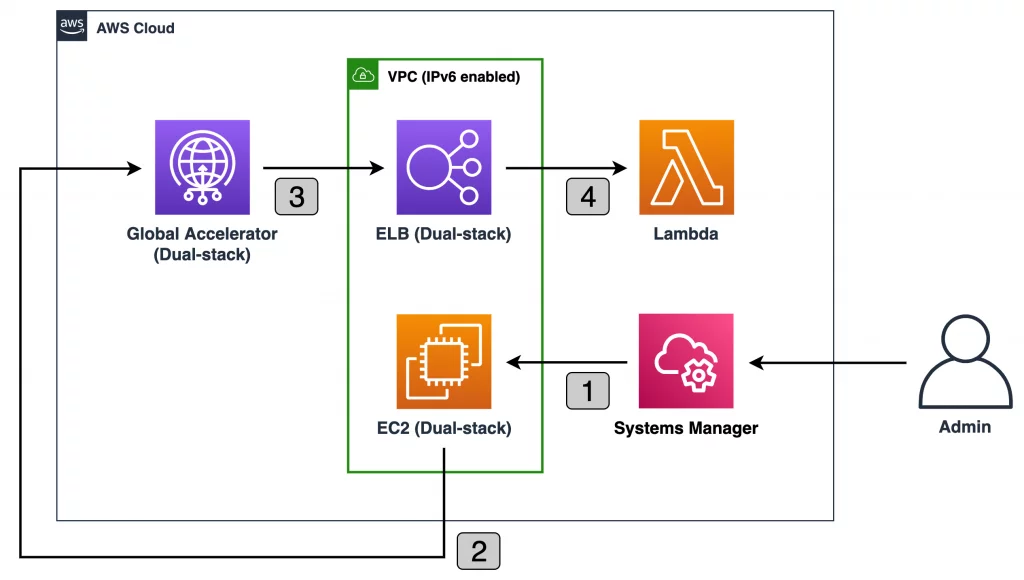
AWS Global Accelerator is a service that enhances the performance and availability of your applications by optimizing the routing of user traffic through AWS’s global network. It uses AWS’s vast global infrastructure to direct user traffic to the most optimal AWS endpoint based on real-time performance metrics. This intelligent routing helps reduce packet loss, jitter, and improve network latency.
By leveraging AWS’s global network, AWS Global Accelerator can boost application performance by up to 60%, which is especially valuable during times of internet congestion or regional network issues.
4. AWS Local Zones
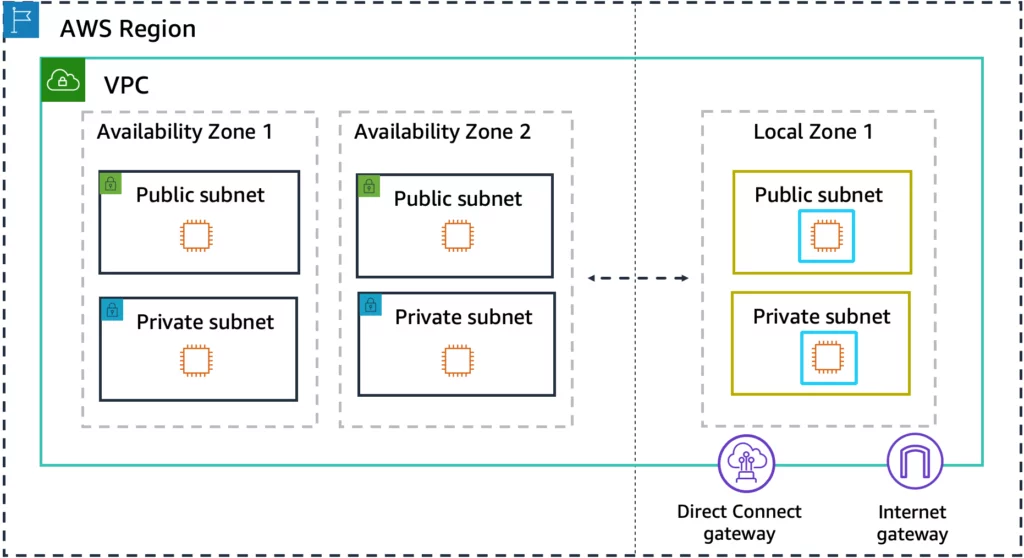
AWS Local Zones extend AWS’s cloud services closer to major metropolitan areas and industry hubs. By positioning compute, storage, and database services in proximity to end users, AWS Local Zones help to significantly reduce network latency for applications requiring real-time processing.
This geographical closeness ensures that data and services are delivered more quickly, providing a faster, more responsive user experience. AWS Local Zones are particularly beneficial for applications that demand low latency and high performance, such as gaming, media processing, and financial trading systems.
Turn Network Latency Challenges into Opportunities for Improvement
Effectively troubleshooting network latency requires a comprehensive approach. Key actions include understanding latency metrics, identifying common causes, using diagnostic tools, and applying targeted strategies. By tackling these areas methodically, you can significantly improve network performance and enhance user satisfaction.
For a powerful solution to network latency, turn to Nestify. Our hosting services leverage advanced CDN technology and robust AWS support to minimize latency and optimize your digital experience. With Nestify’s cutting-edge tools and infrastructure, you can resolve latency issues efficiently and boost your network performance.
Don’t let network latency impede your success. Start a free trial with Nestify today and discover how our top-tier hosting solutions can transform your network.
FAQs on Network Latency
How can I reduce network latency?
To reduce network latency, optimize network routes, manage bandwidth efficiently, upgrade hardware, and use tools to monitor and manage network performance. Implementing CDNs and load balancers can also be effective.
How can advanced hosting solutions help with latency?
Advanced hosting solutions like Nestify’s provide integrated performance monitoring and optimization features. These tools help identify and address latency issues, improving overall network performance.
How can I troubleshoot persistent latency issues?
Persistent latency issues may require a detailed analysis of network performance data and collaboration with your ISP or hosting provider. Providing them with performance metrics and traceroute results can help resolve these issues more efficiently.



