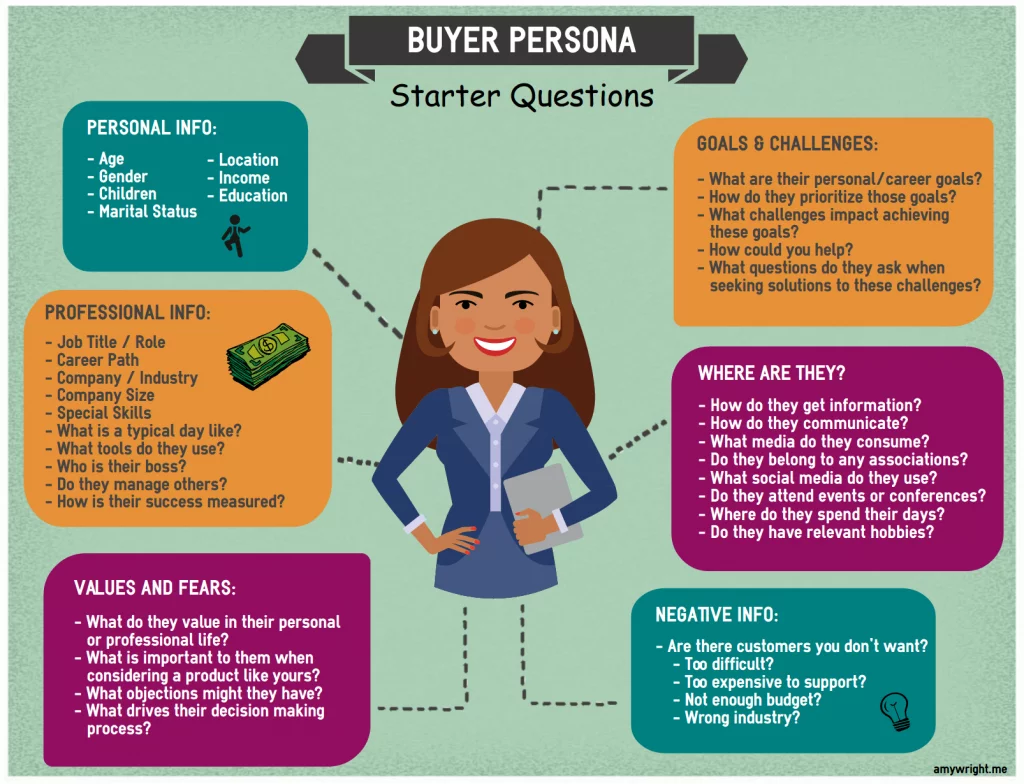
The most successful marketers move beyond mere audience data and numerical metrics, delving deep into understanding their customers as individuals. They ponder over their interests, communication styles, beliefs, and values.
Authentic communication and inspiring action come when you possess an in-depth knowledge of your customers. Addressing their specific needs and desires in a language they resonate with can significantly impact your conversion rates.
However, the challenge arises when attempting to craft a unique marketing message for each individual customer. Striking a balance between specificity and generalization becomes crucial, and this is where the concept of buyer personas becomes instrumental.
What Is a Buyer Persona?
A buyer persona, known as a user persona, marketing persona, or audience persona, is a fictional profile of your ideal customer crafted from market and audience research. It’s an imaginary representation embodying the essential characteristics within your broad audience.
This persona, though imaginary, should encompass demographic and psychographic profiles, behavioral trends, values, desires, pain points, and affiliations. Despite its fictional nature, the persona’s profile should be well-rounded and reflective of real individuals within your target market.
Advantages of Creating Detailed Buyer Personas:

- Precision in Ad Targeting: Detailed buyer personas enable businesses to leverage new customer targeting tools, tailoring campaigns based on diverse demographic and psychographic traits. Paid advertising becomes a potent tool, allowing refined targeting with limited budgets, reaching specific audiences based on factors like location, age, language, education level, and interests.
- Enhanced Clarity and Focus: Buyer personas contribute to more focused and clear communication about customers within a business. By distilling customer knowledge into a single persona, businesses create shared understanding and internal language, transforming generic discussions into nuanced and targeted strategies.
- Strategic Channel Prioritization: Buyer personas assist in prioritizing marketing channels strategically, steering businesses away from spreading resources thinly across multiple platforms. Instead, they facilitate the identification of effective channels based on where the target customers spend their time, ensuring efficient resource allocation.
- Alignment of Content with Audience Preferences: Buyer personas play a crucial role in aligning content with audience preferences. They enable businesses to sharpen their copywriting, design, and content to resonate more effectively with the identified audience. Specific traits, such as location, industry, and entertainment preferences, can be targeted for increased engagement.
- Accessible Insights for All Teams: Buyer personas contribute to informed decision-making across various teams within the business. By consolidating essential customer information in a buyer persona profile, these insights become accessible to all teams, including marketing and support.
- Anticipating Barriers to Purchase: Support teams can use buyer personas to anticipate barriers to purchase, such as prerequisites for product use or language preferences. This results in more effective and customer-centric interactions, enhancing the overall customer experience.
Who Should Contribute to Creating Buyer Personas?
Creating buyer personas involves stakeholders from various departments across the company, ensuring diverse insights are considered. While this may slow down the process, it ensures that perspectives from marketing, sales, customer service, product development, and management are all accounted for.
Including representatives from these five key business departments ensures a holistic approach, incorporating experiences from different facets of the customer journey.
Components of a Buyer Persona Template:
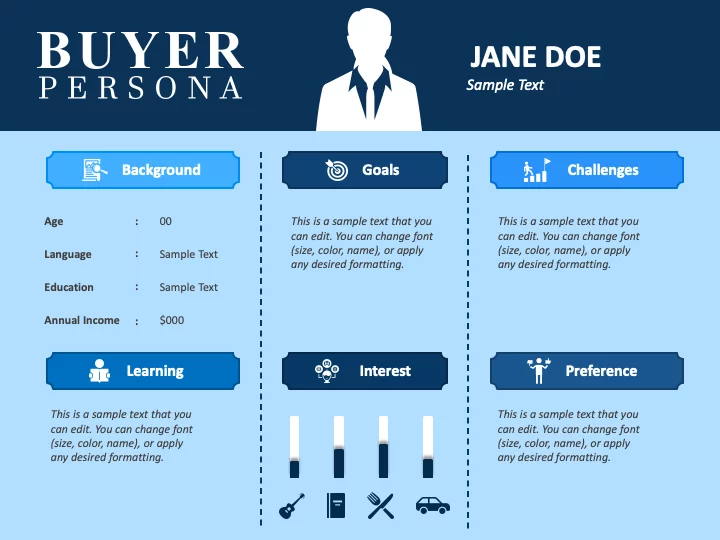
The components of a typical buyer persona template are thoughtfully organized into key sections, each providing nuanced insights into the characteristics of the ideal customer:
- Personal Background:
- This section delves into basic demographic information, including age, gender, income, and education level. These details provide a foundational understanding of the individual’s background.
- Job and Company:
- Outlining the buyer’s professional details, this section covers their job title, responsibilities, and the type of company they are associated with. It sheds light on the buyer’s professional context and environment.
- Goals and Challenges:
- Focusing on the buyer’s aspirations and hurdles, this section articulates their primary goals and challenges. It elucidates what the buyer aims to achieve or resolve with the utilization of your product or service.
- Buying Behavior:
- Exploring the intricacies of the buyer’s purchasing journey, this section delves into how the individual typically researches and evaluates products or services. It unravels their decision-making process and the criteria they consider during the buying process.
- Marketing Messaging:
- This section is dedicated to outlining the key messages and value propositions resonating with the target customer. It explores how these messages can be effectively communicated through various marketing materials to capture the buyer’s attention and engagement.
Buyer Persona vs. Target Market:

It’s crucial to distinguish between a buyer persona and a target market. A target market refers to large groups of people identified by broad demographic or audience segments. For instance, a company selling yoga accessories might define its target market as “women aged 35-45 in urban areas who love yoga.” In contrast, a buyer persona, such as Evelyn in this case, is more specific and descriptive, providing a detailed profile of an individual buyer, including personal details and specific preferences.
Negative Personas:
In the process of identifying buyer personas you aim to attract, it is equally important to acknowledge customer types that may not align with your business goals.
Negative personas represent buyers who consume your time and resources without genuine intent to purchase or with a low likelihood of making a purchase. Examples include Questioning Quinn, who bombards you with inquiries but does not make a purchase, or Returning Rachel, who frequently buys and returns items just before the return period expires. Negative personas can impact your company’s profitability and impede your ability to serve your ideal customers. Crafting marketing messaging with these negative personas in mind is essential to maintaining business focus and efficiency.
How to Create a Buyer Persona in 8 Steps:
1. Interview Your Current Customers
Initiating the creation of a buyer persona should always commence with thorough customer research. If your business is already engaged in selling products, the first step involves interviewing or surveying your existing satisfied customers. This step is pivotal, as it provides real insights directly from your clientele, validating or dispelling any preconceived notions about your target audience.
In conducting persona interviews, there are four essential questions that must be posed to gather comprehensive information:
- Why did you buy our product? This inquiry delves into the motivations behind the purchase, aiding in the development of the “buys for” category and elucidating the rationale for the buying decision.
- What alternatives did you choose us over and why? It is crucial to inquire about alternatives rather than direct competitors. Often, the alternative may not be a competitor but a DIY solution or a different product type. Understanding this helps in tailoring marketing strategies effectively.
- Where did you look for information when making this decision? This question sheds light on the persona’s preferred research channels, guiding the prioritization of marketing spend and outreach efforts.
- Why did you buy this currently, as opposed to earlier or later? Uncovering the timing of the purchase provides insights into critical moments in the customer journey, known as the “buying moment.”
These questions are designed to focus on the customer’s purchasing journey, offering clarity on specific moments that influence a buying decision. While broader customer data, such as interests and goals, is valuable, buyer personas primarily serve the purpose of understanding how your business can uniquely cater to an individual.
If your business is in its early stages and not yet selling, target interviews with customers of products you perceive as competitors. Be cautious when considering interviews with “potential customers” who express intentions to buy your product upon launch, as insights from actual purchasers hold greater significance. For the initial iteration of this exercise, aim for one-on-one conversations with five to 10 customers; if that’s impractical, opt for surveys with a sample size of at least 20.
2. Gather More General Data on Your Audience

Once your customer research is complete, complement it with industry-level data to enhance your understanding. Scrutinize audience data available on your website or social media platforms, delve into industry or market research, and analyze the customer profiles presented by your competitors. This additional information contributes to a more comprehensive grasp of your audience’s interests, goals, and overall lifestyle.
Learn what to add in your website.
3. Define Broad Buyer Personas
Following customer interviews and industry research, you can begin identifying your primary personas. Observe recurring patterns and similarities among customers, encompassing their interests, purchasing behaviors, and characteristics.
Initiate the persona creation process by starting broad before delving into specifics. Recognize that most businesses cater to multiple buyer personas, allowing you to segment distinct customer types into individual profiles.
For instance, consider a fictitious online business, “Sally’s Dog Food,” specializing in manufacturing dog food. From the outset, you can assume two potential customer groups:
- End customers: Individuals purchasing dog food for their pets.
- Wholesale accounts: Businesses interested in selling dog food in their retail and online stores.
With these broad buying groups identified, proceed to further break them down based on the nature of your product. In this example, divide each customer group into two distinct personas:
- For end customers: Dog owners seeking kibble for their pets.
- For wholesale accounts: Veterinarians stocking and selling dog food to their clients.
Now that the initial buyer personas are broadly defined, the next step involves identifying key details about each persona.
4. Identify Useful Details About Your Buyer Personas

Customer research should focus on relevant information that aids in making informed business decisions. The goal is not to delve into minutiae, such as favorite colors or coffee orders, but rather to gather actionable intelligence for selling dog food.
Utilize Facebook, a prominent ad network, for targeted insights aligning with your ideal customer profile. This platform’s ad capabilities allow mapping demographics and psychographics that define your buyer personas.
Common traits incorporated into buyer persona profiles include:
- Location: Where do they reside?
- Age: What is their general age range?
- Gender: The most likely gender of the customer.
- Interests: Hobbies and interests relevant to your product.
- Education: The educational level and field of study.
- Job title: Their profession and job titles.
- Income: Income range and purchasing power.
- Relationship status: Single or married?
- Language: Languages spoken.
- Favorite websites: Websites frequented related to your products.
- Buying motivations: Primary reasons for purchasing your products.
- Buying concerns: Factors that might deter them from buying your products.
Not all questions need answering for each persona; customization is key. The objective is to gain a profound understanding of customers to enhance communication effectiveness.
5. Research Your Buyer Personas

Following the establishment of two to three key personas, embark on a second research phase focused on understanding the buying motivations and psychographic tendencies of these identified personas. This stage delves deeper into individual personas rather than seeking broad patterns.
Explore the following avenues for insights about your ideal customer:
- Your own analytics: Utilize tools like Shopify Analytics Dashboard or Google Analytics for metrics such as languages spoken, browsers used, referral sources, visitor demographics, and device preferences.
- Facebook Audiences: Leverage Facebook‘s audience insights to analyze existing followers and build prospective audiences, gaining a detailed demographic and psychographic profile.
- Competitors: Examine established competitors using tools like SimilarWeb or SEMRush‘s Market Explorer to understand audience interests and behaviors. Explore competitors’ blogs and social media interactions for additional insights.
- Surveys and customer feedback: Conduct surveys or customer interviews to gather qualitative insights into buying motivations and concerns. Tools like Survey Monkey or post-purchase survey apps like Fairing can aid in this research.
- Customer support: Engage with your support or sales team to gather insights into customer pain points, goals, and behaviors. Review conversation logs and satisfaction ratings for crucial personal information.
By tapping into various sources, build a comprehensive understanding of your buyer personas and tailor your marketing strategies accordingly.
6. Compile a Comprehensive Buyer Persona Profile

Merge both quantitative and qualitative research findings, along with prioritized details, into a cohesive buyer persona profile to bring it to life. Utilize a free persona template to systematically organize the amassed information. While the template showcases an example for Sally’s Dog Food, personalize it with traits and characteristics anticipated in your ideal buyer.
7. Validate Your Personas
Conduct a critical gut-check on your buyer personas. Refer back to the list of customers you’ve interviewed and consider whether the persona aligns with at least some of them. Assess whether these personas represent the type of customers your business is best suited to serve. If the answer is affirmative, your buyer persona is deemed ready for implementation.
8. Implement Your Buyer Persona into Strategic Decisions
Armed with a well-defined buyer persona, steer your marketing decisions with your ideal customer in focus. For instance, consider the persona of Chloe the veterinarian and translate it into specific marketing tactics, such as:
- Audience Targeting: Direct marketing efforts towards individuals listing “veterinarian” as their job title on Facebook, or explore alumni networks of prominent veterinary schools.
- Social Media Strategy: Concentrate on building a presence on platforms like Instagram and TikTok, tailoring content to suit the target audience preferences.
- Channel Prioritization: Deprioritize LinkedIn, recognizing that it may not be the optimal channel despite its popularity for B2B sales.
- Expanding Opportunities: Identify expansion signals, such as new veterinary clinic locations, as opportunities to remain relevant to Chloe.
- Competitive Positioning: Develop comparison pages or sales collateral highlighting the brand’s superiority in terms of “quality for price” compared to competitors.
- Local Engagement: Explore a directory of veterinary clinics, engaging in activities like cold calling or dropping in with product samples.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, creating detailed buyer personas offers numerous advantages to businesses, ranging from precise ad targeting and enhanced communication clarity to strategic channel prioritization and alignment of content with audience preferences. These personas serve as valuable tools for informed decision-making across various teams within a business, providing accessible insights that contribute to a more customer-centric approach. It’s crucial to recognize the dynamic nature of buyer personas, emphasizing continuous refinement based on evolving insights and feedback gathered over time.
FAQs on Buyer Personas:
Are buyer personas only relevant for marketing purposes?
No, buyer personas are valuable across various business functions. They inform marketing strategies, assist in product development, and contribute to customer support by anticipating barriers to purchase.
Why is continuous refinement of buyer personas important?
Buyer personas should evolve over time based on new insights and feedback. Continuous refinement ensures that personas remain accurate and relevant, reflecting the changing needs and behaviors of the target audience.
Can negative personas be beneficial?
Yes, negative personas, representing customer types that are not a good fit for the business, can be beneficial. They help businesses avoid wasting resources on customers with a low probability of buying or those who may negatively impact profitability.




