The landscape of open-source cybersecurity tools is vast and distinguished by its diversity. Given the plethora of options available, navigating through these tools can be challenging when deciding where to allocate your time and efforts for learning. The expansive array of open-source cybersecurity solutions offers various features and functionalities, making it crucial to identify the tools that align with your specific needs and objectives. In this evolving field, staying informed about the key players and understanding their strengths can empower cybersecurity enthusiasts and professionals to make informed choices, ensuring that their investment in learning and utilizing these tools is strategic and effective.

Open-source software provides users access to its source code, allowing them to view, modify, and enhance it collaboratively. This approach fosters a highly collaborative and peer-reviewed environment, promoting flexibility and innovation within the software development community. While many open-source programs are free, it’s important to note that not all of them follow this model.
The acronym FOSS stands for Free and Open Source Software, denoting programs that exhibit the characteristics of open-source software and are also free of charge. This distinction emphasizes accessibility and affordability for users
How Transparent, Effective Open-Source Tools Help Boost Cybersecurity

- Community Collaboration: Open source tools benefit from a collaborative community of developers and security experts who continuously contribute to their improvement. This collective effort enhances the tools’ effectiveness against emerging threats.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Many open source cybersecurity tools are available free of charge, making them cost-effective solutions for organizations with budget constraints.
- Transparency and Visibility: The transparent nature of open source tools allows users to inspect the source code, providing visibility into the tool’s functionalities and ensuring there are no hidden vulnerabilities or malicious components.
- Customization and Flexibility: Users have the freedom to customize open source tools to fit their specific security needs, ensuring a tailored and flexible approach to cybersecurity.
- Educational Opportunities: Open source tools offer valuable learning opportunities for cybersecurity professionals. Users can gain hands-on experience, contributing to their skill development and knowledge in the field.
Learn about other SaaS security tools here.
Top Open- Source Cybersecurity Tools for Every Threat
A. Penetration Testing Tools:
Penetration testing tools are critical for identifying vulnerabilities within systems by simulating real-world cyberattacks. These open-source tools allow cybersecurity professionals to proactively assess and enhance the security of networks and applications.
1. ZED Attack Proxy (ZAP)

ZED Attack Proxy (ZAP) is an open-source, all-in-one web application security testing tool. Developed and maintained by a team of dedicated volunteers, ZAP serves as both a scanner and a proxy server. Released in 2010, it has become a crucial tool for scanning web applications, identifying vulnerabilities, and enhancing cybersecurity.
Features:
- Comprehensive Security Testing: ZAP offers a comprehensive set of features, including a passive scanner, web crawler, brute force attack capabilities, directory search, and more.
- Automated Scanning: The tool automatically scans web applications for vulnerabilities and cyber threats, providing a robust defense mechanism.
- Offensive Capabilities: ZAP goes beyond identification, allowing users to exploit discovered vulnerabilities through techniques like SQL injection or XSS.
- Proxy Server Functionality: ZAP acts as a proxy server, enabling users to modify HTTP requests for testing and analysis.
2. Metasploit
Metasploit is a powerful penetration testing tool known for its versatility and user-friendly interface. Used by both white hat and black hat hackers, Metasploit simplifies the process of testing and developing exploits against target machines, making it a fundamental tool for cybersecurity professionals.
Features:
- Exploit Development: Metasploit facilitates the testing and developing of exploits against target machines, identifying security vulnerabilities.
- Automation: The tool can automate the vulnerability scanning process, increasing efficiency.
- Payload Deployment: Even beginners can create and deploy payloads, enhancing the depth and impact of penetration tests.
- Post-Exploit Techniques: Metasploit offers post-exploit techniques to gather further information about a system or network after a successful attack.
- Evasion Techniques: Evasion techniques are included, allowing penetration testers to bypass Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS).
3. John the Ripper
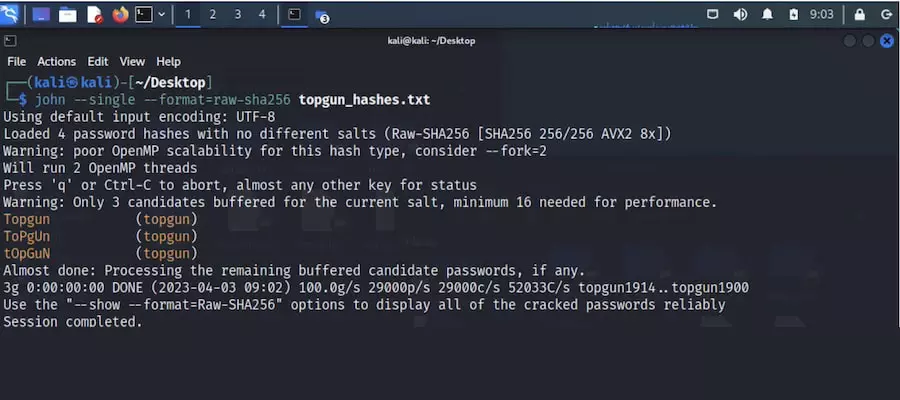
John the Ripper is a renowned open-source password-cracking tool designed to uncover weak passwords through various approaches, including dictionary attacks, brute force, and rainbow table attacks. This command-line tool is widely used for its flexibility and effectiveness.
Features:
- Versatile Password Cracking: John the Ripper employs various modes to crack passwords of varying complexities, including dictionary attacks and brute force.
- Optimized Versions: The tool supports optimized and customized versions created by the community, enhancing its capabilities.
- Multiple Hash Types: Recognizes multiple hash types, making it suitable for cracking a wide range of password hashes.
- Plugin Ecosystem: John the Ripper boasts a plugin ecosystem supported by a growing community, allowing for increased customization.
- User-Friendly: Even users with minimal pen testing experience can effectively utilize John the Ripper.
Discover the potential of pen testing tools here.
B. Network Defense Tools
Detecting and mitigating unwanted or abnormal activities within your network is crucial for maintaining its integrity. Utilize the following open-source tools to enhance network defense and troubleshoot potential issues.
1. Wireshark
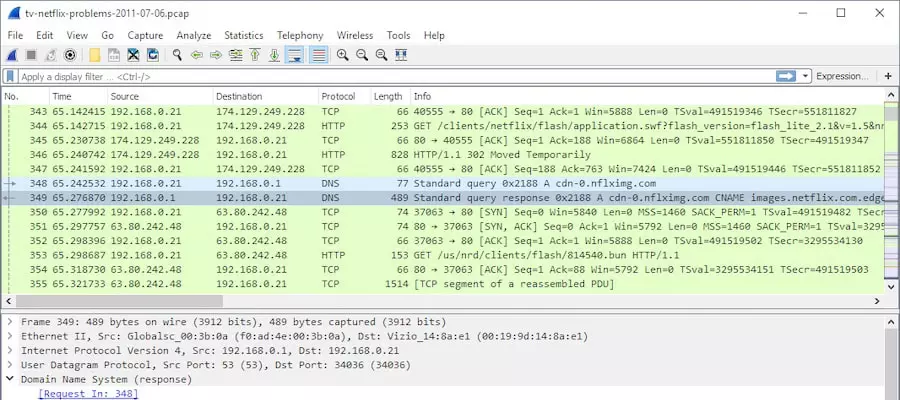
Wireshark is a leading network protocol analyzer extensively employed for network analysis, troubleshooting, forensics, and protocol development. This open-source tool is a fundamental asset for Security Operations Center (SOC) analysts aiming to effectively capture, filter, and visualize network traffic.
Features:
- Free and Open Source: Wireshark is available at no cost, making it accessible to a broad user base.
- User-Friendly Interface: It offers a powerful yet easy-to-use interface, simplifying the identification of complex network issues.
- Cross-Platform Compatibility: Compatible with various operating systems, including Linux, macOS, BSD, Solaris, and Windows.
- Customization: Wireshark supports plugins and scripts, allowing users to customize the tool to suit their needs.
- Widely Adopted: It is widely used by security teams for in-depth network traffic analysis.
2. Nmap
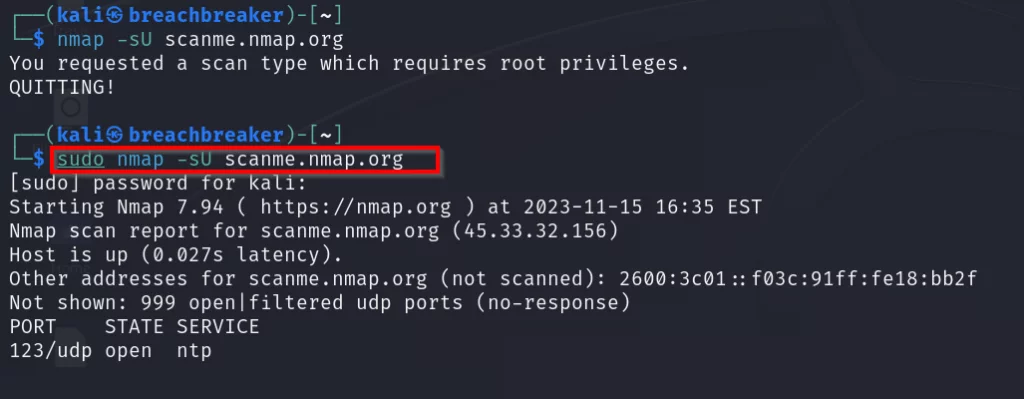
Nmap, short for Network Mapper, is an open-source command-line (CLI) tool designed to scan network IP addresses and ports. This tool is invaluable for identifying open ports, detecting running services, finding vulnerabilities, and mapping network structures.
Features:
- Beginner Friendly: Nmap provides valuable information with simple commands, making it accessible for users with varying levels of expertise.
- GUI Support: For users uncomfortable with the CLI, Nmap offers a Zenmap GUI, ensuring ease of use.
- Comprehensive Network Mapping: It can swiftly map entire networks, providing an overview of network architecture.
- Detailed Information: Nmap offers detailed insights into the operating systems and versions running on scanned devices.
- Scripting Engine: The Nmap Scripting Engine allows the use of scripts for penetration testing and advanced analysis.
3. Snort
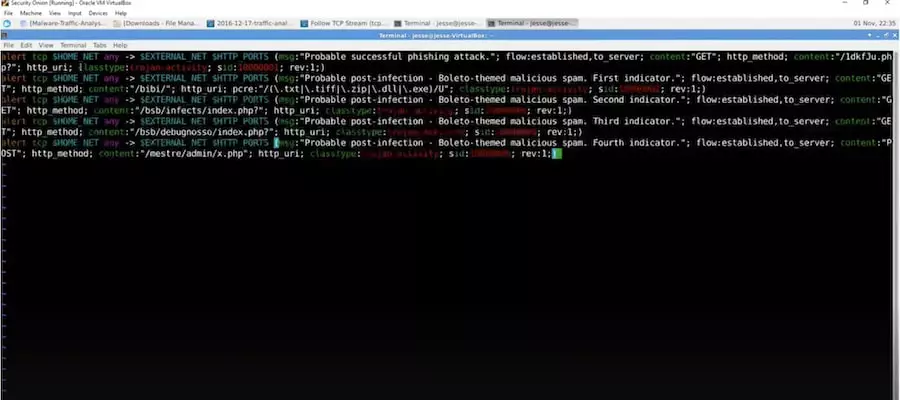
Snort serves as an Intrusion Detection System (IDS) and Intrusion Prevention System (IPS). Additionally, it functions as a packet sniffer and logger. By utilizing predefined and custom rules, Snort employs anomaly, protocol, and signature inspection methods to identify potentially malicious activities on your network.
Features:
- Custom Rule Creation: Users can create unique rules to identify potentially harmful traffic, enhancing precision.
- Flexibility: Snort’s rule language is flexible and easy to learn, allowing for efficient customization.
- Cross-Platform Availability: Available on all major operating systems, ensuring versatility.
- Upgrade Options: The free version allows the creation of complex rules, while a paid version offers even more precision.
- Versatile Capabilities: Snort can be employed for logging, packet sniffing, and functioning as an IDS or IPS.
C. Incident Response and Forensics Tools
Effective incident response and digital forensics are paramount in handling cybersecurity incidents. Below are some of our preferred open-source tools for incident response and forensics.
1. EnCase
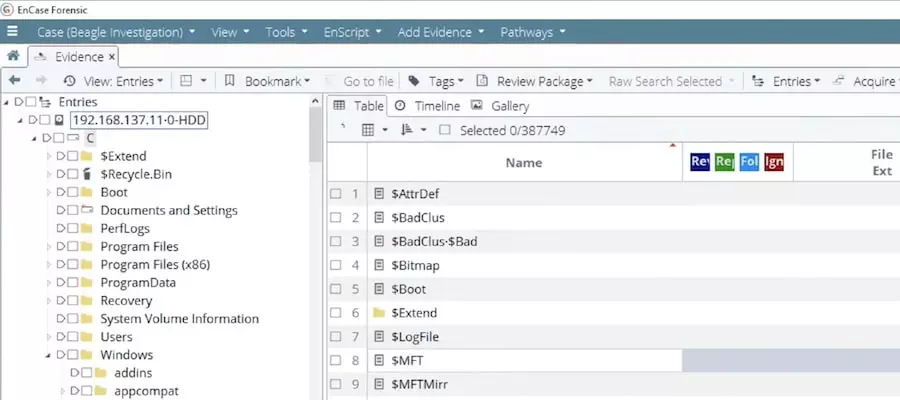
EnCase is a robust digital forensics case management software designed to guide users through the entire digital forensics process. With built-in pathways and workflow templates, EnCase ensures adherence to every step of the forensics procedure.
Features:
- Beginner-Friendly: Provides a written process with step-by-step guidance, making it accessible for beginners.
- GUI Interface: User-friendly graphical interface running on the Windows platform.
- Comprehensive Usage: Suitable for both data acquisition and analysis tasks.
- Bit-by-Bit Analysis: Reads bit-by-bit copies of hard drives, analyzing within slack space to retrieve deleted files.
- Timeline Creation: Automatically generates a comprehensive timeline of crucial events for easy analysis.
2. OSForensics

OSForensics is an extensive digital forensics tool empowering cybersecurity professionals to uncover valuable data for solving crimes or understanding cyber-attacks. It offers free, paid, and perpetual license versions for various user needs.
Features:
- Market Popularity: Arguably one of the most popular digital forensics tools available.
- RAM Data Recovery: Enables forensics teams to recover data from the computer’s RAM.
- Comprehensive Recovery: Recovers passwords, emails, and files users attempted to delete.
- Detailed Analysis: Creates a detailed picture of computer activities, including website visits, USB drive interactions, recent downloads, and login information.
- Report Generation: Easily generates reports and system images for later analysis.
- Additional Tools: Offers powerful and free companion tools such as OSFMount, OSFClone, Volatility Workbench, and ImageUSB.
3. MISP (Malware Information Sharing Platform & Threat Sharing)
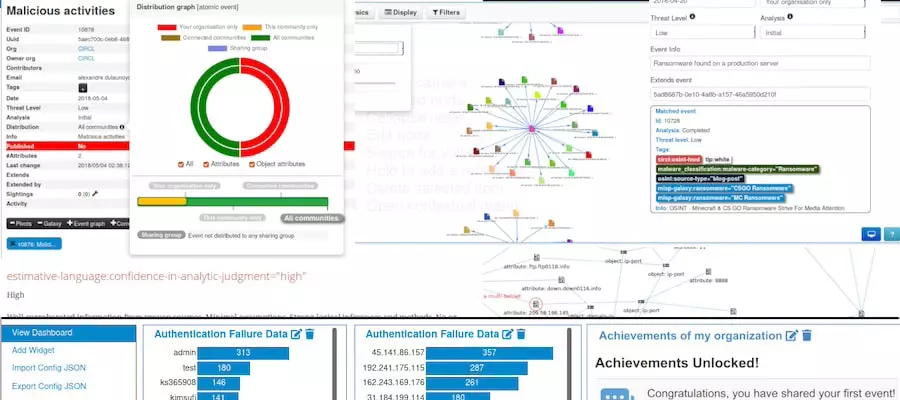
MISP serves as a crucial tool for collecting and sharing indicators of compromise, aiding in quick threat identification and incident response. It plays a vital role in creating and implementing an effective threat intelligence strategy.
Features:
- Threat Intelligence Sharing: Allows organizations to share threat intelligence information using a standardized format.
- User-Friendly Interface: Intuitive end-user interface for ease of use.
- Taxonomy Adjustability: Utilizes an adjustable taxonomy to classify and tag events effectively.
- STIX Support: Supports STIX (Structured Threat Information eXpression) for standardized data formatting and secure data exchange.
- Real-Time Alerts: Provide real-time alerts about the latest threats and vulnerabilities.
D. Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) Systems
Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems play a pivotal role in logging events and comprehending network activities. Below, we delve into some prominent open-source SIEM tools and their distinctive features.
1. AlienVault OSSIM
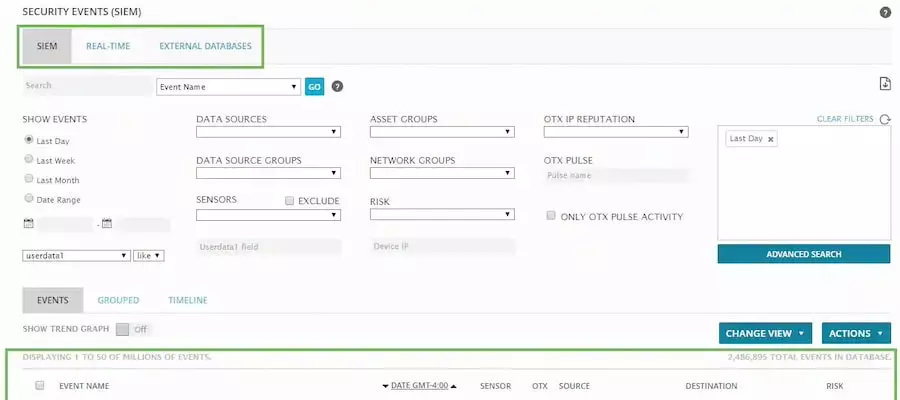
AlienVault OSSIM, acquired by AT&T in 2019, is a robust open-source SIEM solution with various features. Initially developed to address the scarcity of high-quality open-source SIEMs, it seamlessly interacts with other AT&T products to provide real-time insights into malicious activities.
Key Features:
- Integration Flexibility: Easily integrates with various open-source tools, enhancing its adaptability.
- Automated Asset Discovery: Identifies devices on the network through automated asset discovery.
- Anomaly-Based Events: Creates events based on anomalous behavior, aiding in early threat detection.
- Vulnerability Assessment: Functions as a vulnerability assessment tool by scanning the network and generating reports.
- Intrusion Detection: Configurable to work as an Intrusion Detection System (IDS) or Host-based Intrusion Detection System (HIDS).
2. ELK Stack
ELK Stack amalgamates Elasticsearch, Logstash, and Kibana, forming a dynamic and potent open-source SIEM. Elasticsearch serves as the search engine, Logstash is a server-side data processor, and Kibana offers a graphical interface for interaction and visualization.
Key Features:
- Automatic Scaling: Scales effortlessly to accommodate growing usage demands.
- Snapshot Capabilities: Allows easy snapshots of entire clusters or individual nodes for efficient backup.
- CLI Customization: Provides various Command Line Interface (CLI) tools for customization and configuration.
- Built-in Integrations: Facilitates built-in integrations for sending alerts to diverse third-party systems.
- Full and Multi-stack Monitoring: Enables comprehensive monitoring across various stacks.
3. SIEMonster

SIEMonster emerges as a highly customizable open-source SIEM equipped with features like machine learning, virtualization, and human-based behavior correlation. Its adaptability allows seamless integration of third-party tools to address diverse cybersecurity requirements.
Key Features:
- Scalability: Designed for massive projects, offering an impressive ingestion rate of 2 million events per second.
- Built-in Apache NiFi: Includes Apache NiFi for easy scaling and performance maintenance.
- Unified Dashboard: Presents an easy-to-use unified dashboard, enhancing event comprehension.
- Machine Learning Integration: Incorporates machine learning for efficient identification of cyber threats.
- Enterprise Usage: Trusted by significant companies like UMass, RMIT, and BlueScope for enterprise security monitoring.
Learn about security scanner tools here.
E. Identity and Access Management (IAM) Tools
Open-source Identity and Access Management (IAM) tools are critical in authenticating and authorizing user access to company devices. Here, we explore three noteworthy IAM tools and their distinctive features.
1. FreeIPA

FreeIPA is a comprehensive identity and authentication software for the Linux/UNIX environment. It provides centralized authentication, authorization, and account information solutions, contributing to robust IAM capabilities.
Key Features:
- Reputable Foundation: Built on top of well-established open-source products, ensuring reliability.
- Single Sign-On (SSO): Incorporates SSO functionality through the MIT Kerberos feature.
- Graphical and Command Line Interfaces: Offers both a user-friendly GUI and a powerful Command Line Interface (CLI).
- Concentrated Capabilities: Focuses on centralized authentication, authorization, and account information management.
2. OpenIAM:
OpenIAM is a versatile identity and access management platform that equips cybersecurity analysts with a spectrum of capabilities. It facilitates a unified understanding of user access, incorporating features like Role-Based Access Control (RBAC), Single Sign-On (SSO), and robust authentication methods.
Key Features:
- Flexible RBAC Permissions: Offers flexible permissions through Role-Based Access Control.
- Single Sign-On (SSO): Simplifies user access through SSO functionality.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Enhances security with user authentication through MFA.
- User Self-Service Portal: Empowers users with a self-service portal for profile and password management.
- Workflow Engine: Automates identity management-related business processes through a sophisticated workflow engine.
3. Keycloak
Keycloak has gained popularity as an IAM tool due to its seamless integration capabilities within various IT ecosystems. It offers extensive features, including Single Sign-On authentication, social login, user management, and versatile authorization options.
Key Features:
- Single Sign-On (SSO) Authentication: Streamlines user authentication through SSO capabilities.
- Social Network Integration: Allows users to sign in using their social network accounts.
- User Federation: Connects seamlessly to LDAP and Active Directory servers for user federation.
- User-Friendly Consoles: Features easy-to-use admin and account management consoles.
- Role-Based and Customized Authorization: Offers role-based authentication and customizable forms of authorization.
F. Encryption and Cryptography Tools
Encryption tools are essential for securing data at rest and in transit. Open-source encryption and cryptography tools are integral to maintaining data privacy and integrity.
1. GnuPG (GPG)

GnuPG, or GPG, is an open-source software solution that empowers users to encrypt data, create digital signatures, and manage certificates. Renowned for its flexibility in crucial management, GnuPG also integrates access modules for diverse public key directories.
Key Features:
- Secure File and Communication: Ensures the security of files and communication through robust encryption and decryption capabilities.
- Digital Signatures: Verifies and authenticates data integrity by implementing digital signatures.
- Cryptographic Key Management: Can create and manage cryptographic keys for various purposes.
- Email Client Integration: Widely utilized among email clients for secure communication.
- PGP Compatibility: Maintains compatibility with Pretty Good Privacy (PGP) software.
2. OpenSSL
OpenSSL, a command-line tool, offers an open-source solution for generating private keys, creating Certificate Signing Requests (CSRs), installing SSL/TLS certificates, and retrieving certificate information. Widely recognized for its simplicity and powerful capabilities, OpenSSL is extensively used and battle-tested.
Key Features:
- User-Friendly Command Line Interface (CLI): Features an easy-to-use command-line interface for enhanced accessibility.
- Key Algorithm Variety: This feature allows users to choose from a range of key algorithms and sizes to suit specific security needs.
- Versatility: A seemingly simple program with powerful and versatile functionalities.
- Widespread Adoption: Widely used across various platforms and is preinstalled in MacOS and certain Linux distributions.
- Proven Reliability: Gains credibility through extensive usage and testing in real-world scenarios.
G. Endpoint Protection Tools
Safeguard individual systems effectively with these feature-rich free endpoint protection tools.
1. ClamAV

ClamAV is a free antivirus engine designed to detect trojans, viruses, malware, and other threats. ClamAV operates seamlessly across platforms and relies on signatures to identify and thwart malware.
Key Features:
- Command-Line Interface (CLI): Allows for file system scans and email filtering through a user-friendly CLI.
- Gateway and Server Integration: Internet gateways and mail servers are widely utilized for enhanced protection.
- Real-Time Defense on Linux: Offers real-time protection tailored to Linux operating systems.
- Cross-Platform Compatibility: Extends support to Windows, Linux, and macOS, ensuring broad usability.
- Frequent Signature Updates: Keeps the signature database current with multiple daily updates, addressing newly discovered threats.
- Integration with Version Control: Collaborates with version control systems like Git, facilitating change management and analysis sharing.
2. OSSEC
OSSEC, an open-source endpoint protection tool, provides a customizable solution catering to diverse security needs. Offering extensive configuration options, OSSEC enables the creation of custom alert rules and the development of scripts to address security alerts effectively.
Key Features:
- Cross-Platform Support: Works seamlessly across macOS, Windows, Linux, and Solaris environments.
- Regulatory Compliance: Assists organizations in adhering to NIST and PCI DSS regulations.
- Atomic OSSEC Upgrade: Users can opt for Atomic OSSEC, unlocking access to thousands of additional rules and enhanced features.
- Scalability: Easily scalable, making it an ideal choice for businesses experiencing growth.
- Comprehensive Features: Encompasses log analysis, file integrity monitoring, and rootkit detection for a holistic security approach.
3. Wazuh

Wazuh combines Extended Detection and Response (XDR) capabilities with Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) functionality, creating a robust endpoint security program. Proactively collecting data, Wazuh responds to malicious activities like an Intrusion Prevention System (IPS).
Key Features:
- Real-Time Data Collection: Collects and responds to data in real-time for swift threat mitigation.
- CVE Updates: Regularly updates its database with the latest Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures (CVEs) to identify contemporary attack signatures.
- Configuration Monitoring: Monitors system and application configurations to ensure compliance with security policies and standards.
- Out-of-the-Box IPS Protection: Comes equipped with pre-configured Intrusion Prevention System (IPS) protection.
- Cloud-Optimized: Optimized to safeguard cloud environments effectively.
- Docker Security Hardening: Offers features for enhancing Docker container security.
Open-Source Cybersecurity is Key to Defending Your Digital Assets
IIn conclusion, open-source cybersecurity tools provide an essential and robust suite of solutions for addressing a wide range of cybersecurity challenges. These tools, often free and highly transparent, enable users to bolster their network defenses, perform thorough penetration testing, manage identities, and swiftly respond to incidents. The open-source model fosters continuous development, ensuring that these tools stay agile and responsive to the ever-changing nature of cyber threats. By utilizing open-source cybersecurity tools, you not only enhance the security of your digital environment but also contribute to a global network of knowledge-sharing and innovation within the cybersecurity community.
Ready to elevate your cybersecurity? Start your free trial with Nestify today and protect your digital world with powerful, easy-to-use tools – no strings attached.
FAQs on Open-Source Security Tools:
Can open-source tools be customized for specific security needs?
Yes, one of the significant advantages of open-source tools is their flexibility. Developers can customize and extend these tools to meet specific security requirements within an organization.
How do open source SIEM tools enhance security information management?
Open-source Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) tools collect, analyze, and correlate log data from various sources, providing a comprehensive view of an organization’s security landscape. This aids in early threat detection and response.
What role do encryption and cryptography tools play in cybersecurity?
Encryption and cryptography tools ensure data confidentiality and integrity. They secure sensitive information by converting it into unreadable formats, protecting it from unauthorized access.



