Behavioral segmentation is a facet of market segmentation that classifies consumers based on their behaviors, actions, and patterns. Unlike traditional demographic or geographic segmentation, behavioral segmentation delves into the “why” behind consumer choices. This type of segmentation relies on data analytics to uncover insights into how consumers act, what influences their purchasing decisions, and why they opt for specific products or services.

The Six Types of Behavioral Segmentation
1. Purchasing Behavior Segmentation:
Definition: Identifying patterns such as impulse buyers, value-driven buyers, or brand loyalists.
Factors Considered:
- Decision-making process
- Frequency of purchases
- Type of products bought
Example: Crafting targeted campaigns for impulse buyers with limited-time offers, value-driven buyers with discounts on high-quality products, and brand loyalists with exclusive membership perks.
2. Usage-Based Segmentation:
Definition: Categorizing users based on product usage rates – heavy, medium, and light users.
Strategies:
- Targeting heavy users with bulk offers or loyalty programs.
- Focusing on increasing usage for light users through trials or discounts.
Example: Offer exclusive benefits or discounts for heavy users and encourage light users to explore more features through trial periods.
3. Occasion and Timing-Based Segmentation:
Definition: Identifying specific times or occasions when customers are more likely to purchase or use a product.
Approach:
- Offering special holiday promotions.
- Creating anniversary reminders for repeat purchases.
Example: Implementing marketing campaigns with targeted promotions during holidays or creating reminders for special occasions related to the product.
4. Benefit Segmentation:
Definition: Understanding varied expectations and desired benefits from the same product.
Factors Considered:
- Convenience
- Status
- Quality
- Cost-effectiveness
Example: Craft messaging that highlights different benefits, such as convenience, status, quality, or cost-effectiveness, to appeal to diverse customer expectations.
5. Customer Loyalty Segmentation:
Definition: Grouping customers based on their level of loyalty, from passionate advocates to infrequent buyers.
Approach:
- Creating exclusive rewards for loyal customers.
- Implementing re-engagement strategies for infrequent buyers.
Example: Establishing loyalty programs with tiered rewards for frequent customers and launching re-engagement campaigns for customers with lower activity.
6. Engagement Level Segmentation:
Definition: Understanding how customers interact with a brand, whether through social media, surveys, or loyalty programs.
Approach:
- Tailoring social media strategies based on user engagement.
- Implementing targeted surveys or loyalty program incentives.
Example: Adapting content and engagement strategies on social media platforms based on user interactions and encouraging participation in surveys or loyalty programs.
Learn about customer demography here.
Benefits of Behavioral Segmentation:

- Upsell for Frequent Buyers: Identifying and targeting frequent buyers through their purchase behavior enables businesses to implement strategic upsell promotions. Businesses can boost sales by tailoring campaigns to this segment while minimizing marketing costs. Utilizing tools like the Email ROI Calculator allows for precise measurement of campaign success and return on investment.
- Re-Engagement for Inactive Customers: Leveraging loyalty data to identify inactive customers and implementing re-engagement campaigns is a powerful strategy for improving customer retention. By reigniting the interest of customers who may have disengaged, businesses can foster renewed loyalty and prevent customer attrition.
- Luxury Item Positioning for Premium Segments: Benefit segmentation helps businesses understand diverse customer expectations. Positioning luxury items for segments that prioritize premium quality ensures a more resonant marketing message. This targeted approach enhances the perceived value of products among specific customer groups.
- Complementary Product Suggestions: Analyzing customer usage patterns allows businesses to suggest complementary products to customers who regularly purchase specific items. This enhances the customer experience by providing relevant suggestions and opens up opportunities for effective cross-selling and upselling.
- Monitoring Customer Feedback and Interactions: Behavioral segmentation extends beyond purchase history to include customer interactions and feedback. Monitoring these aspects enables businesses to anticipate and respond promptly to negative trends or feedback. This proactive approach to crisis management helps maintain a positive brand image.
- Analyzing Past Purchase Behaviors for Trend Prediction: Utilizing predictive analytics based on past purchase behaviors allows businesses to anticipate upcoming trends. This insight is invaluable for proactive stock management and the implementation of targeted marketing campaigns. By staying ahead of trends, companies can meet customer demands more effectively.
Examples of Behavioral Segmentation:
1. Rothy’s Cross-Selling Excellence for Impulse Buyers
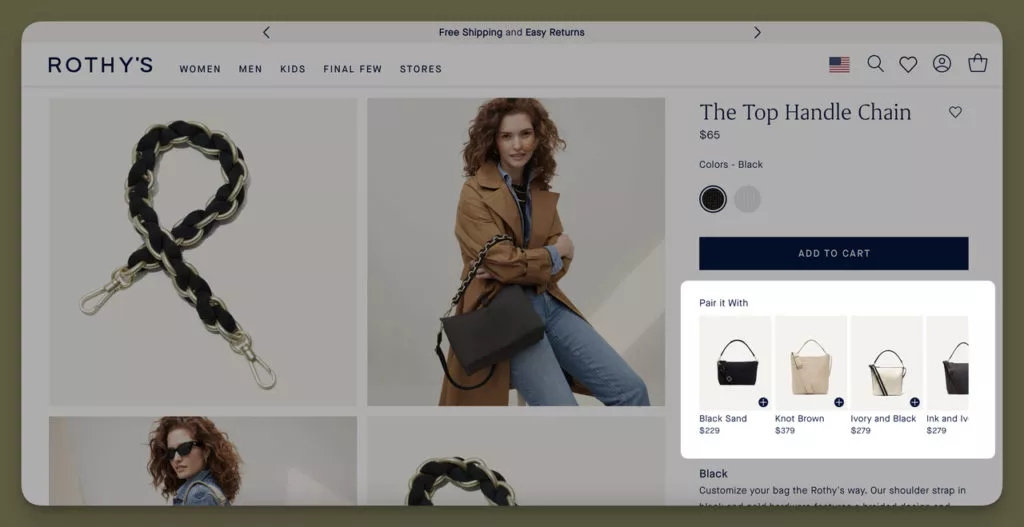
Rothy’s employs a sophisticated cross-selling strategy to capture impulse buyers’ attention. Through implementing a recommendation system on their website, Rothy’s suggests additional products to customers based on their purchase history, creating an enticing “Pair it With” section.
Key Features:
- Recommended Products: A smart recommendation system suggests related products based on customers’ past purchases.
- Cross-Selling Based on Purchase History: Rothy excels in cross-selling by strategically presenting complementary items that align with the customer’s purchase behavior.
Benefits and Strategies:
Rothy’s “Pair it With” section is a prime example of effective cross-selling through behavioral segmentation. The strategy not only increases the basket size by suggesting items that complement past purchases but also caters to buyers’ impulsive natures, who are more likely to indulge in additional items.
2. Starbucks Rewarding High-Value Customers

Starbucks leverages the power of exclusive rewards in its loyalty programs to cultivate high-value customer relationships and encourage frequent and repeat purchases.
Key Features:
- Reward Programs: Starbucks designs loyalty programs with exclusive rewards and benefits to incentivize regular purchases.
- Focus on High-Value Customers: The reward structure is tailored to recognize and appreciate customers with a high lifetime value.
Benefits and Strategies:
Starbucks strategically offers free coffee as a reward, aligning with consumer behavior that values perks and incentives. This approach enhances customer loyalty and promotes the perception of added value for their purchases.
3. Skillshare’s Re-Engagement Mastery
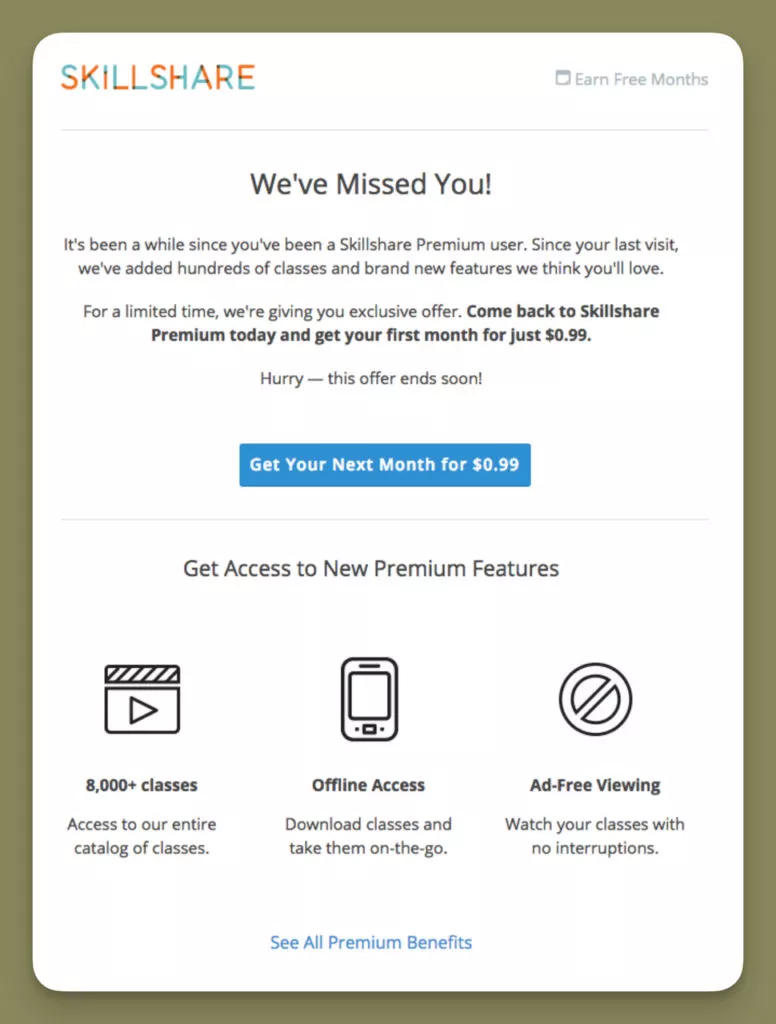
Skillshare employs re-engagement campaigns through personalized ‘We Miss You’ emails, coupled with special offers, targeting customers who have been inactive for a specific period.
Key Features:
- Re-Engagement Emails: Skillshare utilizes personalized ‘We Miss You’ emails to reconnect with inactive customers.
- Urgency and Special Offers: The campaign incorporates a sense of urgency with limited-time offers to prompt quick reactivation.
Benefits and Strategies:
Skillshare’s direct and personal “We Miss You!” approach in the email header is designed to resonate with users emotionally. The addition of a time-sensitive offer creates urgency, compelling inactive users to re-engage promptly.
4. Sephora‘s Savvy Strategy for Heavy Users
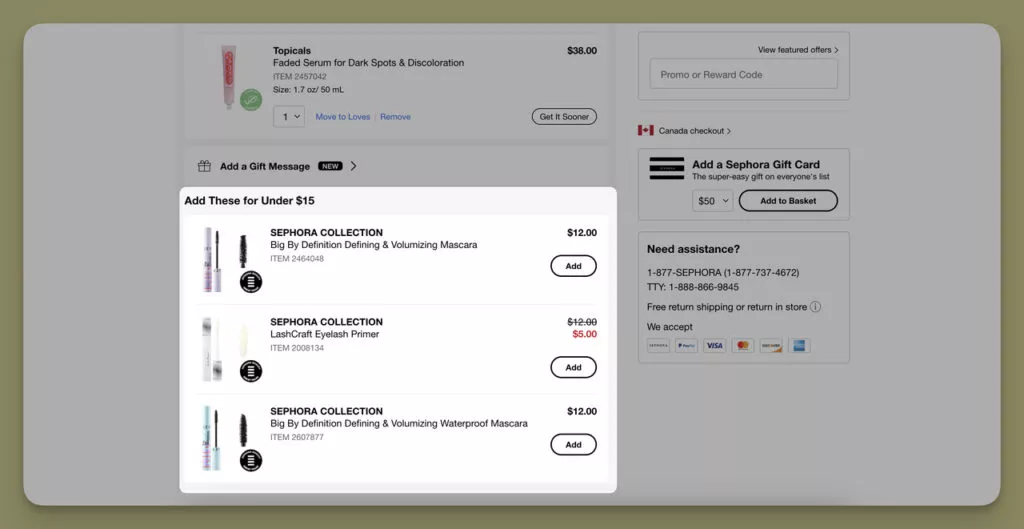
Sephora employs an effective upselling strategy by directly integrating a bulk purchase discount on the product page, explicitly targeting heavy users.
Key Features:
- Upsell Section: Sephora’s shopping cart page strategically includes an upsell section titled “Add These Under $15” for heavy users.
- Limited, Curated Options: The approach minimizes decision fatigue by presenting a limited number of curated options, increasing the likelihood of additional purchases.
Benefits and Strategies:
Sephora’s clever use of behavioral segmentation on the shopping cart page enhances the user experience for heavy users. The upsell section strategically taps into these users’ shopping behavior, seamlessly promoting additional purchases.
5. Terre Blue’s UGC Integration for Authenticity
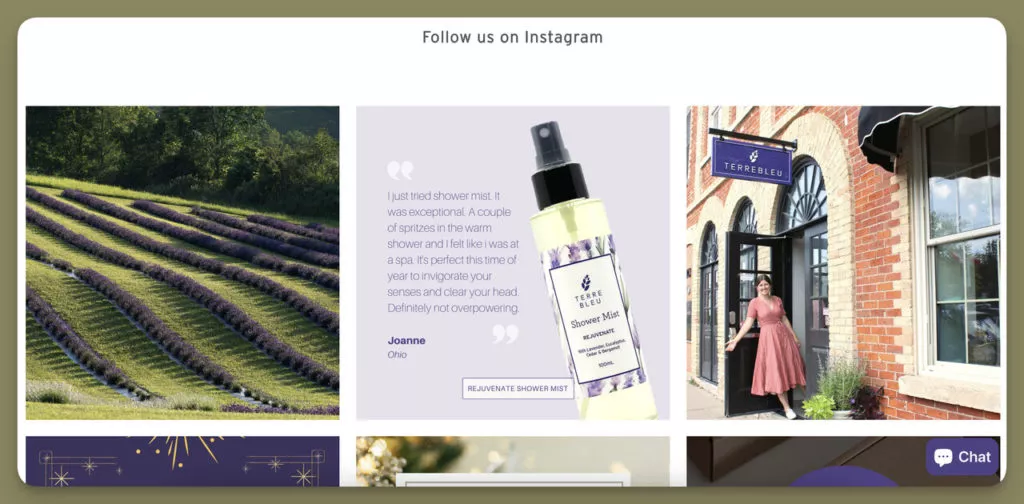
Terre Blue employs User-Generated Content (UGC) integration by encouraging buyers to share their product experiences on social media, creating an authentic connection with low-volume users.
Key Features:
- UGC Integration: Terre Blue encourages buyers to share their experiences on social media, creating a hashtag to aggregate user-generated content.
Benefits and Strategies:
Terre Blue’s use of positive customer testimonials on its homepage serves as compelling social proof, influencing potential customers’ purchasing behavior. This strategy fosters authenticity and trust.
6. Lifesum’s Motivational Progress Tracker
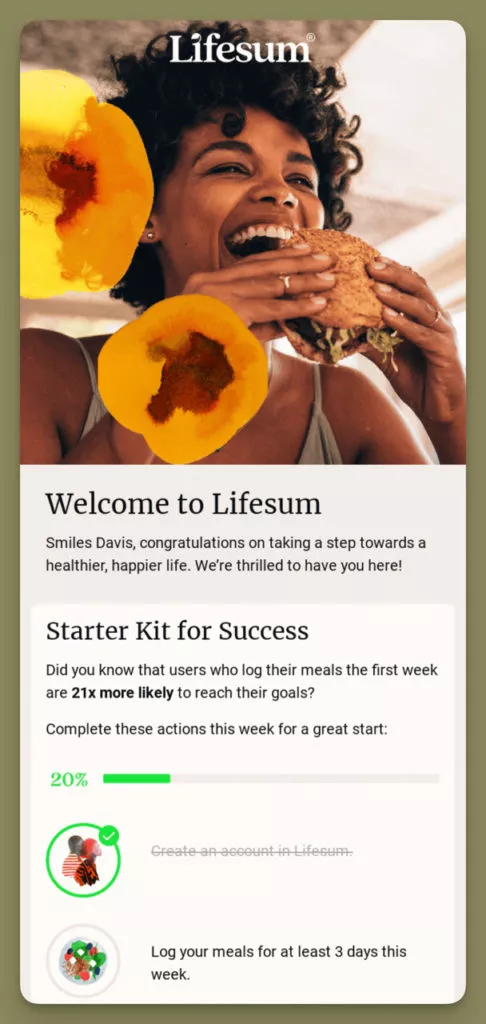
Lifesum incorporates a progress tracker in its emails, visually motivating new users to engage and complete actions, aligning with behavioral trends for goal achievement and satisfaction.
Key Features:
- Progress Tracker: Lifesum’s emails feature a progress tracker that visually motivates new users to complete engagement actions.
Benefits and Strategies:
The progress bar in Lifesum’s emails serves as a visual incentive, appealing to the user’s desire for achievement and goal completion. This strategy enhances user engagement and loyalty.
7. Native’s Customer Milestone Celebration

Native employs a customer milestone email strategy by congratulating users on their purchase and offering rewards to express appreciation for their loyalty.
Key Features:
- Customer Milestone Email: Native acknowledges and rewards users when they achieve a significant milestone, fostering customer loyalty.
Benefits and Strategies:
Recognizing and rewarding customer loyalty is a central element of Native’s strategy. By celebrating customer milestones, the brand enhances user satisfaction and retention.
8. Birkenstock’s Timely Seasonal Popup

Birkenstock implements a seasonal popup strategy by displaying popups or banners on its website during holidays or special events, offering exclusive seasonal products or discounts.
Key Features:
- Seasonal Popup: Birkenstock utilizes popups or banners during specific seasons, creating a sense of urgency for limited-time offers.
Benefits and Strategies:
Birkenstock’s seasonal popup taps into the fear of missing out (FOMO) by indicating that the offer is limited, encouraging quicker decision-making. This strategy leverages timing-based marketing to capture customers’ attention during key seasons.
9. Starbucks’ Routine-Based Engagement on Social Media

Starbucks adopts a routine-based engagement strategy by sending routine posts aligning with daily or weekly activities, such as morning coffee discounts or weekend fun announcements.
Key Features:
- Routine Post: Starbucks sends emails that align with daily routines, enticing followers with morning coffee discounts or weekend announcements.
Benefits and Strategies:
Encouraging followers to integrate Starbucks into their daily routines, such as morning coffee, is a powerful way to build customer habits. This routine-based engagement strengthens brand loyalty.
10. Mailchimp’s Direct Benefit Email

Mailchimp utilizes a direct benefit email strategy by sending emails that focus on specific features of its products and are tailored to the interests of different customer segments.
Key Features:
- Direct Benefit Email: Mailchimp’s email highlights the specific benefits of email marketing.
Benefits and Strategies:
The email directly states the benefits of email marketing, appealing to pragmatic customers seeking clear and tangible advantages. This strategy aligns with benefit-based segmentation.
Steps in Behavioral Customer Segmentation:
Step 1: Data Collection
Start collecting data through website analytics, CRM systems, social media interactions, and customer feedback.
In the initial phase of your behavioral segmentation strategy, gather comprehensive data utilizing various sources. Employ website analytics tools, tap into CRM systems, monitor social media interactions, and actively seek customer feedback. Responsible use of cookies and tracking pixels will provide valuable insights into user behavior, forming the foundation for informed decision-making.
Step 2: Analysis and Insights
Analyze the data to identify patterns and insights.
Dive into the collected data to unveil patterns and derive meaningful insights. Focus on common behaviors such as purchase frequency, average spending, content engagement, and product preferences. This analytical step lays the groundwork for understanding customer behavior and sets the stage for effective segmentation.
Step 3: Segment Creation
Create segments based on frequently observed behaviors.
Create distinct segments that reflect commonly observed behaviors based on the insights gained. Typical features may include new users, repeat customers, cart abandoners, and members of loyalty programs. This segmentation ensures a more targeted and personalized approach to your marketing efforts.
Step 4: Creating Hypothesis and Strategy
Create predictions about each group’s values and create focused ways to address them.
Develop hypotheses about the values and motivations of each segmented group. For example, hypothesize that cart abandoners may be price-sensitive and could be swayed by discounts. Craft-focused strategies are tailored to address each segment’s unique needs and preferences, ensuring a more relevant and impactful marketing approach.
Step 5: Implement Campaigns
Target website visitors and their behaviors, monitor real-time performance and adjust as needed.
Execute targeted campaigns directed at specific segments, aligning with the formulated strategies. Monitor campaign performance in real-time, utilizing analytics tools to assess effectiveness. Be prepared to make timely adjustments, ensuring campaigns stay aligned with evolving customer behavior and market dynamics.
Step 6: Testing and Optimization
Conduct A/B testing for different segments to determine the most effective strategies. Use the results to refine your approach continually.
Engage in A/B testing to compare the effectiveness of different strategies within each segment. Analyze the results to identify the most impactful approaches. Continuously refine your strategies based on evolving insights, ensuring ongoing optimization and adaptability to changing consumer behavior.
Step 7: Feedback Loops
Establish feedback loops through surveys, customer service interactions, and social listening.
Initiate feedback loops to maintain a dynamic understanding of customer sentiment. Employ surveys, encourage customer service interactions, and leverage social listening to gather valuable feedback. Integrating survey popups within campaigns provides a direct channel for customers to share insights, fostering a responsive and customer-centric approach.
Implementing these steps cohesively ensures a robust behavioral segmentation strategy, enhances the effectiveness of your marketing initiatives, and fosters stronger connections with your target audience.
Conclusion:
As reiterated throughout our discussion, the twin pillars of personalization and a profound understanding of customer habits are indispensable elements for successfully implementing marketing strategies.
FAQs on Customer Behavioral Segmentation:
What is an Example of Behavioral Segmentation in the Food Industry?
In the food industry, behavioral segmentation involves categorizing consumers based on their behavior, preferences, and habits related to food choices.
For instance, fast-food chains strategically employ behavioral segmentation by offering lunch promotions during peak hours to cater to the needs of working professionals. Simultaneously, integrating mobile ordering apps caters to tech-savvy consumers seeking convenience.
Moreover, coffee shops like Starbucks leverage their customers’ routines with initiatives such as “happy hour” discounts, aligning marketing efforts with specific consumer habits to enhance effectiveness and customer satisfaction.
What Tools or Platforms are Used for Behavioral Segmentation?
Many tools facilitate behavioral segmentation, spanning CRM platforms such as Salesforce and HubSpot to analytics tools like Google Analytics and Adobe Analytics. Dedicated media like Popupsmart and Segmentify are crucial in executing personalized marketing campaigns.
Difference Between Behavioral Segmentation and Psychographic Segmentation?
Behavioral segmentation centers on understanding how consumers interact with products or services, encompassing their purchasing habits, brand allegiance, and responses to marketing efforts.
In contrast, psychographic segmentation delves into psychological traits, exploring values, attitudes, interests, and lifestyles. This approach seeks to unravel the motivations and deeper reasons influencing consumers’ purchasing decisions, offering a more holistic understanding of their preferences and behaviors.



