Are you wondering about your experience with invalid traffic (IVT)? Unchecked, fake traffic can lead to severe consequences for publishers, including losing ad accounts and other significant business issues.
Did you know that over 40% of all online traffic is deemed invalid? This includes activities generated by bots, click farms, and other fraudulent methods designed to inflate website traffic artificially. Click farms and media buyers often employ such tactics to boost ad clicks artificially or manipulate website analytics. Unfortunately, this trend is growing, posing a substantial challenge to the AdTech industry.
According to recent industry reports:
The projected global waste in digital ad spend due to fake traffic is set to hit $50 billion by 2024. Advanced IVT threats like sophisticated bots, click hijacking, and data center traffic are becoming more prevalent, contributing significantly to the overall IVT problem.
The Impact of Fake Traffic:
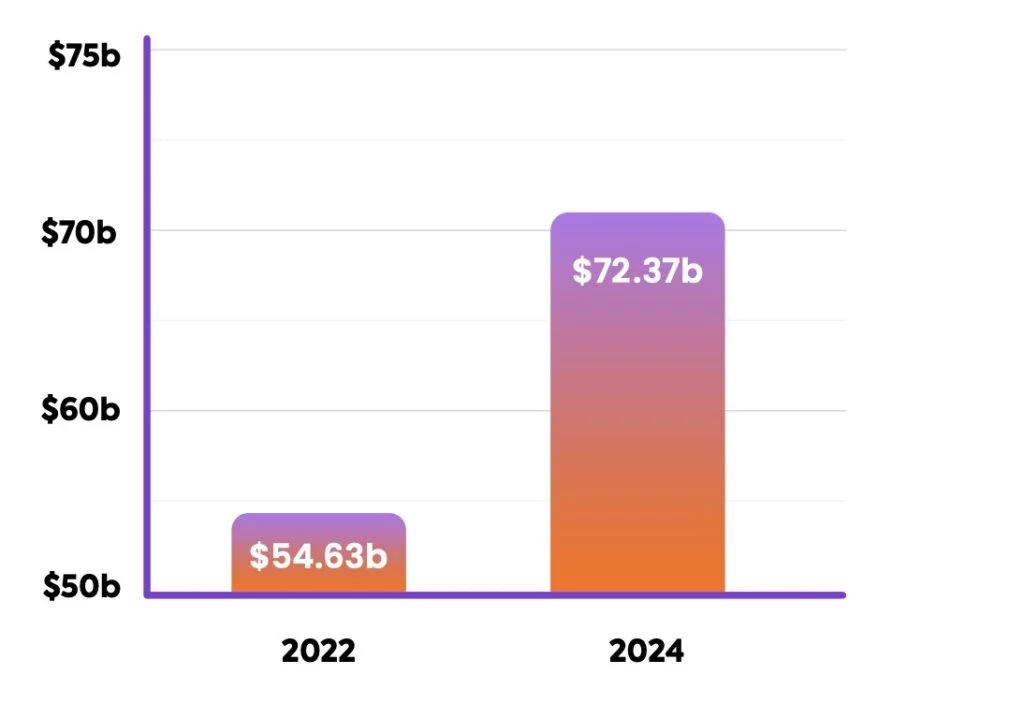
Source: Business of Apps
The impact of invalid traffic (IVT) on digital advertising costs has worsened in 2024. Advertisers will waste over $71 billion on fake or invalid traffic, a 33% increase from the $36 billion wasted in 2022.
This staggering $71 billion in wasted ad spend presents a significant challenge for the digital marketing industry, highlighting the urgent need for effective measures to combat the growing threat of invalid traffic.
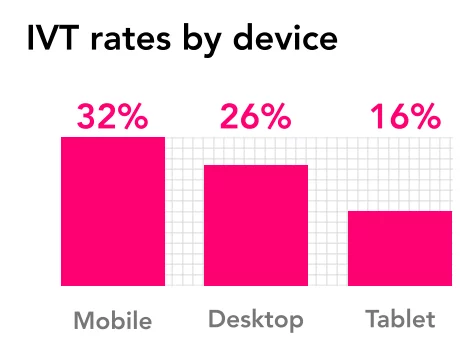
The issue of fake traffic spans various digital advertising channels, with platforms such as LinkedIn, Meta, Bing, X (formerly Twitter), and Pinterest showing exceptionally high rates of invalid traffic.
Even Google’s platforms, which have a lower fake traffic rate of 5.5%, still contribute significantly to wasted ad spend, totaling $16.6 billion.
The combined wasted ad spend on fake traffic across Google and non-Google platforms is projected to reach a massive $71 billion in 2024, underscoring the critical need for the digital marketing industry to address this issue.
Bot Traffic and Website Performance (2024 Edition)
Impact Beyond Advertising Costs:
Invalid traffic advertising costs and distant website traffic statistics, making it challenging for website owners and marketers to gauge user engagement and traffic sources accurately. Approximately 8% of all site traffic is estimated to be invalid, with paid ads contributing 4.9%, direct traffic 7.5%, and organic traffic 5.7%. These statistics emphasize the importance of combating invalid traffic to ensure accurate analytics reflecting real user engagement.
Invalid traffic (IVT) poses significant risks to publishers, impacting their data accuracy, analytics measurements, and revenue streams from advertising. Understanding how IVT operates and its effects is crucial for publishers aiming to maintain their reputation and income stability.
A. Impact on Publishers:
IVT can severely undermine a publisher’s efforts in several ways:
- Data Manipulation: IVT distorts analytics metrics by generating false impressions of visitor engagement and behavior, leading to inaccurate data-driven decisions.
- Monetization Damage: Advertisers rely on accurate traffic metrics to assess the value of ad placements. IVT inflates metrics artificially, which can lead to reduced advertiser confidence and lower bids. In severe cases, advertisers may blacklist sites showing patterns of high IVT.
- Account Suspension: Platforms like Google AdSense and Ad Exchange (AdX) enforce strict policies against invalid activity. Publishers found guilty of IVT face suspensions or even permanent bans, jeopardizing their revenue streams.
B. Detection Signs for IVT:
Identifying IVT early is critical to mitigating its impact. Common indicators include:
- High Bounce Rate: Visitors quickly leaving the site after landing, indicating potential non-human traffic.
- Low Dwell Time: Visitors spending minimal time on pages, suggesting lack of genuine interest.
- Multiple Clicks from Same IP: Unusual activity from a single IP address, indicating potential bot behavior.
- Unexpected Traffic Peaks: Sudden spikes in traffic volume without corresponding increases in conversions or engagement.
- Recurring Traffic Patterns: Regular, predictable traffic peaks, which may indicate automated traffic.
C. Countermeasures and Prevention:
Publishers can employ several strategies to combat IVT and protect their operations:
- Traffic Monitoring: Implement robust analytics tools that detect and filter out invalid traffic patterns.
- Ad Quality Providers: Utilize services from advertising quality providers that offer advanced IVT detection and mitigation solutions.
- Adherence to Policies: Strictly adhere to advertising platform policies to avoid penalties and account suspensions.
- User Experience Optimization: Focus on enhancing user experience to encourage genuine user interaction and reduce bounce rates.
Types of Fake Traffic:
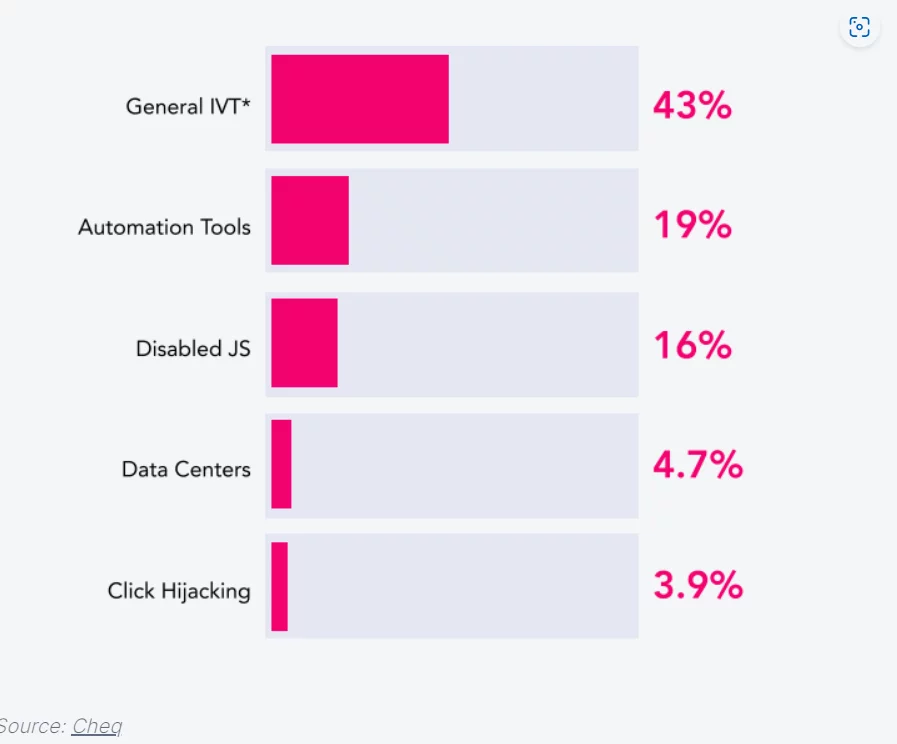
Combatting Invalid Traffic
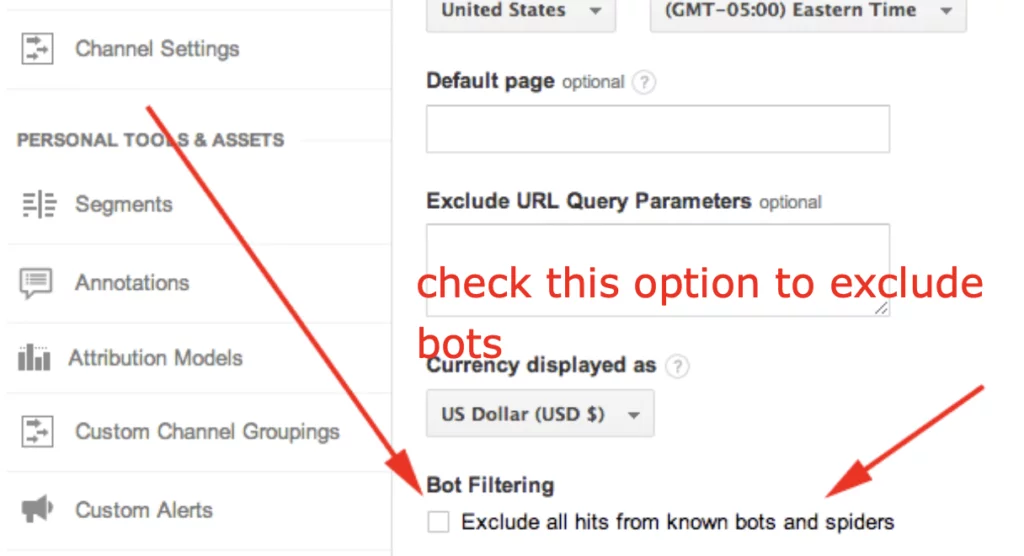
Combatting invalid traffic requires proactive measures and advanced solutions:
- Real-time monitoring and detection.
- Advanced algorithms and machine learning.
- Traffic segmentation and analytics.
- Ad optimization and revenue protection.
Key Features of Invalid Traffic (IVT):
- Definition and Types:
- Definition: Invalid traffic is an artificial or fraudulent activity that generates fake interactions on digital platforms like websites or mobile apps.
- Types: Includes bot-generated traffic, click farms, click hijacking, and other automated or malicious activities to inflate engagement metrics.
- Impact on Advertising Costs:
- Financial Loss: In 2024, advertisers are projected to waste over $71 billion globally on IVT, a 33% increase from 2022. This wastage undermines ROI and affects budget allocation.
- Platform-Specific Issues: Platforms like Google, LinkedIn, Meta, Bing, and others report varying degrees of IVT, contributing to substantial financial losses despite efforts to mitigate fraud.
- Distortion of Website Traffic Metrics:
- Accuracy of Analytics: IVT skews traffic statistics, making it difficult to measure user engagement and traffic sources accurately.
- Percentage Breakdown: Approximately 8% of all website traffic is invalid, with paid ads contributing 4.9%, direct traffic 7.5%, and organic traffic 5.7%. This discrepancy underscores the need for accurate data to inform marketing strategies effectively.
- Prevalent Threats and Trends:
- Sophisticated IVT: Advanced threats include botnets, click hijacking, and traffic originating from data centers, which are increasingly difficult to detect and mitigate.
- Growth Trends: IVT continues to evolve, with increasing sophistication in fraudulent techniques, posing ongoing challenges to the digital advertising ecosystem.
- Industry-Specific Challenges:
- Sectoral Impact: Industries such as insurance, retail, real estate, financial services, and leisure/travel face higher IVT rates due to specific vulnerabilities and targeted fraud tactics.
- Geographical Variances: IVT rates vary by country and region, with the USA, Australia, and Nigeria showing different prevalence rates, influencing global traffic quality metrics.
Breakdown of Invalid Traffic Types:
Automation Tools: These are software applications designed to automate tasks like filling out forms or clicking on links. In recent analyses, they accounted for 20.1% of all fraudulent traffic. Automation tools operate without human intervention, artificially inflating website traffic metrics and engagement statistics.
Click Hijacking: This deceptive technique involves redirecting a user’s click to a different website or advertisement without their knowledge or consent. Click hijacking increased significantly by 125% in 2022 and contributed to 16.6% of invalid traffic. It undermines user trust and can lead to misleading performance metrics for advertisers.
Disabled JavaScript (JS): Disabling JavaScript prevents websites from tracking user behavior and displaying ads, effectively bypassing ad-blocking mechanisms. In 2022, disabled JS accounted for 13.6% of all invalid traffic, impacting websites’ ability to measure user engagement and ad effectiveness accurately.
Virtual Private Networks (VPN): VPNs are tools that mask a user’s IP address and geographical location, making it appear that traffic originates from different locations. This anonymity makes it challenging to distinguish legitimate users from fraudulent ones. VPNs contributed 13.6% to the total fake traffic, complicating efforts to combat invalid traffic effectively.
Scrapers: Scrapers are automated bots that extract data from websites without permission. They accounted for 9.1% of all fake traffic, posing significant challenges to maintaining data integrity and intellectual property rights for website owners.
Data Centers: These facilities handle large volumes of data and often generate traffic that does not represent genuine user engagement. Data center traffic constituted 9.0% of all invalid traffic, reflecting the scale of automated activities that skew website analytics and advertising metrics.
Malicious Bots are sophisticated software programs designed to execute harmful activities such as stealing data, disrupting services, or committing fraud. They accounted for 8.1% of all invalid traffic, posing security risks and undermining the reliability of online services.
False Representation involves misleading advertising or marketing practices that misrepresent products or services. In 2022, false representation contributed 3.6% of all fake traffic, deceiving users and advertisers alike while inflating engagement metrics.
Proxy Servers: Proxies act as intermediaries between users and the internet, masking the user’s identity and location. They accounted for 1.8% of invalid traffic, complicating efforts to distinguish between genuine users and fraudulent activities.
Tool Tools for Invalid/Fake Traffic Detection:
1. Pingdom
Pingdom is well-regarded for its robust uptime monitoring capabilities and real-time alerts, making it a popular choice among website owners seeking reliable performance monitoring.
Features:
- Uptime Monitoring: Continuously monitors website uptime and downtime, ensuring immediate alerts when issues arise.
- Performance Reports: Provides detailed insights into website performance metrics, aiding in troubleshooting and optimization.
- User-Friendly Interface: Designed to be intuitive, catering to both beginners and experienced users alike.
Pros:
- Reliability: Known for accurate uptime monitoring and prompt alerts.
- Ease of Use: User-friendly interface simplifies navigation and setup.
- Comprehensive Reports: Detailed performance reports facilitate informed decision-making.
Cons:
- Cost: Higher pricing compared to some competitors.
- Feature Limitations: May lack some advanced features found in other platforms.
2. UptimeRobot
UptimeRobot offers a versatile monitoring solution with a free basic plan, appealing to smaller websites or those with budget constraints.
Features:
- Free Basic Plan: Monitors uptime with alerts via email, SMS, or push notifications.
- Customizable Alerts: Alerts can be tailored to specific thresholds or downtime durations.
- Paid Plans: Include additional features such as response time monitoring and more detailed reporting.
Pros:
- Cost-Effective: Free plan available with essential monitoring features.
- Alert Flexibility: Multiple notification options ensure timely issue awareness.
- Scalability: Paid plans offer expanded functionality for growing needs.
Cons:
- Feature Restrictions: Advanced features are limited to paid subscriptions.
- Support Accessibility: Support options may be limited compared to premium services.
3. StatusCake
StatusCake excels in comprehensive monitoring, specializing in website speed, server, and domain monitoring across various platforms.
Features:
- Versatile Monitoring: Covers multiple aspects including speed, server uptime, and domain health.
- Customizable Alerts: Alerts can be configured based on specific thresholds or types of issues.
- Detailed Reports: Provides comprehensive reports to track performance trends and identify bottlenecks.
Pros:
- Versatility: Suitable for websites of all sizes with its broad monitoring capabilities.
- Ease of Use: User-friendly interface facilitates quick setup and navigation.
- Detailed Analysis: Offers in-depth insights into performance metrics and trends.
Cons:
- Integration Challenges: May require additional setup for seamless integration with other tools.
- Cost Considerations: Costs may increase with added features or extensive monitoring needs.
4. Site24x7
Site24x7 offers a comprehensive monitoring solution covering website performance, application monitoring, and infrastructure health, powered by AI-driven anomaly detection.
Features:
- Comprehensive Monitoring: Monitors website performance, applications, and infrastructure components.
- AI-Powered Anomaly Detection: Proactively identifies and alerts on unusual behavior or performance deviations.
- Root Cause Analysis: Helps in diagnosing issues and determining underlying causes.
Pros:
- Proactive Monitoring: AI capabilities enable early detection and resolution of potential issues.
- Holistic Coverage: Comprehensive monitoring across multiple layers ensures robust site health.
- Advanced Tools: Offers tools for detailed performance analysis and troubleshooting.
Cons:
- Complexity: Advanced features may require familiarity or training to leverage effectively.
- Cost Structure: Pricing may be higher, particularly for startups or smaller websites.
5. Datadog
Datadog, known primarily for infrastructure monitoring, also offers robust website monitoring capabilities, ideal for large-scale websites and complex environments.
Features:
- Infrastructure Monitoring: Monitors server infrastructure and network performance.
- Customizable Dashboards: Provides tailored dashboards for visualizing data and performance metrics.
- Integration: Extensive integrations with other tools and platforms for comprehensive monitoring.
Pros:
- Scalability: Designed for large-scale deployments and complex environments.
- Customization: Highly customizable dashboards and alerts to suit specific monitoring needs.
- Integration Ecosystem: Integrates seamlessly with a wide range of third-party tools and services.
Cons:
- Cost: Higher pricing, especially for extensive use or advanced feature sets.
- Complexity: May be overwhelming for smaller websites or less technically inclined users.



